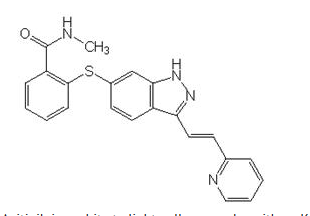
Axitinib
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aparna Vuppala, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Axitinib is an antineoplastic agent that is FDA approved for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) after failure of one prior systemic therapy.. Common adverse reactions include .
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC)
- INLYTA is indicated for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) after failure of one prior systemic therapy.
Recommended Dosing
- The recommended starting oral dose of INLYTA is 5 mg twice daily. Administer INLYTA doses approximately 12 hours apart with or without food [see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.3)]. INLYTA should be swallowed whole with a glass of water.
- If the patient vomits or misses a dose, an additional dose should not be taken. The next prescribed dose should be taken at the usual time.
Dose Modification Guidelines
- Dose increase or reduction is recommended based on individual safety and tolerability.
- Over the course of treatment, patients who tolerate INLYTA for at least two consecutive weeks with no adverse reactions >Grade 2 (according to the Common Toxicity Criteria for Adverse Events [CTCAE]), are normotensive, and are not receiving anti-hypertension medication, may have their dose increased. When a dose increase from 5 mg twice daily is recommended, the INLYTA dose may be increased to 7 mg twice daily, and further to 10 mg twice daily using the same criteria.
- Over the course of treatment, management of some adverse drug reactions may require temporary interruption or permanent discontinuation and/or dose reduction of INLYTA therapy [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5)]. If dose reduction from 5 mg twice daily is required, the recommended dose is 3 mg twice daily. If additional dose reduction is required, the recommended dose is 2 mg twice daily.
- Strong CYP3A4/5 Inhibitors: The concomitant use of strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors should be avoided (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin, atazanavir, indinavir, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, telithromycin, and voriconazole). Selection of an alternate concomitant medication with no or minimal CYP3A4/5 inhibition potential is recommended. *Although INLYTA dose adjustment has not been studied in patients receiving strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors, if a strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitor must be co-administered, a dose decrease of INLYTA by approximately half is recommended, as this dose reduction is predicted to adjust the axitinib area under the plasma concentration vs time curve (AUC) to the range observed without inhibitors. The subsequent doses can be increased or decreased based on individual safety and tolerability. If co-administration of the strong inhibitor is discontinued, the INLYTA dose should be returned (after 3 – 5 half-lives of the inhibitor) to that used prior to initiation of the strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitor [see DRUG INTERACTIONS (7.1) and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.3)].
- Hepatic Impairment: No starting dose adjustment is required when administering INLYTA to patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A). Based on the pharmacokinetic data, the INLYTA starting dose should be reduced by approximately half in patients with baseline moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B). The subsequent doses can be increased or decreased based on individual safety and tolerability. INLYTA has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Axitinib in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Axitinib in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Axitinib in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Axitinib in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Axitinib in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- None
Warnings
Hypertension and Hypertensive Crisis
- In a controlled clinical study with INLYTA for the treatment of patients with RCC, hypertension was reported in 145/359 patients (40%) receiving INLYTA and 103/355 patients (29%) receiving sorafenib. Grade 3/4 hypertension was observed in 56/359 patients (16%) receiving INLYTA and 39/355 patients (11%) receiving sorafenib. Hypertensive crisis was reported in 2/359 patients (<1%) receiving INLYTA and none of the patients receiving sorafenib. The median onset time for hypertension (systolic blood pressure >150 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure >100 mmHg) was within the first month of the start of INLYTA treatment and blood pressure increases have been observed as early as 4 days after starting INLYTA. Hypertension was managed with standard antihypertensive therapy. Discontinuation of INLYTA treatment due to hypertension occurred in 1/359 patients (<1%) receiving INLYTA and none of the patients receiving sorafenib [see ADVERSE REACTIONS (6.1)].
- Blood pressure should be well-controlled prior to initiating INLYTA. Patients should be monitored for hypertension and treated as needed with standard anti-hypertensive therapy. In the case of persistent hypertension despite use of anti-hypertensive medications, reduce the INLYTA dose. Discontinue INLYTA if hypertension is severe and persistent despite anti-hypertensive therapy and dose reduction of INLYTA, and discontinuation should be considered if there is evidence of hypertensive crisis. If INLYTA is interrupted, patients receiving antihypertensive medications should be monitored for hypotension [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.2)].
Arterial Thromboembolic Events
- In clinical trials, arterial thromboembolic events have been reported, including deaths. In a controlled clinical study with INLYTA for the treatment of patients with RCC, Grade 3/4 arterial thromboembolic events were reported in 4/359 patients (1%) receiving INLYTA and 4/355 patients (1%) receiving sorafenib. Fatal cerebrovascular accident was reported in 1/359 patients (<1%) receiving INLYTA and none of the patients receiving sorafenib [see ADVERSE REACTIONS (6.1)].
- In clinical trials with INLYTA, arterial thromboembolic events (including transient ischemic attack, cerebrovascular accident, myocardial infarction, and retinal artery occlusion) were reported in 17/715 patients (2%), with two deaths secondary to cerebrovascular accident.
- Use INLYTA with caution in patients who are at risk for, or who have a history of, these events. INLYTA has not been studied in patients who had an arterial thromboembolic event within the previous 12 months.
Venous Thromboembolic Events
- In clinical trials, venous thromboembolic events have been reported, including deaths. In a controlled clinical study with INLYTA for the treatment of patients with RCC, venous thromboembolic events were reported in 11/359 patients (3%) receiving INLYTA and 2/355 patients (1%) receiving sorafenib. Grade 3/4 venous thromboembolic events were reported in 9/359 patients (3%) receiving INLYTA (including pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, retinal vein occlusion and retinal vein thrombosis) and 2/355 patients (1%) receiving sorafenib. Fatal pulmonary embolism was reported in 1/359 patients (<1%) receiving INLYTA and none of the patients receiving sorafenib. In clinical trials with INLYTA, venous thromboembolic events were reported in 22/715 patients (3%), with two deaths secondary to pulmonary embolism.
- Use INLYTA with caution in patients who are at risk for, or who have a history of, these events. INLYTA has not been studied in patients who had a venous thromboembolic event within the previous 6 months.
Hemorrhage
- In a controlled clinical study with INLYTA for the treatment of patients with RCC, hemorrhagic events were reported in 58/359 patients (16%) receiving INLYTA and 64/355 patients (18%) receiving sorafenib. Grade 3/4 hemorrhagic events were reported in 5/359 (1%) patients receiving INLYTA (including cerebral hemorrhage, hematuria, hemoptysis, lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and melena) and 11/355 (3%) patients receiving sorafenib. Fatal hemorrhage was reported in 1/359 patients (<1%) receiving INLYTA (gastric hemorrhage) and 3/355 patients (1%) receiving sorafenib.
- INLYTA has not been studied in patients who have evidence of untreated brain metastasis or recent active gastrointestinal bleeding and should not be used in those patients. If any bleeding requires medical intervention, temporarily interrupt the INLYTA dose.
Cardiac Failure
- In a controlled clinical study with INLYTA for the treatment of patients with RCC, cardiac failure was reported in 6/359 patients (2%) receiving INLYTA and 3/355 patients (1%) receiving sorafenib. Grade 3/4 cardiac failure was observed in 2/359 patients (1%) receiving INLYTA and 1/355 patients (<1%) receiving sorafenib. *Fatal cardiac failure was reported in 2/359 patients (1%) receiving INLYTA and 1/355 patients (<1%) receiving sorafenib. Monitor for signs or symptoms of cardiac failure throughout treatment with INLYTA. Management of cardiac failure may require permanent discontinuation of INLYTA.
