Profenamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 93% |
| Elimination half-life | 1 to 2 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
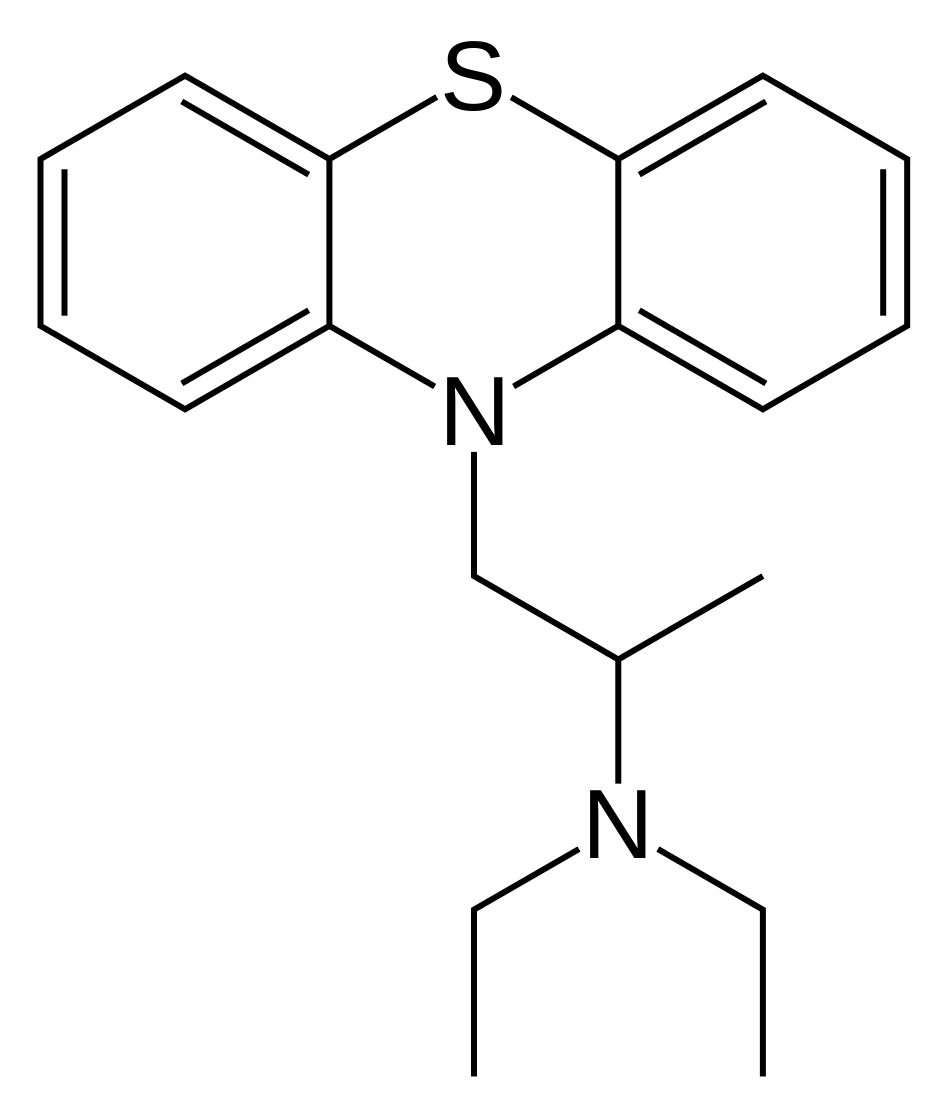
| Formula | C19H24N2S |
| Molar mass | 312.473 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Profenamine |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Profenamine Most cited articles on Profenamine |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Profenamine |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Profenamine at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Profenamine at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Profenamine
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Profenamine Discussion groups on Profenamine Patient Handouts on Profenamine Directions to Hospitals Treating Profenamine Risk calculators and risk factors for Profenamine
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Profenamine |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Profenamine (INN, trade names Parsidol, Parsidan, Parkin), also known as ethopropazine (BAN), is a phenothiazine derivative used as an antiparkinsonian agent that has anticholinergic, antihistamine, and antiadrenergic actions. It is also used in the alleviation of the extrapyramidal syndrome induced by drugs such as other phenothiazine compounds, but, like other compounds with antimuscarinic properties, is of no value against tardive dyskinesia.