Esophagus
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
|
WikiDoc Resources for Esophagus |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Esophagus |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Esophagus at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Esophagus at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Esophagus
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Esophagus Discussion groups on Esophagus Directions to Hospitals Treating Esophagus Risk calculators and risk factors for Esophagus
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Esophagus |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
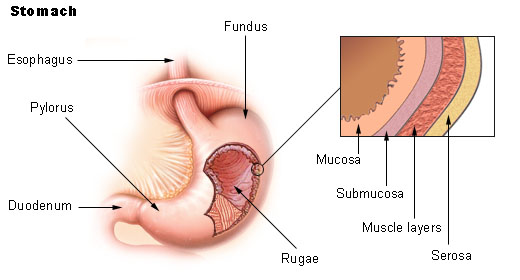
The esophagus (also spelled oesophagus/œsophagus, Greek Template:Polytonic), or gullet is an organ in vertebrates which consists of a muscular tube through which food passes from the pharynx to the stomach. In humans, the esophagus is continuous with the laryngeal part of the pharynx at the level of the C6 vertebra.
Functioning
Food is passed through the esophagus by using the process of peristalsis. Specifically, it connects the pharynx, which is the body cavity that is common to the digestive factory and respiratory system with the stomach, where the second stage of digestion is initiated.
The esophagus is lined with mucous membrane, and is more deeply lined with muscle that acts with peristaltic action to move swallowed food down to the stomach.
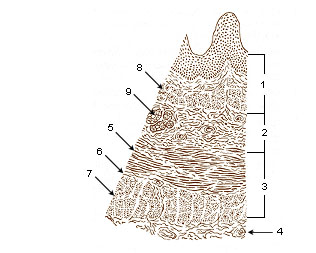
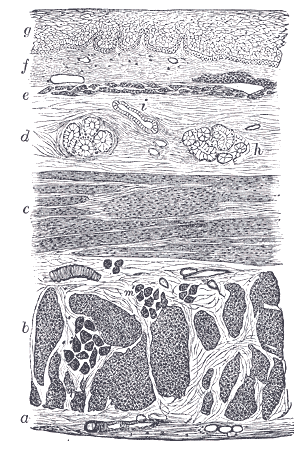
Histology
The layers of the esophagus are as follows:[1]
- mucosa
- nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium: is rapidly turned over, and serves a protective effect due to the high volume transit of food, saliva and mucous.
- lamina propria: sparse.
- muscularis mucosae: smooth muscle
submucosa: Contains the mucous secreting glands (esophageal glands), and connective structures termed papillae.
- muscularis externa (or "muscularis propria"): composition varies in different parts of the esophagus, to correspond with the conscious control over swallowing in the upper portions and the autonomic control in the lower portions:
- upper third, or superior part: striated muscle
- middle third, smooth muscle and striated muscle,
- inferior third: predominantly smooth muscle.
- adventitia
Gastroesophageal junction
The junction between the esophagus and the stomach (the gastroesophageal junction or GE junction) is not actually considered a valve, although it is sometimes called the cardiac sphincter, cardia or cardias, but is actually more of a stricture.
Etymology
It derives from Greek; hiοiσω -oeso, future tense of the verb φερω-to bring and from the verb έφαγον,-phagus, past tense of τρώγω-to eat. The word "esophagus" is the result of the "o" being dropped from the oe (or œ) in "oesophagus". This vowel does not exist in English but in most other Indoeuropean languages as œ, ö, or ø. In mostly the rest of the non-US world, and according standard international latin and greek medical nomemclature, the spelling oesophagus (similarly œsophagus, ösofagus, or øsofagus) is used.
Esophageal diseases and conditions
Many people experience a burning sensation in their chest occasionally, caused by stomach acids refluxing into the esophagus, normally called heartburn. Extended exposure to heartburn may erode the lining of the esophagus, leading potentially to Barrett's esophagus which is associated an increased risk of adenocarcinoma most commonly found in the distal one-third of the oesophagus.
Some people also experience a sensation known as globus esophagus, where it feels as if a ball is lodged in the lower part of the esophagus.
The following are additional diseases and conditions that affect the oesophagus:
- Achalasia
- Chagas disease
- Caustic injury to the esophagus
- Esophageal atresia and Tracheoesophageal fistula
- Esophageal cancer
- Esophageal web
- Esophagitis
- GERD
- Hiatus hernia
- Mallory-Weiss syndrome
- Neurogenic dysphagia
- Schatzki's ring
- Zenker's Diverticulum
- Boerhaave syndrome
Additional images
-
Layers of the esophagus.
-
Mid esophageal mass
-
Stomach
-
Accessory digestive system.
