Lenvatinib
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1];
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
Title
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
ConditionName:
|
Overview
Lenvatinib is a that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of . There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include .
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Thyroid cancer (DTC).
LENVIMA is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally recurrent or metastatic, progressive, radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC).
Dosing Information
Recommended Dose
- The recommended daily dose of LENVIMA is 24 mg (two 10 mg capsules and one 4 mg capsule) orally taken once daily with or without food . Continue LENVIMA until disease progression or until unacceptable toxicity occurs.
- Take LENVIMA at the same time each day. If a dose is missed and cannot be taken within 12 hours, skip that dose and take the next dose at the usual time of administration.
- Severe Renal or Hepatic Impairment
- The recommended dose of LENVIMA is 14 mg taken orally once daily in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance [CLcr] less than 30 mL/min calculated by the Cockroft-Gault equation) or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C).
Dose Modifications
- Hypertension
- Assess blood pressure prior to and periodically during treatment. Initiate or adjust medical management to control blood pressure prior to and during treatment
- Withhold LENVIMA for Grade 3 hypertension that persists despite optimal antihypertensive therapy; resume at a reduced dose (see Table 1) when hypertension is controlled at less than or equal to Grade 2.
- Discontinue LENVIMA for life-threatening hypertension.
- Cardiac dysfunction or hemorrhage
- Discontinue for a Grade 4 event.
- Withhold LENVIMA for development of Grade 3 event until improved to Grade 0 or 1 or baseline.
- Either resume at a reduced dose (see Table 1) or discontinue LENVIMA depending on the severity and persistence of the adverse event.
- Arterial thrombotic event
- Discontinue LENVIMA following an arterial thrombotic event. Renal failure and impairment or hepatotoxicity Withhold LENVIMA for development of Grade 3 or 4 renal failure/impairment or hepatotoxicity until resolved to Grade 0 to 1 or baseline.
- Either resume at a reduced dose (see Table 1) or discontinue LENVIMA depending on the severity and persistence of renal impairment or hepatotoxicity.
- Discontinue LENVIMA for hepatic failure.
- Proteinuria
- Withhold LENVIMA for ≥2 grams of proteinuria/24 hours.
- Resume at a reduced dose (see Table 1) when proteinuria is <2 gm/24 hours.
- Discontinue LENVIMA for nephrotic syndrome. Gastrointestinal perforation or fistula formation
- Discontinue LENVIMA in patients who develop gastrointestinal perforation or lifethreatening fistula.
- QT prolongation
- Withhold LENVIMA for the development of Grade 3 or greater QT interval prolongation.
- Resume LENVIMA at a reduced dose (see Table 1) when QT prolongation resolves to Grade 0 or 1 or baseline.
- Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS)
- Withhold for RPLS until fully resolved. Upon resolution, resume at a reduced dose or discontinue LENVIMA depending on the severity and persistence of neurologic symptoms.
- Manage other adverse reactions according to the instructions in Table 1. Based on the absence of clinical experience, there are no recommendations on resumption of dosing in patients with Grade 4 clinical adverse reactions that resolve.
tABLE02
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Lenvatinib in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Lenvatinib in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Lenvatinib in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Lenvatinib in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Lenvatinib in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- None.
Warnings
|
Title
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
ConditionName:
|
Hypertension
- In Study 1 hypertension was reported in 73% of LENVIMA-treated patients and 16% of patients in the placebo group . The median time to onset of new or worsening hypertension was 16 days for LENVIMA-treated patients. The incidence of Grade 3 hypertension was 44% as compared to 4% for placebo, and the incidence of Grade 4 hypertension was less than 1% in LENVIMA-treated patients and none in the placebo group.
- Control blood pressure prior to treatment with LENVIMA. Monitor blood pressure after 1 week, then every 2 weeks for the first 2 months, and then at least monthly thereafter during treatment with LENVIMA. Withhold LENVIMA for Grade 3 hypertension despite optimal antihypertensive therapy; resume at a reduced dose when hypertension is controlled at less than or equal to Grade 2. Discontinue LENVIMA for life-threatening hypertension .
Cardiac Dysfunction
- In Study 1, cardiac dysfunction, defined as decreased left or right ventricular function, cardiac failure, or pulmonary edema, was reported in 7% of LENVIMA-treated patients (2% Grade 3 or greater) and 2% (no Grade 3 or greater) of patients in the placebo group. The majority of these cases in LENVIMA-treated patients (14 of 17 cases) were based on findings of decreased ejection fraction as assessed by echocardiography. Six of 261 (2%) LENVIMA-treated patients in Study 1 had greater than 20% reduction in ejection fraction as measured by echocardiography compared to no patients who received placebo.
