Dapagliflozin / saxagliptin: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 295: | Line 295: | ||
| melting_point = | | melting_point = | ||
}} | }} | ||
|mechAction=( | |mechAction=*Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2), expressed in the proximal renal tubules, is responsible for the majority of the reabsorption of filtered glucose from the tubular lumen. Dapagliflozin is an inhibitor of SGLT2. By inhibiting SGLT2, dapagliflozin reduces reabsorption of filtered glucose and lowers the renal threshold for glucose, and thereby increases urinary glucose excretion. | ||
|structure=( | |||
| | |structure= | ||
|PK=( | |||
|PD======General===== | |||
*Increases in the amount of glucose excreted in the urine were observed in healthy subjects and in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus following the administration of dapagliflozin (see Figure 1). Dapagliflozin doses of 5 or 10 mg per day in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus for 12 weeks resulted in excretion of approximately 70 grams of glucose in the urine per day at Week 12. A near maximum glucose excretion was observed at the dapagliflozin daily dose of 20 mg. This urinary glucose excretion with dapagliflozin also results in increases in urinary volume. | |||
[[image:Dapagliflozin_Pharmacodynamics_Table.png|none|thumb|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
=====Cardiac Electrophysiology===== | |||
*Dapagliflozin was not associated with clinically meaningful prolongation of QTc interval at daily doses up to 150 mg (15 times the recommended maximum dose) in a study of healthy subjects. In addition, no clinically meaningful effect on QTc interval was observed following single doses of up to 500 mg (50 times the recommended maximum dose) of dapagliflozin in healthy subjects. | |||
|PK======Absorption===== | |||
*Following oral administration of dapagliflozin, the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) is usually attained within 2 hours under fasting state. The Cmax and AUC values increase dose proportionally with increase in dapagliflozin dose in the therapeutic dose range. The absolute oral bioavailability of dapagliflozin following the administration of a 10 mg dose is 78%. Administration of dapagliflozin with a high-fat meal decreases its Cmax by up to 50% and prolongs Tmax by approximately 1 hour, but does not alter AUC as compared with the fasted state. These changes are not considered to be clinically meaningful and dapagliflozin can be administered with or without food. | |||
=====Distribution===== | |||
*Dapagliflozin is approximately 91% protein bound. Protein binding is not altered in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. | |||
=====Metabolism===== | |||
*The metabolism of dapagliflozin is primarily mediated by UGT1A9; CYP-mediated metabolism is a minor clearance pathway in humans. Dapagliflozin is extensively metabolized, primarily to yield dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide, which is an inactive metabolite. Dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide accounted for 61% of a 50 mg [14C]-dapagliflozin dose and is the predominant drug-related component in human plasma. | |||
=====Elimination===== | |||
*Dapagliflozin and related metabolites are primarily eliminated via the renal pathway. Following a single 50 mg dose of [14C]-dapagliflozin, 75% and 21% total radioactivity is excreted in urine and feces, respectively. In urine, less than 2% of the dose is excreted as parent drug. In feces, approximately 15% of the dose is excreted as parent drug. The mean plasma terminal half-life (t½) for dapagliflozin is approximately 12.9 hours following a single oral dose of FARXIGA 10 mg. | |||
=====Specific Populations===== | |||
=====''Renal Impairment''===== | |||
*At steady state (20 mg once-daily dapagliflozin for 7 days), patients with type 2 diabetes with mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment (as determined by eGFR) had geometric mean systemic exposures of dapagliflozin that were 45%, 2.04-fold, and 3.03-fold higher, respectively, as compared to patients with type 2 diabetes with normal renal function. Higher systemic exposure of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with renal impairment did not result in a correspondingly higher 24-hour urinary glucose excretion. The steady-state 24-hour urinary glucose excretion in patients with type 2 diabetes and mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment was 42%, 80%, and 90% lower, respectively, than patients with type 2 diabetes with normal renal function. The impact of hemodialysis on dapagliflozin exposure is not known. | |||
=====''Hepatic Impairment''===== | |||
*In subjects with mild and moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh classes A and B), mean Cmax and AUC of dapagliflozin were up to 12% and 36% higher, respectively, as compared to healthy matched control subjects following single-dose administration of 10 mg dapagliflozin. These differences were not considered to be clinically meaningful. In patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C), mean Cmax and AUC of dapagliflozin were up to 40% and 67% higher, respectively, as compared to healthy matched controls. | |||
=====''Effects of Age, Gender, Race, and Body Weight on Pharmacokinetics''===== | |||
*Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis, age, gender, race, and body weight do not have a clinically meaningful effect on the pharmacokinetics of dapagliflozin and thus, no dose adjustment is recommended. | |||
=====''Pediatric''===== | |||
*Pharmacokinetics in the pediatric population has not been studied. | |||
=====Drug Interactions===== | |||
=====''In Vitro Assessment of Drug Interactions''===== | |||
*In in vitro studies, dapagliflozin and dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide neither inhibited CYP 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, or 3A4, nor induced CYP 1A2, 2B6, or 3A4. Dapagliflozin is a weak substrate of the P-glycoprotein (P-gp) active transporter, and dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide is a substrate for the OAT3 active transporter. Dapagliflozin or dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide did not meaningfully inhibit P-gp, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3 active transporters. Overall, dapagliflozin is unlikely to affect the pharmacokinetics of concurrently administered medications that are P-gp, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3 substrates. | |||
=====''Effects of Other Drugs on Dapagliflozin''===== | |||
*Table 6 shows the effect of coadministered drugs on the pharmacokinetics of dapagliflozin. No dose adjustments are recommended for dapagliflozin. | |||
[[image:Dapagliflozin_Pharmacokinetics_Table_1.png|none|thumb|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
=====''Effects of Dapagliflozin on Other Drugs''===== | |||
*Table 7 shows the effect of dapagliflozin on other coadministered drugs. Dapagliflozin did not meaningfully affect the pharmacokinetics of the coadministered drugs. | |||
[[image:Dapagliflozin_Pharmacokinetics_Table_2.png|none|thumb|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
|nonClinToxic=(Description) | |nonClinToxic=(Description) | ||
|clinicalStudies=*The efficacy of CALQUENCE was based upon Trial LY-004 titled “An Open-label, Phase 2 Study of ACP-196 in Subjects with Mantle Cell Lymphoma” (NCT02213926). Trial LY-004 enrolled a total of 124 patients with MCL who had received at least one prior therapy. | |clinicalStudies=*The efficacy of CALQUENCE was based upon Trial LY-004 titled “An Open-label, Phase 2 Study of ACP-196 in Subjects with Mantle Cell Lymphoma” (NCT02213926). Trial LY-004 enrolled a total of 124 patients with MCL who had received at least one prior therapy. | ||
Revision as of 03:32, 13 July 2018
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Yashasvi Aryaputra[2];
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Dapagliflozin / saxagliptin is a Acetylcholine release inhibitor, Adrenergic receptor agonist that is FDA approved for the (type of indication of drug) of a list of indications, separated by commas.. Common adverse reactions include a list of adverse reactions, separated by commas..
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Contraindications
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Warnings
Conidition 1
(Description)
Conidition 2
(Description)
Conidition 3
(Description)
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Condition 2
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Postmarketing Experience
(Description)
Drug Interactions
- Drug 1
- Drug 2
- Drug 3
- Drug 4
- Drug 5
Drug 1
(Description)
Drug 2
(Description)
Drug 3
(Description)
Drug 4
(Description)
Drug 5
(Description)
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
(Description)
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Dapagliflozin / saxagliptin in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
(Description)
Nursing Mothers
(Description)g
Pediatric Use
(Description)
Geriatic Use
(Description)
Gender
(Description)
Race
(Description)
Renal Impairment
(Description)
Hepatic Impairment
(Description)
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
(Description)
Immunocompromised Patients
(Description)
Others
(Description)
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
(Oral/Intravenous/etc)
Monitoring
Condition 1
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 2
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 3
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Dapagliflozin / saxagliptin and IV administrations.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
(Description)
Management
(Description)
Chronic Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
(Description)
Management
(Description)
Pharmacology
Dapagliflozin / saxagliptin
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| ? | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | ? |
| ATC code | ? |
| PubChem | ? |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | ? |
| Mol. mass | ? |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | ? |
Mechanism of Action
- Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2), expressed in the proximal renal tubules, is responsible for the majority of the reabsorption of filtered glucose from the tubular lumen. Dapagliflozin is an inhibitor of SGLT2. By inhibiting SGLT2, dapagliflozin reduces reabsorption of filtered glucose and lowers the renal threshold for glucose, and thereby increases urinary glucose excretion.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Dapagliflozin / saxagliptin Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
General
- Increases in the amount of glucose excreted in the urine were observed in healthy subjects and in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus following the administration of dapagliflozin (see Figure 1). Dapagliflozin doses of 5 or 10 mg per day in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus for 12 weeks resulted in excretion of approximately 70 grams of glucose in the urine per day at Week 12. A near maximum glucose excretion was observed at the dapagliflozin daily dose of 20 mg. This urinary glucose excretion with dapagliflozin also results in increases in urinary volume.

