Schistosomiasis
| Schistosomiasis | |
 | |
|---|---|
| Skin vesicles created by the penetration of Schistosoma. Source: CDC | |
| ICD-10 | B65 |
| ICD-9 | 120 |
| MeSH | D012552 |
|
Schistosomiasis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Schistosomiasis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Schistosomiasis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Clinical features
Many infections are subclinically symptomatic, with mild anemia and malnutrition being common in endemic areas. Acute schistosomiasis (Katayama's fever) may occur weeks after the initial infection, especially by S. mansoni and S. japonicum. Manifestations include:
- Abdominal pain
- Cough
- Diarrhea
- Eosinophilia - extremely high eosinophil granulocyte count.
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Hepatosplenomegaly - the enlargement of both the liver and the spleen.
Occasionally central nervous system lesions occur: cerebral granulomatous disease may be caused by ectopic S. japonicum eggs in the brain, and granulomatous lesions around ectopic eggs in the spinal cord from S. mansoni and S. haematobium infections may result in a transverse myelitis with flaccid paraplegia. Continuing infection may cause granulomatous reactions and fibrosis in the affected organs, which may result in manifestations that include:
- Colonic polyposis with bloody diarrhea (Schistosoma mansoni mostly);
- Portal hypertension with hematemesis and splenomegaly (S. mansoni, S. japonicum);
- Cystitis and ureteritis (S. haematobium) with hematuria, which can progress to bladder cancer;
- Pulmonary hypertension (S. mansoni, S. japonicum, more rarely S. haematobium);
- Glomerulonephritis; and central nervous system lesions.
Laboratory diagnosis
Microscopic identification of eggs in stool or urine is the most practical method for diagnosis. The stool exam is the more common of the two. For the measurement of eggs in the feces of presenting patients the scientific unit used is epg or eggs per gram. Stool examination should be performed when infection with S. mansoni or S. japonicum is suspected, and urine examination should be performed if S. haematobium is suspected.
Eggs can be present in the stool in infections with all Schistosoma species. The examination can be performed on a simple smear (1 to 2 mg of fecal material). Since eggs may be passed intermittently or in small amounts, their detection will be enhanced by repeated examinations and/or concentration procedures (such as the formalin-ethyl acetate technique). In addition, for field surveys and investigational purposes, the egg output can be quantified by using the Kato-Katz technique (20 to 50 mg of fecal material) or the Ritchie technique.
Eggs can be found in the urine in infections with (recommended time for collection: between noon and 3 PM) S. japonicum' and with S. intercalatum. Detection will be enhanced by centrifugation and examination of the sediment. Quantification is possible by using filtration through a nucleopore membrane of a standard volume of urine followed by egg counts on the membrane. Investigation of S. haematobium should also include a pelvic x-ray as bladder wall calcificaition is highly characteristic of chronic infection.
Recently a field evaluation of a novel handheld microscope was undertaken in Uganda for the diagnosis of intestinal schistosomiasis by a team led by Dr. Russell Stothard who heads the Schistosomiasis Control Iniative at the Natural History Museum, London. His report abstract may be found here: [2]
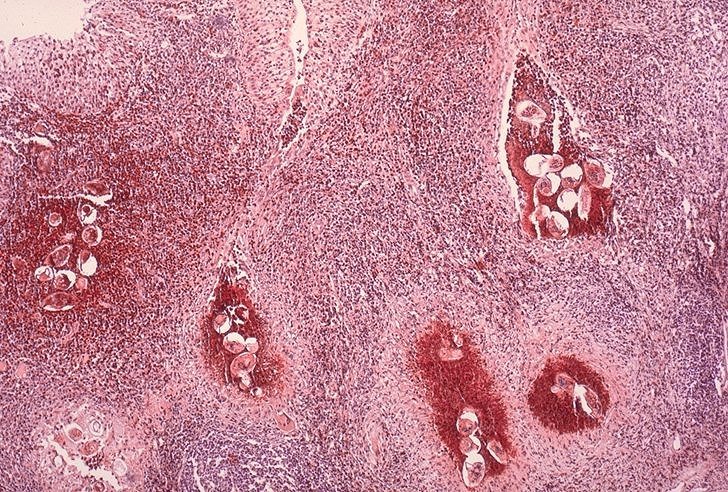
Tissue biopsy (rectal biopsy for all species and biopsy of the bladder for S. haematobium) may demonstrate eggs when stool or urine examinations are negative.
The eggs of S. haematobium are ellipsoidal with a terminal spine, S. mansoni eggs are also ellipsoidal but with a lateral spine, S. japonicum eggs are spheroidal with a small knob.
Antibody detection can be useful in both clinical management and for epidemiologic surveys.
Treatment
Schistosomiasis is readily treated using a single oral dose of the drug Praziquantel. While Praziquantel is safe and highly effective in curing an infected patient, it does not prevent re-infection by cercariae and is thus not an optimum treatment for people living in endemic areas. As with other major parasitic diseases, there is ongoing and extensive research into developing a vaccine that will prevent the parasite from completing its life cycle in humans.