- Monitor patients for clinical symptoms or signs of cardiac decompensation. Withhold LENVIMA for development of Grade 3 cardiac dysfunction until improved to Grade 0 or 1 or baseline. Either resume at a reduced dose or discontinue LENVIMA depending on the severity and persistence of cardiac dysfunction. Discontinue LENVIMA for Grade 4 cardiac dysfunction .
Arterial Thromboembolic Events
- In Study 1, arterial thromboembolic events were reported in 5% of LENVIMA-treated patients and 2% of patients in the placebo group. The incidence of arterial thromboembolic events of Grade 3 or greater was 3% in LENVIMA-treated patients and 1% in the placebo group.
- Discontinue LENVIMA following an arterial thrombotic event. The safety of resuming LENVIMA after an arterial thromboembolic event has not been established and LENVIMA has not been studied in patients who have had an arterial thromboembolic event within the previous 6 months
Hepatotoxicity
- In Study 1, 4% of LENVIMA-treated patients experienced an increase in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and 5% experienced an increase in aspartate aminotransferase (AST) that was Grade 3 or greater. No patients in the placebo group experienced Grade 3 or greater increases in ALT or AST. Across clinical studies in which 1108 patients received LENVIMA, hepatic failure (including fatal events) was reported in 3 patients and acute hepatitis was reported in 1 patient.
- Monitor liver function before initiation of LENVIMA, then every 2 weeks for the first 2 months, and at least monthly thereafter during treatment. Withhold LENVIMA for the development of Grade 3 or greater liver impairment until resolved to Grade 0 to 1 or baseline. Either resume at a reduced dose or discontinue LENVIMA depending on the severity and persistence of hepatotoxicity. Discontinue LENVIMA for hepatic failure .
Proteinuria
- In Study 1, proteinuria was reported in 34% of LENVIMA-treated patients and 3% of patients in the placebo group. The incidence of Grade 3 proteinuria in LENVIMA-treated patients was 11% compared to none in the placebo group.
- Monitor for proteinuria before initiation of, and periodically throughout treatment. If urine dipstick proteinuria greater than or equal to 2+ is detected, obtain a 24 hour urine protein. Withhold LENVIMA for ≥2 grams of proteinuria/24 hours and resume at a reduced dose when proteinuria is <2 gm/24 hours. Discontinue LENVIMA for nephrotic syndrome .
Renal Failure and Impairment
- In Study 1, events of renal impairment were reported in 14% of LENVIMA-treated patients compared to 2% of patients in the placebo group. The incidence of Grade 3 or greater renal failure or impairment was 3% in LENVIMA-treated patients and 1% in the placebo group. The primary risk factor for severe renal impairment in LENVIMA-treated patients was dehydration/hypovolemia due to diarrhea and vomiting.
- Withhold LENVIMA for development of Grade 3 or 4 renal failure/impairment until resolved to Grade 0 to 1 or baseline. Either resume at a reduced dose or discontinue LENVIMA depending on the severity and persistence of renal impairment
Gastrointestinal Perforation and Fistula
- Formation In Study 1, events of gastrointestinal perforation or fistula were reported in 2% of LENVIMA-treated patients and 0.8% of patients in the placebo group. *Discontinue LENVIMA in patients who develop gastrointestinal perforation or lifethreatening fistula
QT Interval Prolongation
- In Study 1, QT/QTc interval prolongation was reported in 9% of LENVIMA-treated patients and 2% of patients in the placebo group. The incidence of QT interval prolongation of Grade 3 or greater was 2% in LENVIMA-treated patients compared to no reports in the placebo group. Monitor electrocardiograms in patients with congenital long QT syndrome, congestive heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, or those who are taking drugs known to prolong the QT interval, including Class Ia and III antiarrhythmics.
- Monitor and correct electrolyte abnormalities in all patients. Withhold LENVIMA for the development of Grade 3 or greater QT interval prolongation. Resume LENVIMA at a reduced dose when QT prolongation resolves to Grade 0 or 1 or baseline
Hypocalcemia
- In Study 1, 9% of LENVIMA-treated patients experienced Grade 3 or greater hypocalcemia compared to 2% in the placebo group. In most cases hypocalcemia responded to replacement and dose interruption/dose reduction .
- Monitor blood calcium levels at least monthly and replace calcium as necessary during LENVIMA treatment. Interrupt and adjust LENVIMA dosing as necessary depending on severity, presence of ECG changes, and persistence of hypocalcemia
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome
- Across clinical studies in which 1108 patients received LENVIMA, there were 3 reported events of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS). Confirm the diagnosis of RPLS with MRI. Withhold for RPLS until fully resolved. Upon resolution, resume at a reduced dose or discontinue LENVIMA depending on the severity and persistence of neurologic symptoms
Hemorrhagic Events
- In Study 1, hemorrhagic events occurred in 35% of LENVIMA-treated patients and in 18% of the placebo group. However, the incidence of Grade 3-5 hemorrhage was similar between arms at 2% and 3%, respectively. The most frequently reported hemorrhagic event was epistaxis (11% Grade 1 and 1% Grade 2). Discontinuation due to hemorrhagic events occurred in 1% of LENVIMA-treated patients.
