Chronic cholecystitis MRI: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{Cholecystitis}} | {{Cholecystitis}} | ||
==MRI== | ==MRI== | ||
* MRI with MR cholangiopancreatography in the emergency setting provides rapid, noninvasive, and confident diagnosis of acute cholecystitis and associated gall bladder disease (gall stones)<ref name="pmid22447440">{{cite journal |author=Tonolini M, Ravelli A, Villa C, Bianco R |title=Urgent MRI with MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) of acute cholecystitis and related complications: diagnostic role and spectrum of imaging findings |journal=[[Emergency Radiology]] |volume=19 |issue=4 |pages=341–8 |year=2012 |month=August |pmid=22447440 |doi=10.1007/s10140-012-1038-z |url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10140-012-1038-z |accessdate=2012-08-20}}</ref>. | * MRI with MR cholangiopancreatography in the emergency setting provides rapid, noninvasive, and confident diagnosis of acute cholecystitis and associated gall bladder disease (gall stones)<ref name="pmid22447440">{{cite journal |author=Tonolini M, Ravelli A, Villa C, Bianco R |title=Urgent MRI with MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) of acute cholecystitis and related complications: diagnostic role and spectrum of imaging findings |journal=[[Emergency Radiology]] |volume=19 |issue=4 |pages=341–8 |year=2012 |month=August |pmid=22447440 |doi=10.1007/s10140-012-1038-z |url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10140-012-1038-z |accessdate=2012-08-20}}</ref>. | ||
| Line 49: | Line 48: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Needs overview]] | |||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | |||
[[Category:Hepatology]] | |||
[[Category:Inflammations]] | |||
[[Category:General surgery]] | |||
[[Category:Emergency medicine]] | |||
[[Category:Signs and symptoms]] | |||
[[Category:Disease]] | |||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
Revision as of 23:42, 2 February 2013
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
|
Chronic cholecystitis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Chronic cholecystitis MRI On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Chronic cholecystitis MRI |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Chronic cholecystitis MRI |
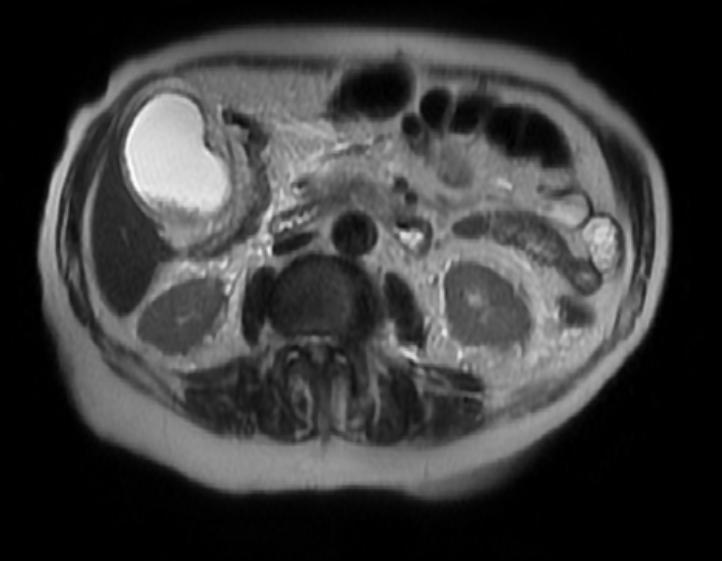
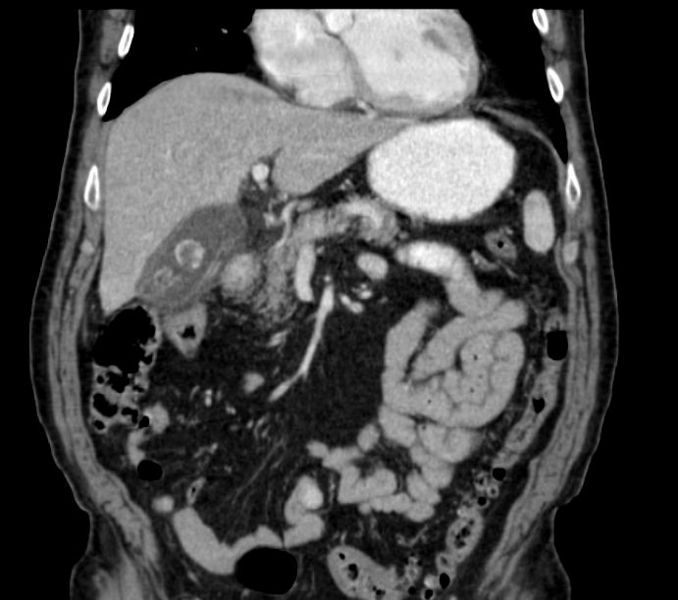
MRI
- MRI with MR cholangiopancreatography in the emergency setting provides rapid, noninvasive, and confident diagnosis of acute cholecystitis and associated gall bladder disease (gall stones)[1].
- Finding on MRI include
- Gall bladder distension
- Intraluminal sludge
- Gallstones
- Impacted stones obstructing the neck of the gall bladder neck
- Cystic duct obstruction
- Thickening of the gall bladder wall
- Abnormal signal intensity due to edematous stratification
- Pericholecystic and perihepatic fluid
- Increased enhancement of the gall bladder wall and adjacent liver parenchyma with intravenous paramagnetic contrast is used
- Complications can be identified at early stage like
- Gangrene
- Perforation
- Pericholecystic abscess
- Intrahepatic fistulization
Images
MR images demonstrates findings that are consistent with acute cholecystitis (pericholicystic fluid, GB wall thickening)
References
- ↑ Tonolini M, Ravelli A, Villa C, Bianco R (2012). "Urgent MRI with MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) of acute cholecystitis and related complications: diagnostic role and spectrum of imaging findings". Emergency Radiology. 19 (4): 341–8. doi:10.1007/s10140-012-1038-z. PMID 22447440. Retrieved 2012-08-20. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help)