Cardiac Electrophysiology
- Dapagliflozin was not associated with clinically meaningful prolongation of QTc interval at daily doses up to 150 mg (15 times the recommended maximum dose) in a study of healthy subjects. In addition, no clinically meaningful effect on QTc interval was observed following single doses of up to 500 mg (50 times the recommended maximum dose) of dapagliflozin in healthy subjects.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
- Following oral administration of dapagliflozin, the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) is usually attained within 2 hours under fasting state. The Cmax and AUC values increase dose proportionally with increase in dapagliflozin dose in the therapeutic dose range. The absolute oral bioavailability of dapagliflozin following the administration of a 10 mg dose is 78%. Administration of dapagliflozin with a high-fat meal decreases its Cmax by up to 50% and prolongs Tmax by approximately 1 hour, but does not alter AUC as compared with the fasted state. These changes are not considered to be clinically meaningful and dapagliflozin can be administered with or without food.
Distribution
- Dapagliflozin is approximately 91% protein bound. Protein binding is not altered in patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
Metabolism
- The metabolism of dapagliflozin is primarily mediated by UGT1A9; CYP-mediated metabolism is a minor clearance pathway in humans. Dapagliflozin is extensively metabolized, primarily to yield dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide, which is an inactive metabolite. Dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide accounted for 61% of a 50 mg [14C]-dapagliflozin dose and is the predominant drug-related component in human plasma.
Elimination
- Dapagliflozin and related metabolites are primarily eliminated via the renal pathway. Following a single 50 mg dose of [14C]-dapagliflozin, 75% and 21% total radioactivity is excreted in urine and feces, respectively. In urine, less than 2% of the dose is excreted as parent drug. In feces, approximately 15% of the dose is excreted as parent drug. The mean plasma terminal half-life (t½) for dapagliflozin is approximately 12.9 hours following a single oral dose of FARXIGA 10 mg.
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment
- At steady state (20 mg once-daily dapagliflozin for 7 days), patients with type 2 diabetes with mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment (as determined by eGFR) had geometric mean systemic exposures of dapagliflozin that were 45%, 2.04-fold, and 3.03-fold higher, respectively, as compared to patients with type 2 diabetes with normal renal function. Higher systemic exposure of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with renal impairment did not result in a correspondingly higher 24-hour urinary glucose excretion. The steady-state 24-hour urinary glucose excretion in patients with type 2 diabetes and mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment was 42%, 80%, and 90% lower, respectively, than patients with type 2 diabetes with normal renal function. The impact of hemodialysis on dapagliflozin exposure is not known.
Hepatic Impairment
- In subjects with mild and moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh classes A and B), mean Cmax and AUC of dapagliflozin were up to 12% and 36% higher, respectively, as compared to healthy matched control subjects following single-dose administration of 10 mg dapagliflozin. These differences were not considered to be clinically meaningful. In patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C), mean Cmax and AUC of dapagliflozin were up to 40% and 67% higher, respectively, as compared to healthy matched controls.
Effects of Age, Gender, Race, and Body Weight on Pharmacokinetics
- Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis, age, gender, race, and body weight do not have a clinically meaningful effect on the pharmacokinetics of dapagliflozin and thus, no dose adjustment is recommended.
Pediatric
- Pharmacokinetics in the pediatric population has not been studied.
Drug Interactions
In Vitro Assessment of Drug Interactions
- In in vitro studies, dapagliflozin and dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide neither inhibited CYP 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, or 3A4, nor induced CYP 1A2, 2B6, or 3A4. Dapagliflozin is a weak substrate of the P-glycoprotein (P-gp) active transporter, and dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide is a substrate for the OAT3 active transporter. Dapagliflozin or dapagliflozin 3-O-glucuronide did not meaningfully inhibit P-gp, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3 active transporters. Overall, dapagliflozin is unlikely to affect the pharmacokinetics of concurrently administered medications that are P-gp, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3 substrates.
