Penbutolol adverse reactions
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sheng Shi, M.D. [2]
Adverse Reactions
levatol® is usually well tolerated in properly selected patients. Most adverse effects observed during clinical trials have been mild and reversible.
Table 1 lists the adverse reactions reported from 4 controlled studies conducted in the United States involving once-a-day administration of levatol® (at doses ranging from 10 to 120 mg) as monotherapy or in combination with hydrochlorothiazide. levatol® doses above 40 mg/day are not, however, recommended. The table includes only those events where the prevalence rate in the levatol® group was at least 1.5%, or where the reaction is of particular interest.
Over a dose range from 10 to 40 mg, once a day, fatigue, nausea, and sexual impotence occurred at a greater frequency as the dose was increased.
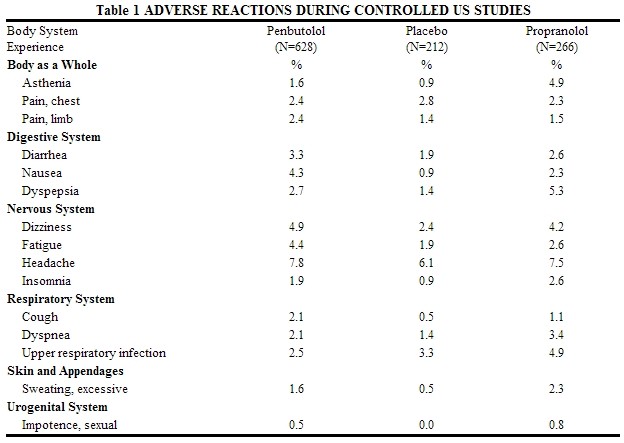 |
In a double-blind clinical trial comparing levatol® (40 mg and greater once a day) and propranolol (40 mg or more twice a day), heart rates of less than 60 beats/min. were recorded at least once in 25% of the patients in the group receiving levatol® and in 37% of the patients in the propranolol group. Corresponding figures for heart rates of less than 50 beats/min. were 1.2% and 6% respectively. No symptoms associated with bradycardia were reported.
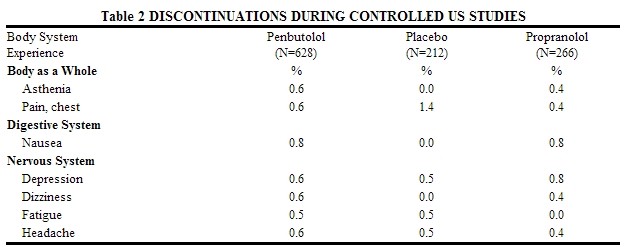
Discontinuations of levatol® because of adverse reactions have ranged between 2.4% and 6.9% of patients in double-blind, parallel, controlled clinical trials, as compared to 1.8% to 4.1% in the corresponding control groups that were given placebo. The frequency and severity of adverse reactions have not increased during long-term administration of levatol®. The prevalence of adverse reactions reported from 4 controlled clinical trials (referred to in Table 1) as reasons for discontinuation of therapy by>0.5% of the levatol® group is listed in Table 2.
 |
Potential Adverse Effects: In addition, certain adverse effects not listed above have been reported with other ß-blocking agents and should also be considered as potential adverse effects of levatol®.
Central Nervous System: Reversible mental depression progressing tocatatonia (an acute syndrome characterized by disorientation for time and place), short-term memory loss, emotional lability, slightly clouded sensorium, and decreased performance (neuropsychometrics).
Cardiovascular: Intensification of AV block (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Allergic: Erythematous rash, fever combined with aching and sore throat, laryngospasm, and respiratory distress.
Hematologic: Agranulocytosis, nonthrombocytopenic and thrombocytopenic purpura.
Gastrointestinal: Mesenteric arterial thrombosis and ischemic colitis.
Miscellaneous: Reversible alopecia and Peyronie’s disease. The oculomucocutaneous syndrome associated with the ß-blocker practolol has not been reported with levatol® during investigational use and extensive foreign clinical experience. [1]
References
- ↑ "LEVATOL (PENBUTOLOL SULFATE) TABLET [ACTIENT PHARMACEUTICALS, LLC]". Retrieved 4 February 2014.