-
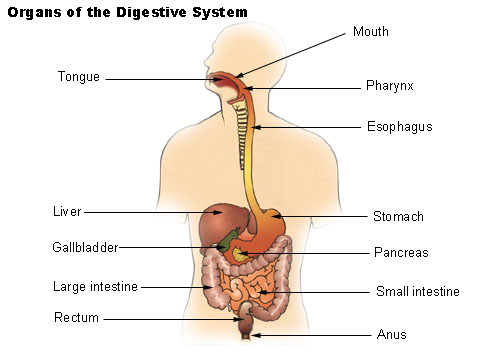
Organs of the digestive tract.
-
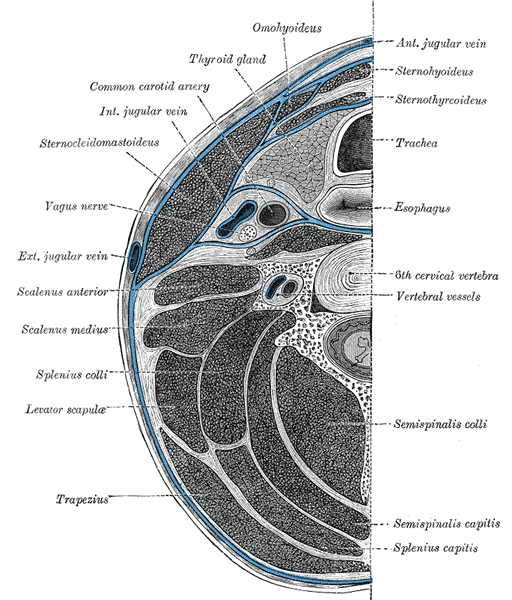
Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra.
-
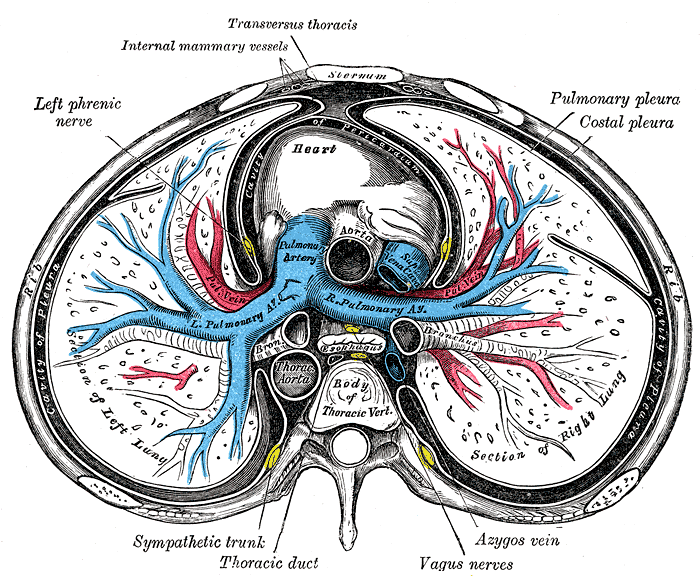
Transverse section of thorax, showing relations of pulmonary artery.
-
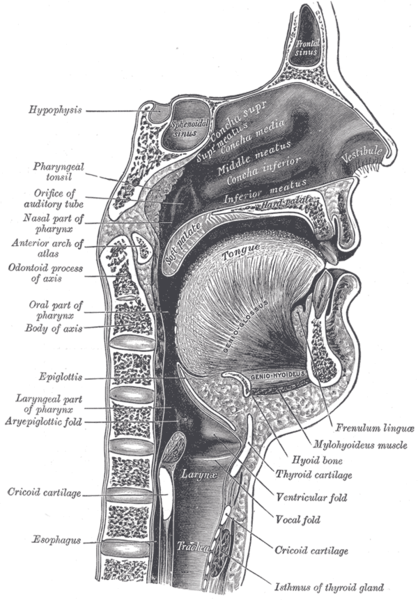
Sagittal section of nose mouth, pharynx, and larynx.
-
Section of the human esophagus. Moderately magnified.
-
Microscopic shot of a cross section of human gastro-esophageal junction wall.
References
- ↑ Histology image: 10801loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
External links
ar:مرئ bs:Jednjak bg:Хранопровод ca:Esòfag cs:Jícen da:Spiserør de:Speiseröhre et:Söögitoru el:Οισοφάγος eo:Ezofago eu:Hestegorri hr:Jednjak id:Esofagus is:Vélinda it:Esofago he:ושט ku:Sorîçik la:Oesophagus lt:Stemplė mk:Хранопровод nl:Slokdarm no:Spiserøret sq:Ezofagu simple:Oesophagus sk:Pažerák sr:Једњак fi:Ruokatorvi sv:Matstrupe uk:Стравохід yi:וושט