Effects of Other Drugs on Dapagliflozin
- Table 6 shows the effect of coadministered drugs on the pharmacokinetics of dapagliflozin. No dose adjustments are recommended for dapagliflozin.

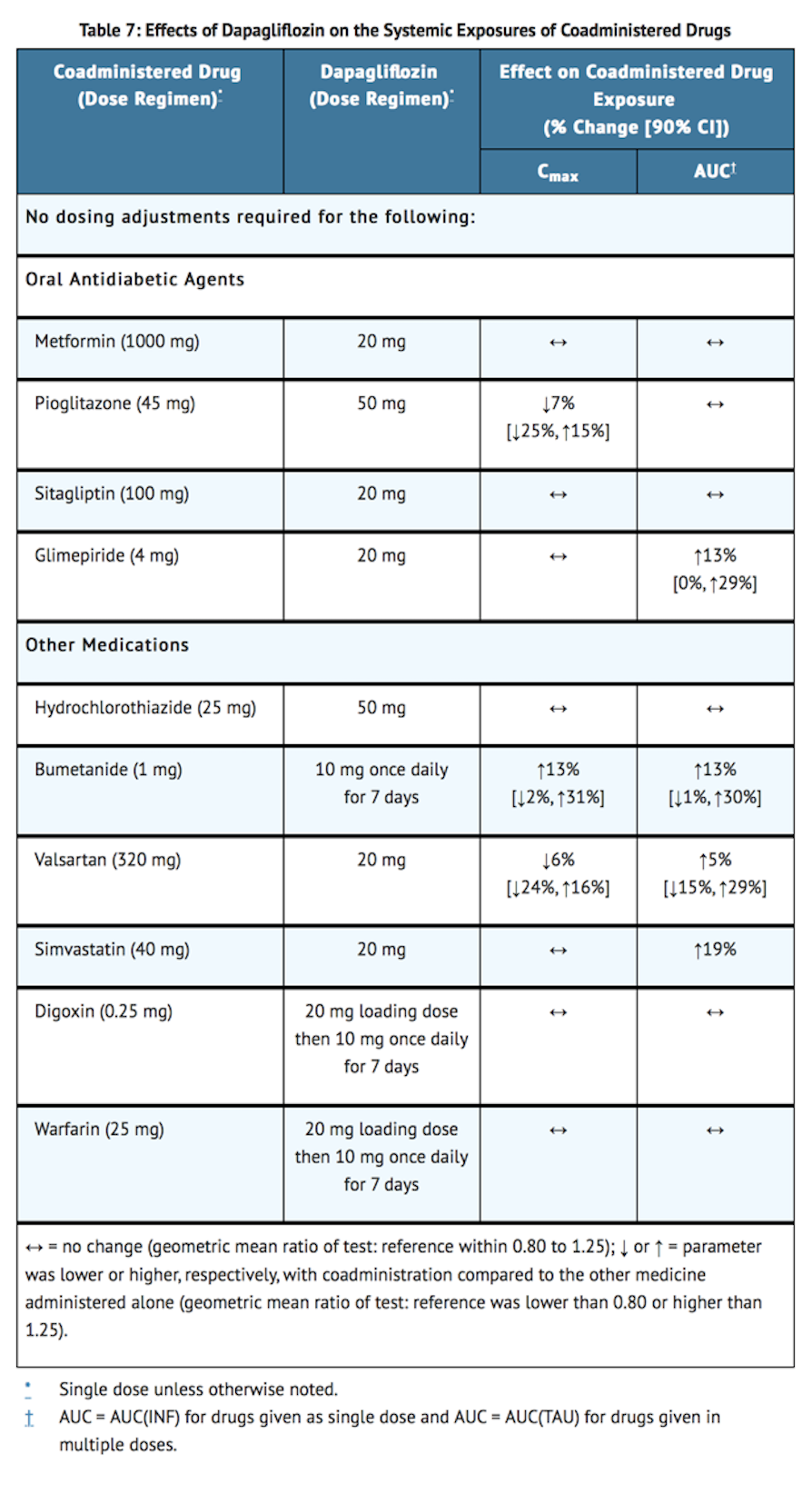
Effects of Dapagliflozin on Other Drugs
- Table 7 shows the effect of dapagliflozin on other coadministered drugs. Dapagliflozin did not meaningfully affect the pharmacokinetics of the coadministered drugs.