- Across clinical studies in which 1108 patients received LENVIMA, Grade 3 or greater hemorrhage was reported in 2% of patients. In Study 1, there was 1 case of fatal intracranial hemorrhage among 16 patients who received lenvatinib and had CNS metastases at baseline.
- Withhold LENVIMA for the development of Grade 3 hemorrhage until resolved to Grade 0 to 1. Either resume at a reduced dose or discontinue LENVIMA depending on the severity and persistence of hemorrhage. Discontinue LENVIMA in patients who experience Grade 4 hemorrhage .
Impairment of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Suppression
- LENVIMA impairs exogenous thyroid suppression. In Study 1, 88% of all patients had a baseline thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) level less than or equal to 0.5 mU/L. In those patients with a normal TSH at baseline, elevation of TSH level above 0.5 mU/L was observed post baseline in 57% of LENVIMA-treated patients as compared with 14% of patients receiving placebo.
- Monitor TSH levels monthly and adjust thyroid replacement medication as needed in patients with DTC.
Embryofetal Toxicity
- Based on its mechanism of action and data from animal reproduction studies, LENVIMA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of lenvatinib during organogenesis at doses below the recommended human dose resulted in embryotoxicity, fetotoxicity, and teratogenicity in rats and rabbits. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with LENVIMA and for at least 2 weeks following completion of therapy
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- The following adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the label
- Hypertension Cardiac Dysfunction
- Arterial Thromboembolic Events
- Hepatotoxicity
- Proteinuria
- Renal Failure and Impairment
- Gastrointestinal Perforation and Fistula Formation
- QT Interval Prolongation
- Hypocalcemia
- Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome
- Hemorrhagic Events
- Impairment of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Suppression
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
- Safety data obtained in 1108 patients with advanced solid tumors who received LENVIMA as a single agent across multiple clinical studies was used to further characterize risks of serious adverse drug reactions . The median age was 60 years (range 21-89 years). The dose range was 0.2 mg to 32 mg. The median duration of exposure in the entire population was 5.5 months.
- The safety data described below are derived from Study 1 which randomized (2:1) patients with radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer (RAI-refractory DTC) to LENVIMA (n=261) or placebo (n=131) [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The median treatment duration was 16.1 months for LENVIMA and 3.9 months for placebo. Among 261 patients who received LENVIMA in Study 1, median age was 64 years, 52% were women, 80% were White, 18% were Asian, and 2% were Black; 4% identified themselves as having Hispanic or Latino ethnicity.
- In Study 1, the most common adverse reactions observed in LENVIMA-treated patients (greater than or equal to 30%) were, in order of decreasing frequency, hypertension, fatigue, diarrhea, arthralgia/myalgia, decreased appetite, weight decreased, nausea, stomatitis, headache, vomiting, proteinuria, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (PPE) syndrome, abdominal pain, and dysphonia. The most common serious adverse reactions (at least 2%) were pneumonia (4%), hypertension (3%), and dehydration (3%).
- Adverse reactions led to dose reductions in 68% of patients receiving LENVIMA and 5% of patients receiving placebo; 18% of patients discontinued LENVIMA and 5% discontinued placebo for adverse reactions. The most common adverse reactions (at least 10%) resulting in dose reductions of LENVIMA were hypertension (13%), proteinuria (11%), decreased appetite (10%), and diarrhea (10%); the most common adverse reactions (at least 1%) resulting in discontinuation of LENVIMA were hypertension (1%) and asthenia (1%).
- Table 2 presents the percentage of patients in Study 1 experiencing adverse reactions at a higher rate in LENVIMA-treated patients than patients receiving placebo in the double-blind phase of the DTC study.
