WBR0710
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Mohamed Moubarak, M.D. [1]]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 3 |
| Main Category | |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Infectious Disease |
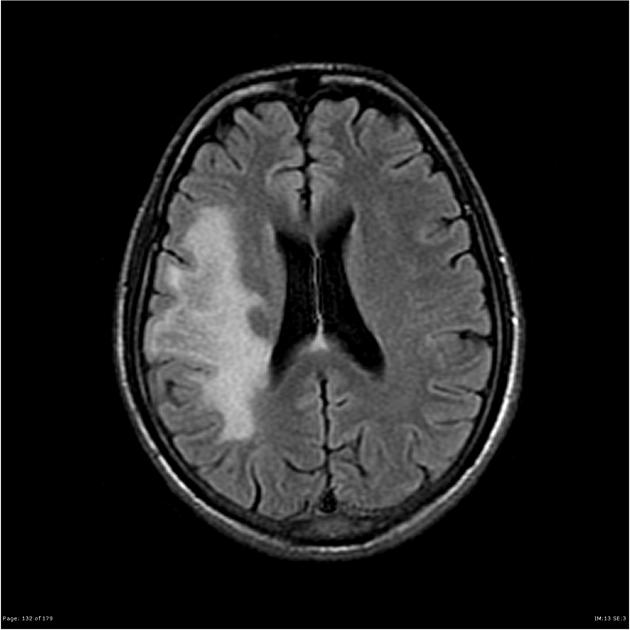
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 30 years old male with AIDS presents to ED complaining of decreased vision on the left side, with tingling sensation and weakness on the left upper and lower extremities. His current medication is zidovudine, lamivudine, and indinavir. Physical examination reveals visual field defects in both eyes, intact papillary reflex. There is an exaggerated deep tendon reflex and diminished sensation of touch and motor power in the left upper and lower extremities. MRI of the brain is shown below. Which of the following the most likely diagnosis? |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy |
| Answer A Explanation | [[AnswerAExp::Correct
Classic MRI findings of PML consist of multiple demyelinating, non enhancing lesions with no mass effect.]] |
| Answer B | AnswerB::Toxoplasmosis |
| Answer B Explanation | [[AnswerBExp::Incorrect
Toxoplasmosis are common with AIDS, but associated with ring-enhancing lesions and show a mass effect on MRI]] |
| Answer C | AnswerC::CNS lymphoma |
| Answer C Explanation | [[AnswerCExp::Incorrect
CNS lymphoma are common with AIDS, but associated with ring-enhancing lesions and show a mass effect on MRI]] |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Brain abscess |
| Answer D Explanation | [[AnswerDExp::Incorrect
Brain abscess are common with AIDS, but associated with ring-enhancing lesions and show a mass effect on MRI]] |
| Answer E | AnswerE::HIV encephalopathy |
| Answer E Explanation | [[AnswerEExp::Incorrect
usually present with dementia as the predominant symptom. Focal neurological deficits are not characteristics of this disease. MRI findings may be similar to PML put usually tends to be symmetrical]] |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::A |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is an opportunistic infection seen in immunocompromised patients. It is caused by JC virus, a human polyomavirus.
PML predominantly involves the cortical white matter, but the brainstem and cerebellum may also be involved. The lesion typically doesn’t produce mass effect, and has a gradual onset of the symptoms. The most common presenting symptoms are hemipariesis and disturbances in speech, vision, and gait. An immunocompromised patient with focal neurological deficits should raise the suspicion for PML, and diagnosis is best confirmed with MRI. Classic MRI findings of PML consist of multiple demyelinating, non enhancing lesions with no mass effect. There is no effective treatment for PML, and the mean duration of survival from the time of diagnosis is six months. |
| Approved | Approved::No |
| Keyword | [[WBRKeyword::HIV]] |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |