Erythromycin/Benzoyl Peroxide
{{DrugProjectFormSinglePage |authorTag={{�SS}} |genericName=Erythromycin/Benzoyl Peroxide |aOrAn=a |drugClass=Macrolide |indication=acne vulgaris |adverseReactions=Application site reaction, Dry skin, Urticaria |blackBoxWarningTitle=TITLE |blackBoxWarningBody=Condition Name: (Content)
|fdaLIADAdult=
[[Acne Vulga�ris]]
- Dosing information
- BENZAMYCIN Topical Gel should be applied twice daily, morning and evening, or as directed by a physician, to affected areas after the skin is thoroughly washed, rinsed with warm water and gently patted dry.
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Erythromycin/Benzoyl Peroxide in adult patients. |offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Erythromycin/Benzoyl Peroxide in adult patients. |fdaLIADPed=Safety and effectiveness of this product in pediatric patients below the age of 12 have not been established. |offLabelPedGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Erythromycin/Benzoyl Peroxide in pediatric patients. |offLabelPedNoGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Erythromycin/Benzoyl Peroxide in pediatric patients. |contraindications=BENZAMYCIN Topical Gel is contraindicated in those individuals who have shown hypersensitivity to any of its components. |warnings=Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with nearly all antibacterial agents, including erythromycin, and may range in severity from mild to life-threatening. Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhea subsequent to the administration of antibacterial agents.
Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon and may permit overgrowth of clostridia. Studies indicate that a toxin produced by Clostridium difficile is one primary cause of "antibiotic-associated colitis."
After the diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis has been established, therapeutic measures should be initiated. Mild cases of pseudomembranous colitis usually respond to drug discontinuation alone. In moderate to severe cases, consideration should be given to management with fluids and electrolytes, protein supplementation and treatment with an antibacterial drug clinically effective against C. difficile colitis. |clinicalTrials=In controlled clinical trials, the incidence of adverse reactions associated with the use of BENZAMYCIN Topical Gel was approximately 3%. These were dryness and urticarial reaction.
The following additional local adverse reactions have been reported occasionally: irritation of the skin including peeling, itching, burning sensation, erythema, inflammation of the face, eyes and nose, and irritation of the eyes. Skin discoloration, oiliness and tenderness of the skin have also been reported.
|postmarketing=FDA Package Insert for Erythromycin/Benzoyl Peroxide contains no information regarding postmarketing experience. |drugInteractions=FDA Package Insert for Erythromycin/Benzoyl Peroxide contains no information regarding Drug Interaction. |FDAPregCat=C |useInPregnancyFDA=Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with BENZAMYCIN Topical Gel or benzoyl peroxide.
There was no evidence of teratogenicity or any other adverse effect on reproduction in female rats fed erythromycin base (up to 0.25% diet) prior to and during mating, during gestation and through weaning of two successive litters.
There are no well-controlled trials in pregnant women with BENZAMYCIN Topical Gel. It also is not known whether BENZAMYCIN Topical Gel can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproductive capacity. BENZAMYCIN Topical Gel should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed. |useInNursing=It is not known whether BENZAMYCIN Topical Gel is excreted in human milk after topical application. However, erythromycin is excreted in human milk following oral and parenteral erythromycin administration. Therefore, caution should be exercised when erythromycin is administered to a nursing woman. |useInPed=Safety and effectiveness of this product in pediatric patients below the age of 12 have not been established. |administration=Applied twice daily, morning and evening, or as directed by a physician, to affected areas after the skin is thoroughly washed, rinsed with warm water and gently patted dry. |monitoring=FDA Package Insert for Erythromycin/Benzoyl Peroxide contains no information regarding Drug Monitoring. |IVCompat=There is limited information about the IV Compatibility. |overdose=FDA Package Insert for Erythromycin/Benzoyl Peroxide contains no information regarding overdose. |mechAction=The exact mechanism by which erythromycin reduces lesions of acne vulgaris is not fully known; however, the effect appears to be due in part to the antibacterial activity of the drug.
