Choledocholithiasis
Template:DiseaseDisorder infobox
|
Choledocholithiasis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Choledocholithiasis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Choledocholithiasis |
For patient information click here
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [2] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
Overview
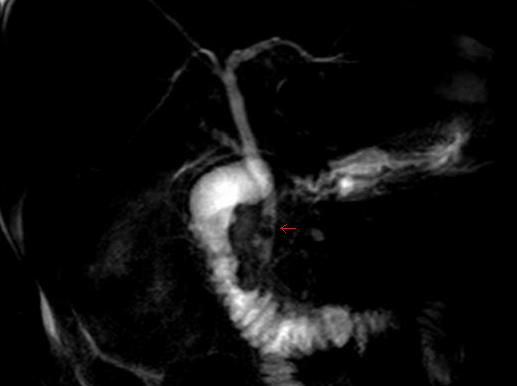
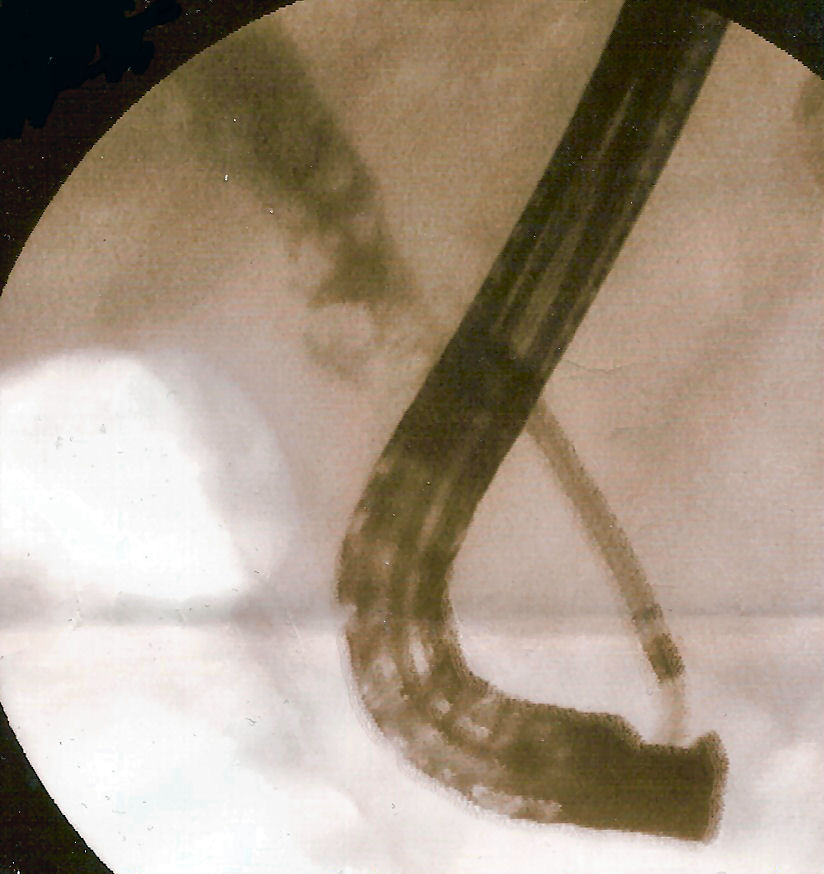
Choledocholithiasis is the presence of gallstones in the common bile duct. This condition causes jaundice and liver cell damage, and is a medical emergency, requiring the endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) procedure or surgical treatment.
A tendency for this disease can be inherited.
Cause
While stones can frequently pass through the common bile duct into the duodenum, some stones may be too large to passthrough the CBD and will cause an obstruction.
Complications
This obstruction leads to jaundice, elevation in alkaline phosphatase, increase in conjugated bilirubin in the blood and increase in cholesterol in the blood. It can also cause acute pancreatitis and ascending cholangitis.
Diagnosis
Doctors can use a blood test of alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin and cholesterol to diagnose choledocholithiasis.
However, ultrasound demonstrating an enlarged common bile duct is the test of choice.
Treatment
Treatment involves removing the stone using ERCP. Typically, the gallbladder is then removed to prevent a future occurrence of common bile duct obstruction.