Nephrologic Disorders and COVID-19
To go to the COVID-19 project topics list, click here.
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sogand Goudarzi, MD [2] Nasrin Nikravangolsefid, MD-MPH [3]
Overview
Nephrologic_Disorders of COVID-19
Nephrologic_Disorders risk factors of COVID-19
Complications
AKI
Pathophysiology
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), which is a primary receptor for SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells, mostly presents in renal tubular epithelial cells as well as lungs and heart.[1]
- Despite kidney injury following COVID-19 infection is less frequent than severe lung injury, ACE2: ACE ratio is higher in the kidneys compared to the respiratory system. (1:1 in the kidneys VS 1:20 in the respiratory system)[1]
- After SARS-CoV-2 enters through the nasal cavity, it may travel to the kidneys and enters the bloodstream leading to severe inflammatory response activation and cytokine storm.
- It is thought that AKI following COVID-19 is the result of[1]
- Sepsis
- Hypovolemia and Hypotension
- Hypoxemia
- Blood clots formation, leading to impaired blood flow in the renal arterioles.
- AKI often occurs at later stages in critically ill patients with COVID-19 following multiple organ failure.
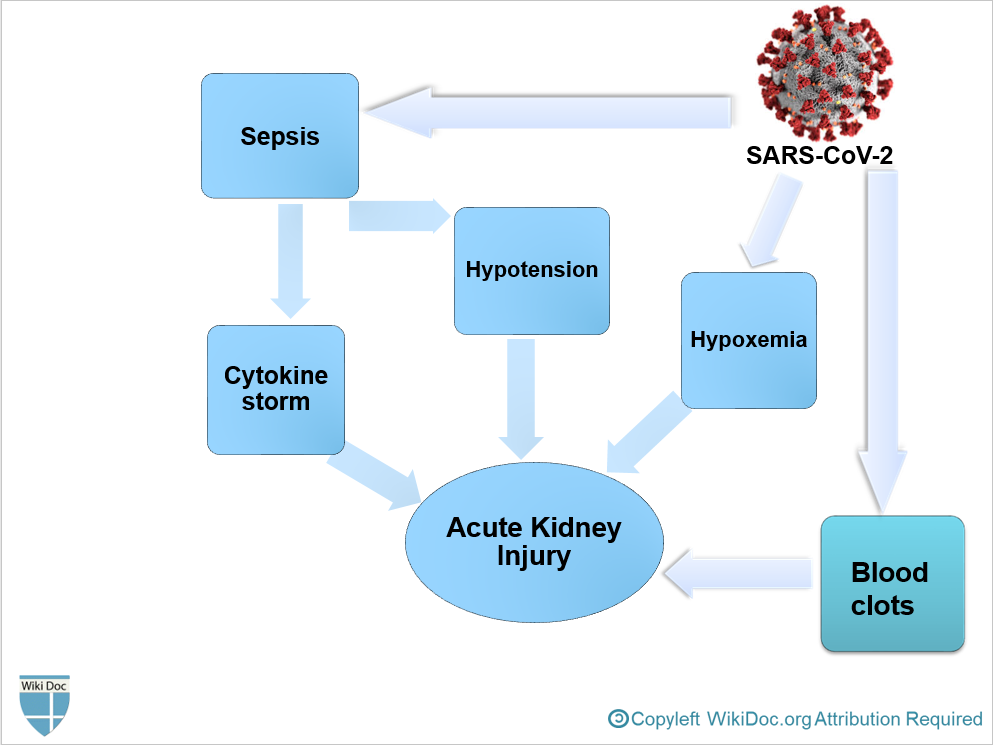
Clinical Features of AKI by SARS-CoV-2
Treatment
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 Malha, Line; Mueller, Franco B.; Pecker, Mark S.; Mann, Samuel J.; August, Phyllis; Feig, Peter U. (2020). "COVID-19 and the Renin-Angiotensin System". Kidney International Reports. 5 (5): 563–565. doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2020.03.024. ISSN 2468-0249.