Benzoyl peroxide has a keratolytic and desquamative effect which may also contribute to its efficacy. Benzoyl peroxide has been shown to be absorbed by the skin where it is converted to benzoic acid. |structure=BENZAMYCIN® Topical Gel contains erythromycin [(3R*, 4S*, 5S*, 6R*, 7R*, 9R*, 11R*, 12R*, 13S*, 14R*)-4-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-α-L-ribo-hexopyranosyl)-oxy]-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyl-6-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-β-D-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]oxacyclotetradecane-2,10-dione]. Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic produced from a strain of Saccharopolyspora erythraea (formerly Streptomyces erythreus). It is a base and readily forms salts with acids.
Chemically, erythromycin is (C37H67NO13). It has the following structural formula:

Erythromycin has the molecular weight of 733.94. It is a white crystalline powder and has a solubility of approximately 1 mg/mL in water and is soluble in alcohol at 25°C.
BENZAMYCIN Topical Gel also contains benzoyl peroxide for topical use. Benzoyl peroxide is an antibacterial and keratolytic agent.
Chemically, benzoyl peroxide is (C14H10O4). It has the following structural formula:

|PD=FDA Package Insert for Erythromycin/Benzoyl Peroxide contains no information regarding Pharmacodynamics.
|PK=FDA Package Insert for Erythromycin/Benzoyl Peroxide contains no information regarding Pharmacokinetics.
|nonClinToxic=====CARCINOGENESIS, MUTAGENESIS AND IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY====
Data from a study using mice known to be highly susceptible to cancer suggests that benzoyl peroxide acts as a tumor promoter. The clinical significance of this is unknown.
No animal studies have been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic and mutagenic potential or effects on fertility of topical erythromycin. However, long-term (2-year) oral studies in rats with erythromycin ethylsuccinate and erythromycin base did not provide evidence of tumorigenicity. There was no apparent effect on male or female fertility in rats fed erythromycin (base) at levels up to 0.25% of diet. |clinicalStudies=FDA Package Insert for Erythromycin/Benzoyl Peroxide contains no information regarding Clinical Studies.
|howSupplied=
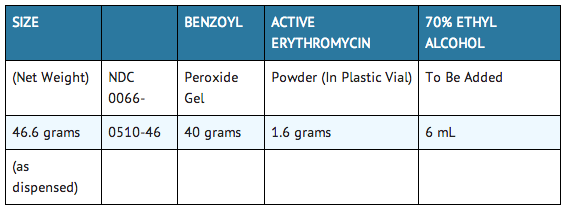
Prior to dispensing, tap vial until all powder flows freely. Add indicated amount of room temperature 70% ethyl alcohol to vial (to the mark) and immediately shake to completely dissolve erythromycin. Add this solution to gel and stir until homogeneous in appearance (1 to 1½ minutes). BENZAMYCIN Topical Gel should then be stored under refrigeration. Do not freeze. Place a 3-month expiration date on the label. |storage=Prior to reconstitution, store at room temperature between 15° and 30°C (59° – 86°F).
After reconstitution, store under refrigeration between 2° and 8°C (36° – 46°F).
Do not freeze. Keep tightly closed. Keep out of the reach of children. |fdaPatientInfo=Patients using BENZAMYCIN Topical Gel should receive the following information and instructions:
This medication is to be used as directed by the physician. It is for external use only. Avoid contact with the eyes, nose, mouth, and all mucous membranes. This medication should not be used for any disorder other than that for which it was prescribed. Patients should not use any other topical acne preparation unless otherwise directed by physician. Patients should report to their physician any signs of local adverse reactions. BENZAMYCIN® Topical Gel may bleach hair or colored fabric.
|alcohol=Alcohol-Erythromycin/Benzoyl Peroxide interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. |brandNames=Benzamycin Pak |lookAlike=Therer is limited information about the look alike drug names. }} {{#subobject:
|Label Page=Erythromycin/Benzoyl Peroxide |Label Name=Erythromycin Benzoyl Peroxide_label_01.jpg
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Erythromycin/Benzoyl Peroxide |Label Name=Erythromycin Benzoyl Peroxide_panel_01.png
}}