Aspergillosis: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
'''For patient information click [[{{PAGENAME}} (patient information)|here]]''' | '''For patient information click [[{{PAGENAME}} (patient information)|here]]''' | ||
<font color="#777777"> | |||
== | ==[[Aspergillosis overview|Overview]]== | ||
== | ==[[Aspergillosis historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== | ||
==[[Aspergillosis pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== | |||
==[[Aspergillosis epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology & Demographics]]== | |||
==[[Aspergillosis risk factors|Risk Factors]]== | |||
== | ==[[Aspergillosis screening|Screening]]== | ||
== | ==[[Aspergillosis causes|Causes]]== | ||
==[[Aspergillosis differential diagnosis|Differentiating Aspergillosis]]== | |||
==[[Aspergillosis natural history|Complications & Prognosis]]== | |||
==Diagnosis== | |||
[[Aspergillosis history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Aspergillosis physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Aspergillosis laboratory tests|Laboratory tests]] | [[Aspergillosis electrocardiogram|Electrocardiogram]] | [[Aspergillosis chest x ray|X Rays]] | [[Aspergillosis CT|CT]] | [[Aspergillosis MRI|MRI]] | [[Aspergillosis echocardiography or ultrasound|Echocardiography or Ultrasound]] | [[Aspergillosis other imaging findings|Other images]] | [[Aspergillosis other diagnostic studies|Alternative diagnostics]] | |||
==Treatment== | |||
[[Aspergillosis medical therapy|Medical therapy]] | [[Aspergillosis surgical therapy|Surgical therapy]] | [[Aspergillosis prevention|Prevention]] | [[Aspergillosis cost-effectiveness of therapy|Financial costs]] | [[Aspergillosis future or investigational therapies|Future therapies]] | |||
==Case Studies== | |||
</font> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<div class="references-small"><references/></div> | <div class="references-small"><references/></div> | ||
Revision as of 16:23, 26 January 2012
| Aspergillosis | |
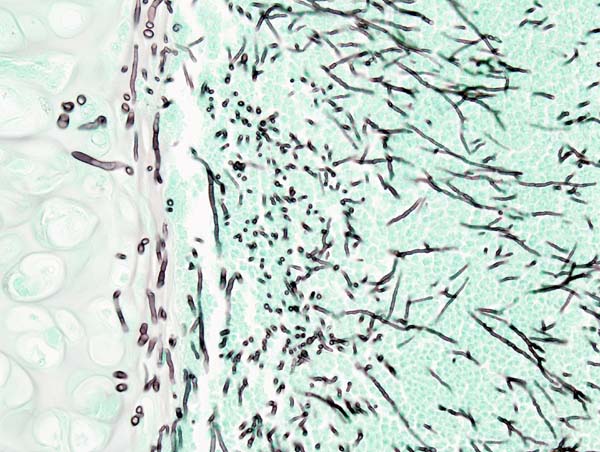 | |
|---|---|
| Histopathologic image of pulmonary invasive aspergillosis in a patient with interstitial pneumonia. Autopsy material. Grocott's methenamine silver stain. | |
| ICD-10 | B44 |
| ICD-9 | 117.3 |
| MedlinePlus | 001326 |
| MeSH | D001228 |
|
Aspergillosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Aspergillosis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Aspergillosis |
For patient information click here
Overview
Historical Perspective
Pathophysiology
Epidemiology & Demographics
Risk Factors
Screening
Causes
Differentiating Aspergillosis
Complications & Prognosis
Diagnosis
History and Symptoms | Physical Examination | Laboratory tests | Electrocardiogram | X Rays | CT | MRI | Echocardiography or Ultrasound | Other images | Alternative diagnostics
Treatment
Medical therapy | Surgical therapy | Prevention | Financial costs | Future therapies
Case Studies
References
External links
- Aspergillus - aspergillus.org.uk
- Aspergillosis -doctorfungus.org
- USGS National Wildlife Health Center - www.nwhc.usgs.gov
de:Aspergillose hr:Aspergiloza nl:Aspergillose uk:Аспергільоз }