Brodie abscess
|
Brodie abscess Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Brodie abscess On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Brodie abscess |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Template:Sk Subacute osteomyelitis; subacute epiphyseal osteomyelitis
Overview
Historical Perspective
Classification
Pathophysiology
Causes
Differentiating Brodie abscess from other Diseases
Epidemiology and Demographics
Risk Factors
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Diagnosis
History and Symptoms | Physical Examination | Laboratory Findings | CT | MRI | Other Imaging Findings | Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
Medical Therapy | Surgery | Secondary Prevention | Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy | Future or Investigational Therapies
Case Studies
Overview
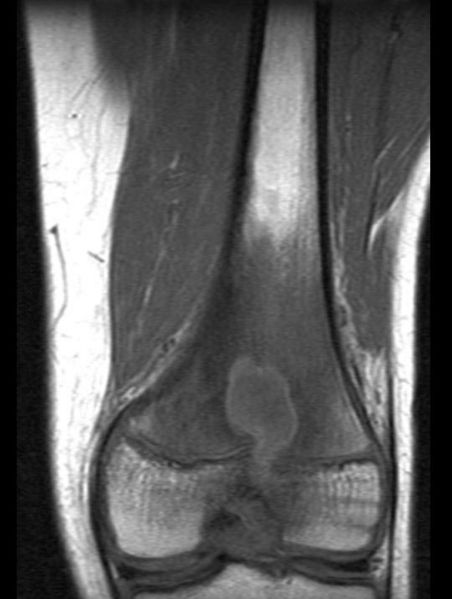
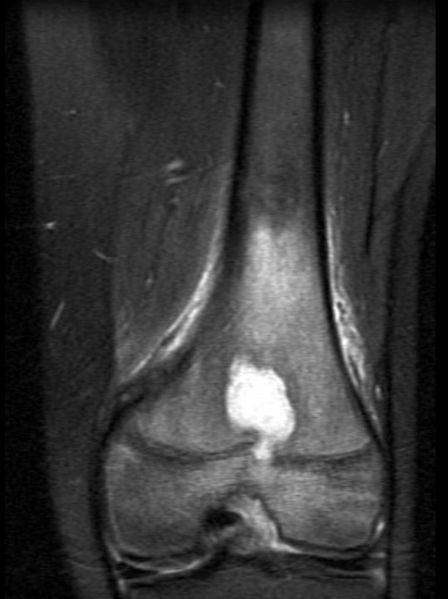
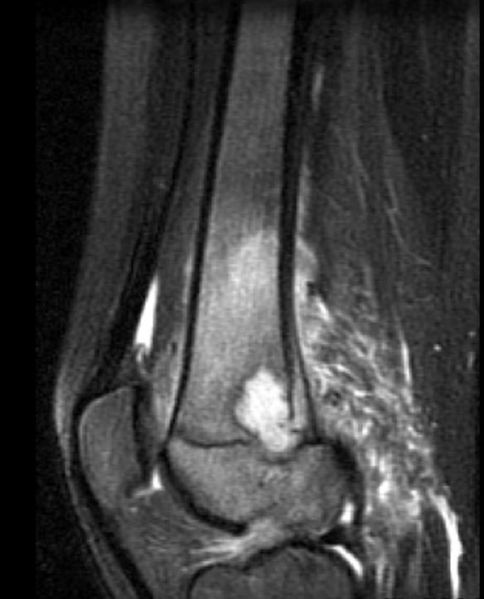
A Brodie abscess is a well defined rim of sclerotic bone surrounding a residual abscess; viable organisms may persist in a Brodie abscess.[1]
Diagnosis
The imaging findings are
- Central area of radiolucency with a surrounding thick rim of reactive bone sclerosis
- Pathognomonic tortuous parallel lucent channels extending toward the growth plate
- Variable degree of periosteal new-bone formation
- Variable associated soft-tissue swelling.
MR images demonstrate a Brodie's abscess
References
- ↑ Brodie abscess: another type of chronic posttraumatic osteomyelitis. Eur Radiol. 2003 Jul;13(7):1750-2. Epub 2003 Feb 7. PMID 12835993