Intrauterine growth retardation
| Intrauterine growth retardation | |
 | |
|---|---|
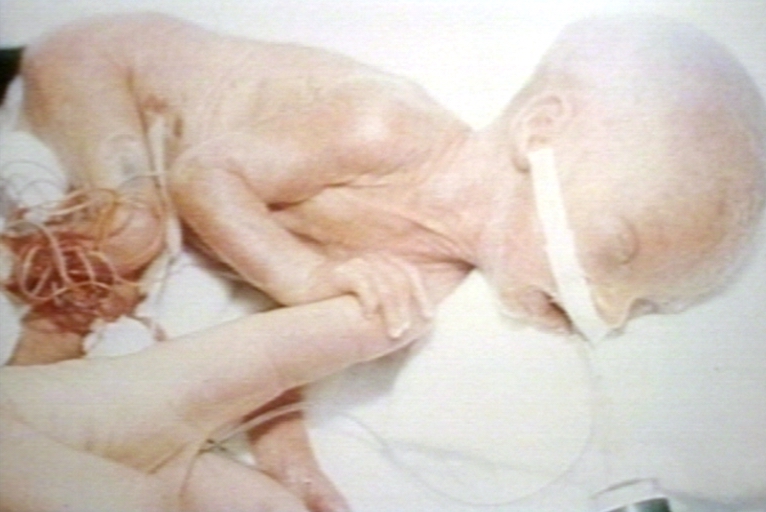
| A premature newborn Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology | |
| MedlinePlus | 001500 |
For patient information, click here
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: : Kalsang Dolma, M.B.B.S.[2]
Synonyms and keywords:Intrauterine growth restriction
Overview
Intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR) refers to persons small for their gestational age
causes
Common Causes
Causes by Organ System
Causes in Alphabetical Order
References
Template:SIB Template:WH Template:WikiDoc Sources
| Cardiovascular | Chronic hypertension, Cyanotic heart disease, Eclampsia, Gestational hypertension, Maternal preclampsia, |
| Chemical / poisoning | Toxin |
| Dermatologic | No underlying causes |
| Drug Side Effect | Phenytoin |
| Ear Nose Throat | No underlying causes |
| Endocrine | Congenital hyperinsulinism, Maturity onset diabetes of the young |
| Environmental | Prolonged high-altitude exposure |
| Gastroenterologic | No underlying causes |
| Genetic | No underlying causes |
| Hematologic | No underlying causes |
| Iatrogenic | No underlying causes |
| Infectious Disease | No underlying causes |
| Musculoskeletal / Ortho | No underlying causes |
| Neurologic | No underlying causes |
| Nutritional / Metabolic | No underlying causes |
| Obstetric/Gynecologic | No underlying causes |
| Oncologic | No underlying causes |
| Opthalmologic | No underlying causes |
| Overdose / Toxicity | No underlying causes |
| Psychiatric | No underlying causes |
| Pulmonary | No underlying causes |
| Renal / Electrolyte | No underlying causes |
| Rheum / Immune / Allergy | No underlying causes |
| Sexual | No underlying causes |
| Trauma | No underlying causes |
| Urologic | No underlying causes |
| Miscellaneous | No underlying causes |