Carboplatin: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)--> | <!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)--> | ||
|fdaLIADAdult====== | |fdaLIADAdult======Initial Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Carcinoma===== | ||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
:* Dosage | :* Dosage | ||
===== | =====Secondary Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Carcinoma===== | ||
* Dosing Information | * Dosing Information | ||
| Line 115: | Line 103: | ||
<!--Contraindications--> | <!--Contraindications--> | ||
|contraindications=* | |contraindications=*Carboplatin injection is contraindicated in patients with a history of severe allergic reactions to cisplatin or other platinum-containing compounds. | ||
*Carboplatin should not be employed in patients with severe bone marrow depression or significant bleeding. | |||
<!--Warnings--> | <!--Warnings--> | ||
|warnings=* | |warnings=* Bone marrow suppression (leukopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia) is dose-dependent and is also the dose-limiting toxicity. Peripheral blood counts should be frequently monitored during carboplatin treatment and, when appropriate, until recovery is achieved. Median nadir occurs at day 21 in patients receiving single-agent carboplatin. In general, single intermittent courses of carboplatin should not be repeated until leukocyte, neutrophil, and platelet counts have recovered. | ||
*Since anemia is cumulative, transfusions may be needed during treatment with carboplatin, particularly in patients receiving prolonged therapy. | |||
*Bone marrow suppression is increased in patients who have received prior therapy, especially regimens including cisplatin. Marrow suppression is also increased in patients with impaired kidney function. Initial carboplatin dosages in these patients should be appropriately reduced (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION) and blood counts should be carefully monitored between courses. The use of carboplatin in combination with other bone marrow suppressing therapies must be carefully managed with respect to dosage and timing in order to minimize additive effects. | |||
*Carboplatin has limited nephrotoxic potential, but concomitant treatment with aminoglycosides has resulted in increased renal and/or audiologic toxicity, and caution must be exercised when a patient receives both drugs. Clinically significant hearing loss has been reported to occur in pediatric patients when carboplatin was administered at higher than recommended doses in combination with other ototoxic agents. | |||
*Carboplatin can induce emesis, which can be more severe in patients previously receiving emetogenic therapy. The incidence and intensity of emesis have been reduced by using premedication with antiemetics. Although no conclusive efficacy data exist with the following schedules of carboplatin, lengthening the duration of single intravenous administration to 24 hours or dividing the total dose over 5 consecutive daily pulse doses has resulted in reduced emesis. | |||
*Although peripheral neurotoxicity is infrequent, its incidence is increased in patients older than 65 years and in patients previously treated with cisplatin. Pre-existing cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity does not worsen in about 70% of the patients receiving carboplatin as secondary treatment. | |||
*Loss of vision, which can be complete for light and colors, has been reported after the use of carboplatin with doses higher than those recommended in the package insert. Vision appears to recover totally or to a significant extent within weeks of stopping these high doses. | |||
*As in the case of other platinum-coordination compounds, allergic reactions to carboplatin have been reported. These may occur within minutes of administration and should be managed with appropriate supportive therapy. There is increased risk of allergic reactions including anaphylaxis in patients previously exposed to platinum therapy. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS and ADVERSE REACTIONS: ALLERGIC REACTIONS.) | |||
*High dosages of carboplatin (more than 4 times the recommended dose) have resulted in severe abnormalities of liver function tests. | |||
*Carboplatin injection may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Carboplatin has been shown to be embryotoxic and teratogenic in rats. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while receiving this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus. Women of childbearing potential should be advised to avoid becoming pregnant. | |||
====Precautions==== | ====Precautions==== | ||
| Line 325: | Line 333: | ||
<!--Clinical Studies--> | <!--Clinical Studies--> | ||
|clinicalStudies= | |clinicalStudies======Use with Cyclophosphamide for Initial Treatment of Ovarian Cancer===== | ||
*In two prospectively randomized, controlled studies conducted by the National Cancer Institute of Canada, Clinical Trials Group (NCIC) and the Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG), 789 chemotherapy naive patients with advanced ovarian cancer were treated with carboplatin or cisplatin, both in combination with cyclophosphamide every 28 days for 6 courses before surgical reevaluation. The following results were obtained from both studies: | |||
T | |||
=====Comparative Toxicity===== | |||
*The pattern of toxicity exerted by the carboplatin-containing regimen was significantly different from that of the cisplatin-containing combinations. Differences between the two studies may be explained by different cisplatin dosages and by different supportive care. | |||
*The carboplatin-containing regimen induced significantly more thrombocytopenia and, in one study, significantly more leukopenia and more need for transfusional support. The cisplatin-containing regimen produced significantly more anemia in one study. However, no significant differences occurred in incidences of infections and hemorrhagic episodes. | |||
*Non-hematologic toxicities (emesis, neurotoxicity, ototoxicity, renal toxicity, hypomagnesemia, and alopecia) were significantly more frequent in the cisplatin-containing arms. | |||
T | |||
=====Use as a Single Agent for Secondary Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Cancer===== | |||
*In two prospective, randomized controlled studies in patients with advanced ovarian cancer previously treated with chemotherapy, carboplatin achieved 6 clinical complete responses in 47 patients. The duration of these responses ranged from 45 to 71 +weeks. | |||
<!--How Supplied--> | <!--How Supplied--> | ||
Revision as of 16:48, 13 January 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1];
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
WARNING
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
|
Overview
Carboplatin is a {{{drugClass}}} that is FDA approved for the treatment of {{{indication}}}. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include .
