Betaine
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
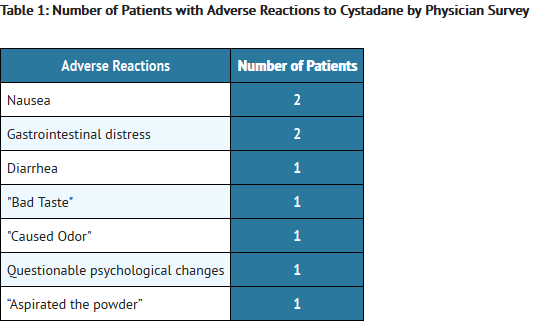
Betaine is a methylating agent that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of homocystinuria due to cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) deficiency, 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) deficiency, and cobalamin cofactor metabolism (CBL) defect. Common adverse reactions include nausea and gastrointestinal distress.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Homocystinuria
- The usual dosage in adult is 6 grams per day administered orally in divided doses of 3 grams twice daily.
- Therapy with Cystadane should be directed by physicians knowledgeable in the management of patients with homocystinuria. Patient response to Cystadane can be monitored by homocysteine plasma levels. Dosage in all patients can be gradually increased until plasma total homocysteine is undetectable or present only in small amounts. Response (by homocysteine plasma levels) usually occurs within several days and steady state within a month. Plasma methionine concentrations should be monitored in patients with CBS deficiency.
- Dosages of up to 20 grams per day have been necessary to control homocysteine levels in some patients. However, one pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic in vitro simulation study indicated minimal benefit from exceeding a twice-daily dosing schedule and a 150 mg/kg/day dosage for Cystadane.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Betaine in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Betaine in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Homocystinuria
- The usual dosage in pediatric patients is 6 grams per day administered orally in divided doses of 3 grams twice daily. In pediatric patients less than 3 years of age, dosage may be started at 100 mg/kg/day divided in twice daily doses, and then increased weekly by 50 mg/kg increments.
- Therapy with Cystadane should be directed by physicians knowledgeable in the management of patients with homocystinuria. Patient response to Cystadane can be monitored by homocysteine plasma levels. Dosage in all patients can be gradually increased until plasma total homocysteine is undetectable or present only in small amounts. Response (by homocysteine plasma levels) usually occurs within several days and steady state within a month. Plasma methionine concentrations should be monitored in patients with CBS deficiency.
- Dosages of up to 20 grams per day have been necessary to control homocysteine levels in some patients. However, one pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic in vitro simulation study indicated minimal benefit from exceeding a twice-daily dosing schedule and a 150 mg/kg/day dosage for Cystadane.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Betaine in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Betaine in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Condition1
Warnings
- Description
Precautions
- Description
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Betaine in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Betaine in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Betaine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Betaine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betaine with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betaine with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betaine with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betaine with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betaine with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betaine in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betaine in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Betaine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Betaine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Betaine in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Betaine in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Betaine in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Betaine Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Betaine in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Betaine in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Betaine in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Betaine in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Betaine Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Betaine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Betaine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Betaine in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Betaine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- CYSTADANE®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "CYSTADANE - betaine powder, for solution".
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Betaine |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Betaine |Label Name=Betaine11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Betaine |Label Name=Betaine11.png
}}