Vestibular nerve
Template:Infobox Nerve Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
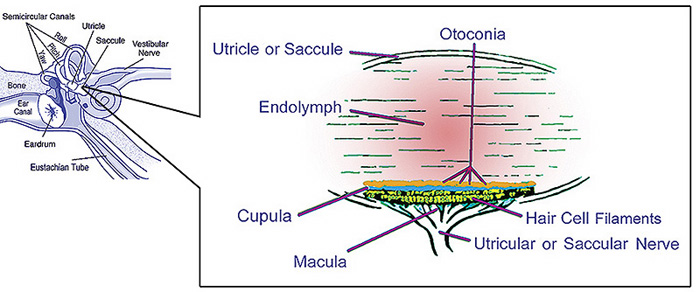
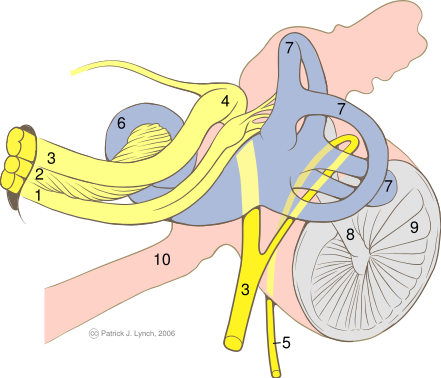
The vestibular nerve is one of the two branches of the Vestibulocochlear nerve (the cochlear nerve being the other). It goes to the semicircular canals via the vestibular ganglion. It receives positional information.
Axons of the vestibular nerve synapse in the vestibular nucleus on the lateral floor and wall of the fourth ventricle in the pons and medulla.
It arises from bipolar cells in the vestibular ganglion, ganglion of Scarpa, which is situated in the upper part of the outer end of the internal auditory meatus.
Branches
The peripheral fibers divide into three branches:
- the superior branch passes through the foramina in the area vestibularis superior and ends in the utricle and in the ampullae of the superior and lateral semicircular ducts;
- the fibers of the inferior branch traverse the foramina in the area vestibularis inferior and end in the saccule;
- the posterior branch runs through the foramen singulare and supplies the ampulla of the posterior semicircular duct.
See also
Additional images
-
Illustration of otolith organs
-
Ear internal anatomy