Nonclinical Toxicology
(Description)
Clinical Studies
- The efficacy of CALQUENCE was based upon Trial LY-004 titled “An Open-label, Phase 2 Study of ACP-196 in Subjects with Mantle Cell Lymphoma” (NCT02213926). Trial LY-004 enrolled a total of 124 patients with MCL who had received at least one prior therapy.
- The median age was 68 (range 42 to 90) years, 80% were male, and 74% were Caucasian. At baseline, 93% of patients had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1. The median time since diagnosis was 46.3 months and the median number of prior treatments was 2 (range 1 to 5), including 18% with prior stem cell transplant. Patients who received prior treatment with BTK inhibitors were excluded. The most common prior regimens were CHOP-based (52%) and ARA-C (34%). At baseline, 37% of patients had at least one tumor with a longest diameter ≥ 5 cm, 73% had extra nodal involvement including 51% with bone marrow involvement. The simplified MIPI score (which includes age, ECOG score, and baseline lactate dehydrogenase and white cell count) was intermediate in 44% and high in 17% of patients.
- CALQUENCE was administered orally at 100 mg twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The median dose intensity was 98.5%. Tumor response was assessed according to the Lugano Classification for Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL). The major efficacy outcome of Trial LY-004 was overall response rate (ORR) and the median follow-up was 15.2 months.

Lymphocytosis
- Upon initiation of CALQUENCE, a temporary increase in lymphocyte counts (defined as absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) increased ≥ 50% from baseline and a post baseline assessment ≥ 5 x 109) in 31.5% of patients in Trial LY-004. The median time to onset of lymphocytosis was 1.1 weeks and the median duration of lymphocytosis was 6.7 weeks.
How Supplied
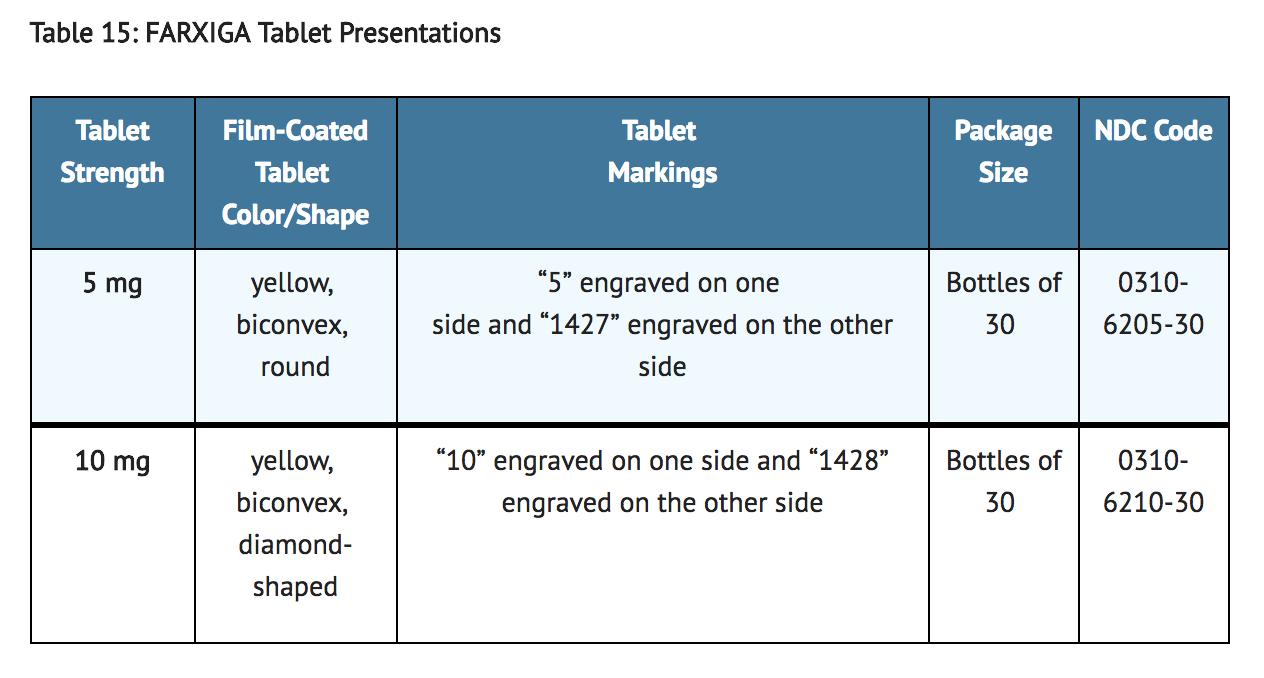
- FARXIGA (dapagliflozin) tablets have markings on both sides and are available in the strengths and packages listed in Table 15.