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Initial Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Carcinoma
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Secondary Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Carcinoma
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Carboplatin in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Carboplatin in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Carboplatin in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Carboplatin in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Carboplatin in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Carboplatin injection is contraindicated in patients with a history of severe allergic reactions to cisplatin or other platinum-containing compounds.
- Carboplatin should not be employed in patients with severe bone marrow depression or significant bleeding.
Warnings
|
WARNING
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
|
- Bone marrow suppression (leukopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia) is dose-dependent and is also the dose-limiting toxicity. Peripheral blood counts should be frequently monitored during carboplatin treatment and, when appropriate, until recovery is achieved. Median nadir occurs at day 21 in patients receiving single-agent carboplatin. In general, single intermittent courses of carboplatin should not be repeated until leukocyte, neutrophil, and platelet counts have recovered.
- Since anemia is cumulative, transfusions may be needed during treatment with carboplatin, particularly in patients receiving prolonged therapy.
- Bone marrow suppression is increased in patients who have received prior therapy, especially regimens including cisplatin. Marrow suppression is also increased in patients with impaired kidney function. Initial carboplatin dosages in these patients should be appropriately reduced (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION) and blood counts should be carefully monitored between courses. The use of carboplatin in combination with other bone marrow suppressing therapies must be carefully managed with respect to dosage and timing in order to minimize additive effects.
- Carboplatin has limited nephrotoxic potential, but concomitant treatment with aminoglycosides has resulted in increased renal and/or audiologic toxicity, and caution must be exercised when a patient receives both drugs. Clinically significant hearing loss has been reported to occur in pediatric patients when carboplatin was administered at higher than recommended doses in combination with other ototoxic agents.
- Carboplatin can induce emesis, which can be more severe in patients previously receiving emetogenic therapy. The incidence and intensity of emesis have been reduced by using premedication with antiemetics. Although no conclusive efficacy data exist with the following schedules of carboplatin, lengthening the duration of single intravenous administration to 24 hours or dividing the total dose over 5 consecutive daily pulse doses has resulted in reduced emesis.
- Although peripheral neurotoxicity is infrequent, its incidence is increased in patients older than 65 years and in patients previously treated with cisplatin. Pre-existing cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity does not worsen in about 70% of the patients receiving carboplatin as secondary treatment.
- Loss of vision, which can be complete for light and colors, has been reported after the use of carboplatin with doses higher than those recommended in the package insert. Vision appears to recover totally or to a significant extent within weeks of stopping these high doses.
- As in the case of other platinum-coordination compounds, allergic reactions to carboplatin have been reported. These may occur within minutes of administration and should be managed with appropriate supportive therapy. There is increased risk of allergic reactions including anaphylaxis in patients previously exposed to platinum therapy. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS and ADVERSE REACTIONS: ALLERGIC REACTIONS.)
- High dosages of carboplatin (more than 4 times the recommended dose) have resulted in severe abnormalities of liver function tests.
- Carboplatin injection may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Carboplatin has been shown to be embryotoxic and teratogenic in rats. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while receiving this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus. Women of childbearing potential should be advised to avoid becoming pregnant.
Precautions
- Description
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Carboplatin in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Carboplatin in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Carboplatin in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Carboplatin during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Carboplatin with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Carboplatin with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Carboplatin with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Carboplatin with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Carboplatin with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Carboplatin in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Carboplatin in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Carboplatin in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Carboplatin in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Carboplatin in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Carboplatin in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Carboplatin in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Carboplatin Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
- Carboplatin, like cisplatin, produces predominantly interstrand DNA cross-links rather than DNA-protein cross-links. This effect is apparently cell-cycle nonspecific. The aquation of carboplatin, which is thought to produce the active species, occurs at a slower rate than in the case of cisplatin. Despite this difference, it appears that both carboplatin and cisplatin induce equal numbers of drug-DNA cross-links, causing equivalent lesions and biological effects. The differences in potencies for carboplatin and cisplatin appear to be directly related to the difference in aquation rates.