table03
- In addition the following laboratory abnormalities (all Grades) occurred in greater than 5% of LENVIMA-treated patients and at a rate that was two-fold or higher than in patients who received placebo: hypoalbuminemia, increased alkaline phosphatase, hypomagnesemia, hypoglycemia, hyperbilirubinemia, hypercalcemia, hypercholesterolemia, increased serum amylase, and hyperkalemia.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Lenvatinib in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
- Effect of Other Drugs on Lenvatinib No dose adjustment of LENVIMA is recommended when co-administered with CYP3A, Pglycoprotein (P-gp), and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) inhibitors and CYP3A and P-gp inducer
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Risk Summary Based on its mechanism of action and data from animal reproduction studies, LENVIMA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman . In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of lenvatinib during organogenesis at doses below the recommended human dose resulted in embryotoxicity, fetotoxicity, and teratogenicity in rats and rabbits [see Data]. There are no available human data informing the drug-associated risk. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown; however, the background risk in the U.S. general population of major birth defects is 2-4% and of miscarriage is 15-20% of clinically recognized pregnancies. Data Animal Data In an embryofetal development study, daily oral administration of lenvatinib mesylate at doses greater than or equal to 0.3 mg/kg [approximately 0.14 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area (BSA)] to pregnant rats during organogenesis resulted in dose-related decreases in mean fetal body weight, delayed fetal ossifications, and doserelated increases in fetal external (parietal edema and tail abnormalities), visceral, and skeletal anomalies. Greater than 80% postimplantation loss was observed at 1.0 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.5 times the recommended human dose based on BSA). Daily oral administration of lenvatinib mesylate to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis resulted in fetal external (short tail), visceral (retroesophageal subclavian artery), and skeletal anomalies at doses greater than or equal to 0.03 mg/kg (approximately 0.03 times the human dose of 24 mg based on body surface area). At the 0.03 mg/kg dose, increased postimplantation loss, including 1 fetal death, was also observed. Lenvatinib was abortifacient in rabbits, resulting in late abortions in approximately one-third of the rabbits treated at a dose level of 0.5 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.5 times the recommended clinical dose of 24 mg based on BSA).
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Lenvatinib in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Lenvatinib during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
Risk Summary It is not known whether LENVIMA is present in human milk. However, lenvatinib and its metabolites are excreted in rat milk at concentrations higher than in maternal plasma Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from LENVIMA, advise women to discontinue breastfeeding during treatment with LENVIMA. Data Animal Data Following administration of radiolabeled lenvatinib to lactating Sprague Dawley rats, lenvatinib-related radioactivity was approximately 2 times higher (based on AUC) in milk compared to maternal plasma.
Pediatric Use
- The safety and effectiveness of LENVIMA in pediatric patients have not been established. Juvenile Animal Data Daily oral administration of lenvatinib mesylate to juvenile rats for 8 weeks starting on postnatal day 21 (approximately equal to a human pediatric age of 2 years) resulted in growth retardation (decreased body weight gain, decreased food consumption, and decreases in the width and/or length of the femur and tibia) and secondary delays in physical development and reproductive organ immaturity at doses greater than or equal to 2 mg/kg (approximately 1.2 to 5 times the clinical exposure by AUC at the recommended human dose). Decreased length of the femur and tibia persisted following 4 weeks of recovery. In general, the toxicologic profile of lenvatinib was similar between juvenile and adult rats, though toxicities including broken teeth at all dose levels and mortality at the 10 mg/kg/day dose level (attributed to primary duodenal lesions) occurred at earlier treatment time-points in juvenile rats.
Geriatic Use
Of 261 patients who received LENVIMA in Study 1, 118 (45.2%) were greater than or equal to 65 years of age and 29 (11.1%) were greater than or equal to 75 years of age. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Lenvatinib with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Lenvatinib with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment. In patients with severe renal impairment, the recommended dose is 14 mg taken once daily. Patients with end stage renal disease were not studied
Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. In patients with severe hepatic impairment, the recommended dose is 14 mg taken once daily
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
Contraception Based on its mechanism of action, LENVIMA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with LENVIMA and for at least 2 weeks following completion of therapy. Infertility Females LENVIMA may result in reduced fertility in females of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. Males LENVIMA may result in damage to male reproductive tissues leading to reduced fertility of unknown duration
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Lenvatinib in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Lenvatinib in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Lenvatinib in the drug label.
Overdosage
There is no specific antidote for overdose with LENVIMA. Due to the high plasma protein binding, lenvatinib is not expected to be dialyzable [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].Adverse reactions in patients receiving single doses of LENVIMA as high as 40 mg were similar to the adverse events reported in the clinical studies at the recommended dose.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Lenvatinib Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
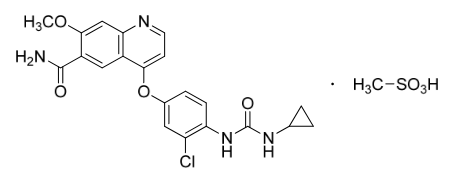
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Lenvatinib in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Lenvatinib in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Lenvatinib in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Lenvatinib in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Lenvatinib Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Lenvatinib |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Lenvatinib |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Lenvatinib in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Lenvatinib interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Lenvatinib |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Lenvatinib |Label Name=Lenvatinib11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Lenvatinib |Label Name=Lenvatinib11.png
}}