Tibialis posterior muscle
Template:Infobox Muscle Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [2] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
Overview
The Tibialis posterior is the most central of all the leg muscles.
It is the key stabilising muscle of the lower leg.
Origin and insertion
It originates on the inner posterior borders of the tibia and fibula. It is also attached to the interosseous membrane, which attaches to the tibia and fibula.
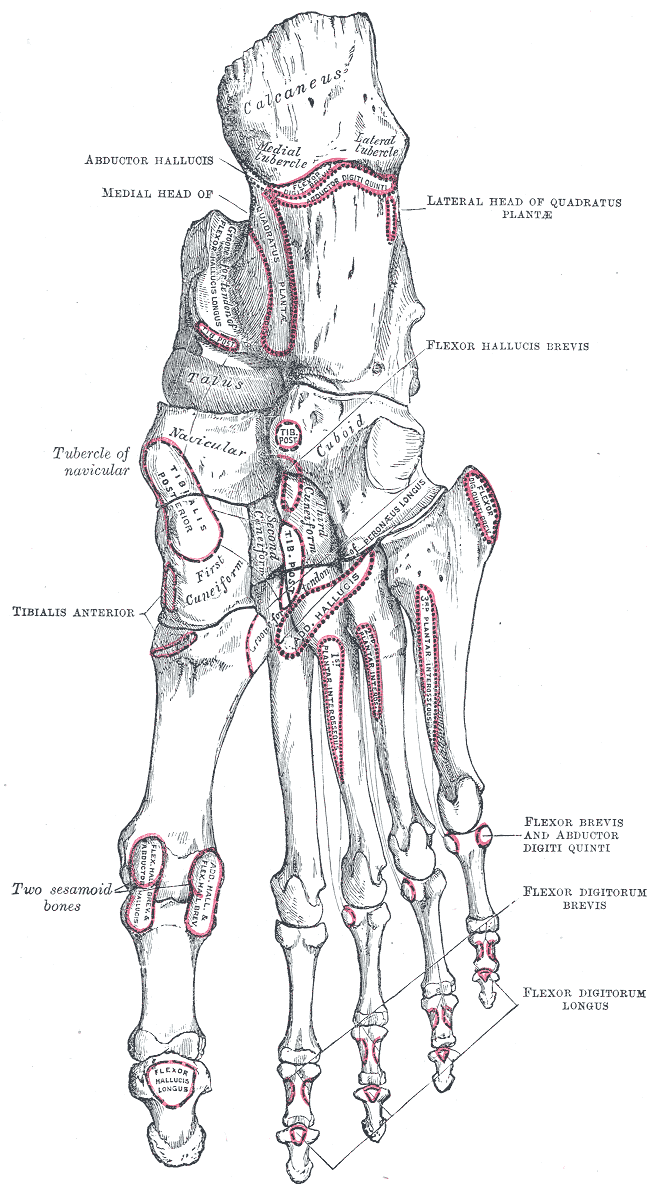
The tendon of tibialis posterior the decends down posterior to the medial malleolus and to the plantar surface of the foot where it inserts on to the tuberosity of the navicular, the first and third cuneiforms, the cuboid and the second, third and fourth metatarsals.
Function
As well as being a key muscle for stabilisation, the tibialis posterior muscle also contracts to produce inversion of the foot and assists in the plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle.
Additional images
-
Bones of the right leg. Posterior surface.
-
Bones of the right foot. Plantar surface.
-
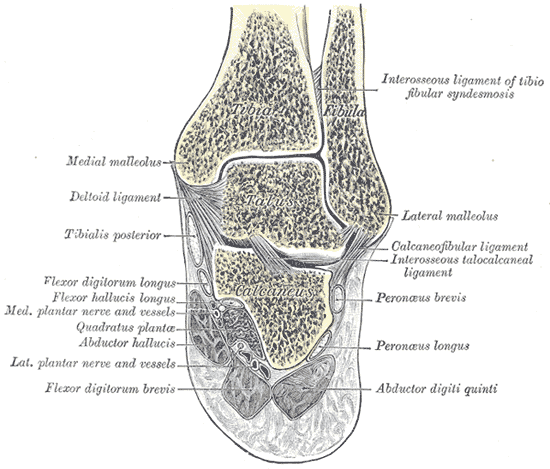
Coronal section through right talocrural and talocalcaneal joints.
-
Muscles of the back of the leg. Deep layer.
-
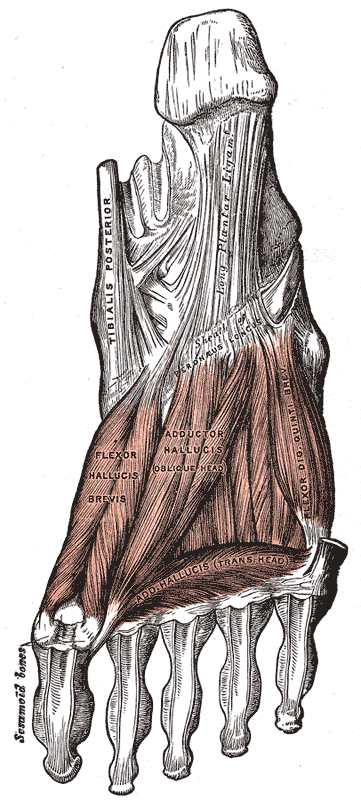
Muscles of the sole of the foot. Third layer.
-
The popliteal, posterior tibial, and peroneal arteries.
External links
- Template:MuscleLoyola
- Template:SUNYAnatomyLabs
- Template:EMedicineDictionary
- Diagram at washington.edu
- Diagram at latrobe.edu.au
Template:Muscles of lower limb
de:Musculus tibialis posterior he:השריר השוקתי האחורי Template:WikiDoc Sources