Gastrointestinal Perforation and Fistula Formation
- In a controlled clinical study with INLYTA for the treatment of patients with RCC, gastrointestinal perforation was reported in 1/359 patients (<1%) receiving INLYTA and none of the patients receiving sorafenib. In clinical trials with INLYTA, gastrointestinal perforation was reported in 5/715 patients (1%), including one death. In addition to cases of gastrointestinal perforation, fistulas were reported in 4/715 patients (1%).
- Monitor for symptoms of gastrointestinal perforation or fistula periodically throughout treatment with INLYTA.
Thyroid Dysfunction
- In a controlled clinical study with INLYTA for the treatment of patients with RCC, hypothyroidism was reported in 69/359 patients (19%) receiving INLYTA and 29/355 patients (8%) receiving sorafenib. Hyperthyroidism was reported in 4/359 patients (1%) receiving INLYTA and 4/355 patients (1%) receiving sorafenib. In patients who had thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) <5 μU/mL before treatment, elevations of TSH to ≥10 μU/mL occurred in 79/245 patients (32%) receiving INLYTA and 25/232 patients (11%) receiving sorafenib [see ADVERSE REACTIONS (6.1)].
- Monitor thyroid function before initiation of, and periodically throughout, treatment with INLYTA. Treat hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism according to standard medical practice to maintain euthyroid state.
Wound Healing Complications
- No formal studies of the effect of INLYTA on wound healing have been conducted.
- Stop treatment with INLYTA at least 24 hours prior to scheduled surgery. The decision to resume INLYTA therapy after surgery should be based on clinical judgment of adequate wound healing.
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome
- In a controlled clinical study with INLYTA for the treatment of patients with RCC, reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS) was reported in 1/359 patients (<1%) receiving INLYTA and none of the patients receiving sorafenib [see ADVERSE REACTIONS (6.1)]. There were two additional reports of RPLS in other clinical trials with INLYTA.
- RPLS is a neurological disorder which can present with headache, seizure, lethargy, confusion, blindness and other visual and neurologic disturbances. Mild to severe hypertension may be present. Magnetic resonance imaging is necessary to confirm the diagnosis of RPLS. Discontinue INLYTA in patients developing RPLS. *The safety of reinitiating INLYTA therapy in patients previously experiencing RPLS is not known.
Proteinuria
- In a controlled clinical study with INLYTA for the treatment of patients with RCC, proteinuria was reported in 39/359 patients (11%) receiving INLYTA and 26/355 patients (7%) receiving sorafenib. Grade 3 proteinuria was reported in 11/359 patients (3%) receiving INLYTA and 6/355 patients (2%) receiving sorafenib [see ADVERSE REACTIONS (6.1)].
- Monitoring for proteinuria before initiation of, and periodically throughout, treatment with INLYTA is recommended. For patients who develop moderate to severe proteinuria, reduce the dose or temporarily interrupt INLYTA treatment.
Elevation of Liver Enzymes
- In a controlled clinical study with INLYTA for the treatment of patients with RCC, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevations of all grades occurred in 22% of patients on both arms, with Grade 3/4 events in <1% of patients on the INLYTA arm and 2% of patients on the sorafenib arm.
- Monitor ALT, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and bilirubin before initiation of and periodically throughout treatment with INLYTA.
Hepatic Impairment
- The systemic exposure to axitinib was higher in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B) compared to subjects with normal hepatic function. A dose decrease is recommended when administering INLYTA to patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B). INLYTA has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C) [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.2), USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.6), and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY (12.3)].
Precautions
- Description
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Axitinib in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Axitinib in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Axitinib in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Axitinib during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Axitinib with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Axitinib with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Axitinib with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Axitinib with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Axitinib with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Axitinib in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Axitinib in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Axitinib in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Axitinib in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Axitinib in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Axitinib in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Axitinib in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Axitinib Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Axitinib in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Axitinib in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Axitinib in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Axitinib in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Axitinib Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Axitinib |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Axitinib |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Axitinib in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Axitinib interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Axitinib
|Pill Name=No image.jpg
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Axitinib |Label Name=Axitinib11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Axitinib |Label Name=Axitinib11.png
}}