Storage
- Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F).
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Dapagliflozin / saxagliptin |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel


{{#ask: Label Page::Dapagliflozin / saxagliptin |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Instructions
- Instruct patients to read the Medication Guide before starting treatment with FARXIGA and to reread it each time the prescription is renewed.
- Inform patients of the potential risks and benefits of FARXIGA and of alternative modes of therapy. Also inform patients about the importance of adherence to dietary instructions, regular physical activity, periodic blood glucose monitoring and HbA1c testing, recognition and management of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, and assessment of diabetes complications. Advise patients to seek medical advice promptly during periods of stress such as fever, trauma, infection, or surgery, as medication requirements may change.
- Instruct patients to take FARXIGA only as prescribed. If a dose is missed, advise patients to take it as soon as it is remembered unless it is almost time for the next dose, in which case patients should skip the missed dose and take the medicine at the next regularly scheduled time. Advise patients not to take two doses of FARXIGA at the same time.
- Inform patients that the most common adverse reactions associated with use of FARXIGA are genital mycotic infections, nasopharyngitis, and urinary tract infections.
- Instruct patient to immediately inform her healthcare provider if she is pregnant or plans to become pregnant. Based on animal data, FARXIGA may cause fetal harm in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
- Instruct patient to immediately inform her healthcare provider if she is breastfeeding or planning to breastfeed. It is not known if FARXIGA is excreted in breast milk; however, based on animal data, FARXIGA may cause harm to nursing infants.
Hypotension
- Inform patients that symptomatic hypotension may occur with FARXIGA and advise them to contact their healthcare provider if they experience such symptoms. Inform patients that dehydration may increase the risk for hypotension, and to have adequate fluid intake.
Genital Mycotic Infections in Females (e.g., Vulvovaginitis)
- Inform female patients that vaginal yeast infections may occur and provide them with information on the signs and symptoms of vaginal yeast infections. Advise them of treatment options and when to seek medical advice.
Ketoacidosis
- Inform patients that ketoacidosis is a serious life-threatening condition. Cases of ketoacidosis have been reported during use of FARXIGA. Instruct patients to check ketones (when possible) if symptoms consistent with ketoacidosis occur even if blood glucose is not elevated. If symptoms of ketoacidosis (including nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, tiredness and labored breathing) occur, instruct patients to discontinue FARXIGA and seek medical advice immediately.
Acute Kidney Injury
- Inform patients that acute kidney injury has been reported during use of FARXIGA. Advise patients to seek medical advice immediately if they have reduced oral intake (due to acute illness or fasting) or increased fluid losses (due to vomiting, diarrhea, or excessive heat exposure), as it may be appropriate to temporarily discontinue FARXIGA use in those settings.
Serious Urinary Tract Infections
- Inform patients of the potential for urinary tract infections, which may be serious. Provide them with information on the symptoms of urinary tract infections. Advise them to seek medical advice promptly if such symptoms occur.
Genital Mycotic Infections in Males (e.g., Balanitis)
- Inform male patients that yeast infections of the penis (e.g., balanitis or balanoposthitis) may occur, especially in patients with prior history. Provide them with information on the signs and symptoms of balanitis and balanoposthitis (rash or redness of the glans or foreskin of the penis). Advise them of treatment options and when to seek medical advice.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Inform patients that serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., urticaria and angioedema) have been reported with FARXIGA. Advise patients to immediately report any signs or symptoms suggesting allergic reaction or angioedema, and to take no more of the drug until they have consulted prescribing physicians.
Bladder Cancer
- Inform patients to promptly report any signs of macroscopic hematuria or other symptoms potentially related to bladder cancer.
Pregnancy
- Advise pregnant patients of the potential risk to a fetus with treatment with FARXIGA. Instruct patients to immediately inform their healthcare provider if pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
Lactation
- Advise patients that use of FARXIGA is not recommended while breastfeeding.
Laboratory Tests
- Due to its mechanism of action, patients taking FARXIGA will test positive for glucose in their urine.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Dapagliflozin / saxagliptin interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor regarding the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Farxiga
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Dapagliflozin / saxagliptin Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Drug Shortage
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.