Structure
- Carboplatin Injection is for intravenous administration. Each mL contains equivalent to 10 mg of carboplatin in Water for Injection. No other preservatives or additives are present. Carboplatin injection is supplied as a sterile, pyrogen-free, 10 mg/mL aqueous solution of carboplatin. Carboplatin is a platinum coordination compound. The chemical name for carboplatin is platinum, diammine [1,1-cyclobutanedicarboxylato(2-)-O,O’]-,(SP-4-2), and carboplatin has the following structural formula:
- Carboplatin is a crystalline powder with the molecular formula of C6H12N2O4Pt and a molecular weight of 371.25. It is soluble in water at a rate of approximately 14 mg/mL, and the pH of a 1% solution is 5-7. It is sparingly soluble in water, very slightly soluble in acetone and in alcohol.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Carboplatin in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
- In patients with creatinine clearances of about 60 mL/min or greater, plasma levels of intact carboplatin decay in a biphasic manner after a 30-minute intravenous infusion of 300 mg/m2 to 500 mg/m2 of carboplatin. The initial plasma half-life (alpha) was found to be 1.1 to 2 hours (n=6), and the postdistribution plasma half-life (beta) was found to be 2.6 to 5.9 hours (n=6). The total body clearance, apparent volume of distribution and mean residence time for carboplatin are 4.4 L/hour, 16 L and 3.5 hours, respectively. The Cmax values and areas under the plasma concentration versus time curves from 0 to infinity (AUC inf) increase linearly with dose, although the increase was slightly more than dose proportional. Carboplatin, therefore, exhibits linear pharmacokinetics over the dosing range studied (300 mg/m2 to 500 mg/m2).
- Carboplatin is not bound to plasma proteins. No significant quantities of protein-free, ultrafilterable platinum-containing species other than carboplatin are present in plasma. However, platinum from carboplatin becomes irreversibly bound to plasma proteins and is slowly eliminated with a minimum half-life of 5 days.
- The major route of elimination of carboplatin is renal excretion. Patients with creatinine clearances of approximately 60 mL/min or greater excrete 65% of the dose in the urine within 12 hours and 71% of the dose within 24 hours. All of the platinum in the 24-hour urine is present as carboplatin. Only 3% to 5% of the administered platinum is excreted in the urine between 24 and 96 hours. There are insufficient data to determine whether biliary excretion occurs.
- In patients with creatinine clearances below 60 mL/min the total body and renal clearances of carboplatin decrease as the creatinine clearance decreases. Carboplatin dosages should therefore be reduced in these patients (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
- The primary determinant of carboplatin clearance is glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and this parameter of renal function is often decreased in elderly patients. Dosing formulas incorporating estimates of GFR (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION) to provide predictable carboplatin plasma AUCs should be used in elderly patients to minimize the risk of toxicity.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Carboplatin in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
Use with Cyclophosphamide for Initial Treatment of Ovarian Cancer
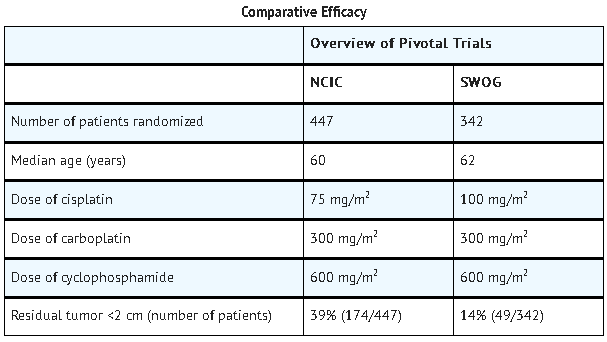
- In two prospectively randomized, controlled studies conducted by the National Cancer Institute of Canada, Clinical Trials Group (NCIC) and the Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG), 789 chemotherapy naive patients with advanced ovarian cancer were treated with carboplatin or cisplatin, both in combination with cyclophosphamide every 28 days for 6 courses before surgical reevaluation. The following results were obtained from both studies:
T
Comparative Toxicity
- The pattern of toxicity exerted by the carboplatin-containing regimen was significantly different from that of the cisplatin-containing combinations. Differences between the two studies may be explained by different cisplatin dosages and by different supportive care.
- The carboplatin-containing regimen induced significantly more thrombocytopenia and, in one study, significantly more leukopenia and more need for transfusional support. The cisplatin-containing regimen produced significantly more anemia in one study. However, no significant differences occurred in incidences of infections and hemorrhagic episodes.
- Non-hematologic toxicities (emesis, neurotoxicity, ototoxicity, renal toxicity, hypomagnesemia, and alopecia) were significantly more frequent in the cisplatin-containing arms.
T
Use as a Single Agent for Secondary Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Cancer
- In two prospective, randomized controlled studies in patients with advanced ovarian cancer previously treated with chemotherapy, carboplatin achieved 6 clinical complete responses in 47 patients. The duration of these responses ranged from 45 to 71 +weeks.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Carboplatin Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Carboplatin |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Carboplatin |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Carboplatin in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Carboplatin interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Carboplatin
|Pill Name=No image.jpg
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Carboplatin |Label Name=Carboplatin11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Carboplatin |Label Name=Carboplatin11.png
}}