Antimony has been used in the past to treat the disease. In low doses, this toxic metalloid bonds to sulfur atoms in enzymes used by the parasite and kills it without harming the host. This treatment is not referred to in present-day peer-review scholarship; Praziquantel is universally used. Outside of the US, there is a second drug available for treating Schistosoma mansoni (exclusively) called Oxamniquine.
Mirazid, a new Egyptian drug, is under investigation for oral treatment of the disease.
Experiments have shown medicinal Castor oil as an oral anti-penetration agent to prevent Schistosomiasis and that praziquantel's effectiveness depended upon the vehicle used to administer the drug (e.g., Cremophor / Castor oil).[1]
Additionally Dr Chidzere of Zimbabwe researched the Gopo Berry (Phytolacca dodecandra) during the 1980's and found that the Gopo Berry could be used in the control of the freshwater snails which carry the bilharzia disease (Schistosomiasis parasite). Dr Chidzere in his interview to Andrew Blake (1989) reported concerns of muti-national chemical companies keen to rubbish the Gopu Berry alternative for snail control [2]. Reputedly Gopo Berries from hotter Ethiopia climates yield the best results. Later studies were between 1993-95 by the Danish Research Network for international health. [3]
Prevention through good design
The main focus of prevention is eliminating the water-borne snails which are natural reservoirs for the disease. This is usually done by identifying bodies of water, such as lakes, ponds, etc., which are infested, forbidding or warning against swimming and adding niclosamide, acrolein, copper sulfate, etc., to the water in order to kill the snails.
Unfortunately for many years from the 1950s onwards, despite the efforts of some clinicians to get civil engineers to take it into account in their designs, civil engineeers built vast dam and irrigation schemes, oblivious of the fact that they would cause a massive rise in water-borne infections from schistosomiasis, even though with a little care the schemes could have been designed to minimise such effects, the detailed specifications having been laid out in various UN documents since the 1950s. Irrigation schemes can be designed to make it hard for the snails to colonise the water, and to reduce the contact with the local population. [4]
Failure for engineers to take this into account is an interesting example of the Relevance Paradox and is a good example of the failure of formal education and information systems to transmit tacit knowledge.
Prevention and hygiene
Prevention is best accomplished by eliminating the water-dwelling snails which are the natural reservoir of the disease. Acrolein, copper sulfate, and niclosamide can be used for this purpose. Recent studies have suggested that snail populations can be controlled by the introduction or augmentation of existing crayfish populations; as with all ecological interventions, however, this technique must be approached with caution.
Individuals can guard against schistosomiasis infection by avoiding bodies of water known or likely to harbor the carrier snails.
In 1989, Aklilu Lemma and Legesse Wolde-Yohannes received the Right Livelihood Award for their research on the sapindus-Plant (Phytolacca dodecandra), as a preventative measure for the disease.
Histopathology: Rectum, Schistosomiasis
{{#ev:youtube|9VpqxnPRvL8}}
See also
References
- ↑ "Schistosoma mansoni: experimental chemoprophylaxis in mice using oral anti-penetration agents". pubmed. Retrieved 2007-01-25.
- ↑ The Gopu Berry p33. Part 4 School Journal number.2 1989 Dept of Education Wellington N.Z
- ↑ http://enrecahealth.ku.dk/postgrad_dbl_en/chihaka_abs/
- ↑ Charnock, Anne (1980) Taking Bilharziasis out of the irrigation equation. New Civil Engineer, 7 August. 1980 Bilharzia caused by poor civil engineering design due to ignorance of cause and prevention
External links
- World Health Organization Partners for Parasite Control website
- World Health Organization fact sheet on the disease
- Wellcome animation of the life cycle of the parasite
- Schistosomiasis Control Initiative
- CONTRAST, a research project on optimized schistosomiasis control in Sub-saharan Africa
- World Health Organization Tropical Disease Research programme
- Cambridge University Schistosomiasis Research Group
- York University Schistosomiasis Research Group
- Schistosomiasis (Bilharzia) Control and Prevention: The Carter Center Schistosomiasis Control Program
- Links to Schistosomiasis pictures (Hardin MD/Univ of Iowa)
- FIOCRUZ - Schistomiasis Research Group
- Sandler Center for Basic Research in Parasitic Diseases, University of California San Francisco
- Vacine developed in Queensland, Australia
- DBL - Centre for Health Research and Development
- 10. Charnock, Anne (1980) Taking Bilharziasis out of the irrigation equation. New Civil Engineer, 7 August. Bilharzia caused by poor civil engineering design due to ignorance of cause and prevention.
Template:Link FA
Template:Helminthiases
ar:بلهارسيا
de:Schistosomiasis
eo:Helika febro
it:Schistosomiasi
lt:Šistosomozė
nl:Schistosomiasis
fi:Skistosomiaasi
sv:Snäckfeber