Fungal meningitis laboratory findings: Difference between revisions
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) |
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{CMG}}; '''Assistant Editor(s)-in-Chief:''' [[User:Rim Halaby|Rim Halaby]] | {{CMG}}; '''Assistant Editor(s)-in-Chief:''' [[User:Rim Halaby|Rim Halaby]] | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
A lumbar puncture is essential for the diagnosis of fungal meningitis and initiation of the appropriate treatment. The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of a patient having bacterial meningitis is distinguished by the presence of lymphocytosis, low glucose level and high proteins level. Specific CSF stains and cultures as well as serologies help in determining the specific nature of the causative fungi. | |||
==Laboratory Findings== | ==Laboratory Findings== | ||
===The General Characteristic CSF Findings | ===The General Characteristic CSF Findings in Fungal Meningitis:=== | ||
*Mononuclear or lymphocytic pleocytosis | *Mononuclear or lymphocytic pleocytosis | ||
*An elevated protein concentration | *An elevated protein concentration | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
*''[[Blastomyces dermatitidis]]'' | *''[[Blastomyces dermatitidis]]'' | ||
**Fungal stain and culture of CSF | **Fungal stain and culture of CSF | ||
**Biopsy and culture of skin | **Biopsy and culture of skin and lung lesions | ||
**Antibody detection in serum | **Antibody detection in serum | ||
*''[[Cryptococcus neoformans]]'' | *''[[Cryptococcus neoformans]]'' | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
*''[[Sporothrix schenckii]]'' | *''[[Sporothrix schenckii]]'' | ||
**Antibody detection in CSF and serum | **Antibody detection in CSF and serum | ||
CSF culture<ref>Koroshetz WJ. Chapter 382. Chronic and Recurrent Meningitis. In: Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J, eds. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 18th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2012.</ref> | **CSF culture<ref>Koroshetz WJ. Chapter 382. Chronic and Recurrent Meningitis. In: Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J, eds. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 18th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2012.</ref> | ||
===Fungal Stains=== | ===Fungal Stains=== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
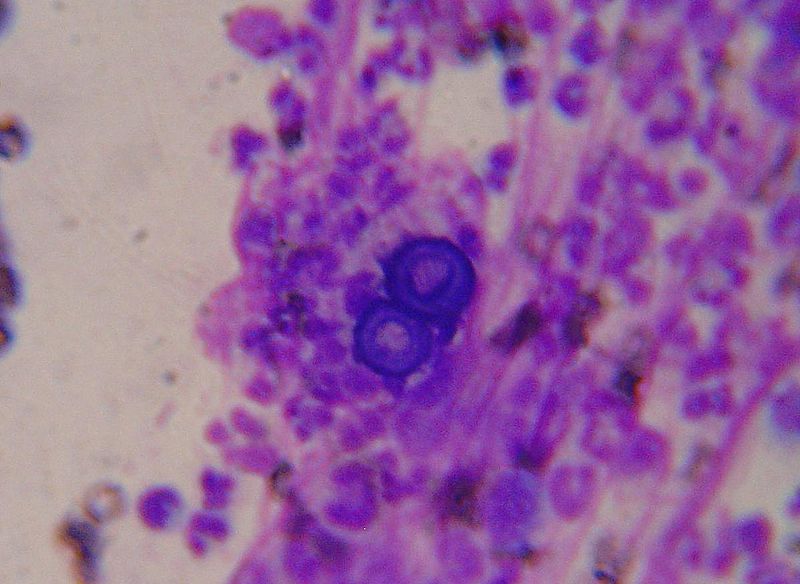
Blastomycosis.JPG|Blastomyces:Broad based budding | Blastomycosis.JPG|Blastomyces: Broad based budding | ||
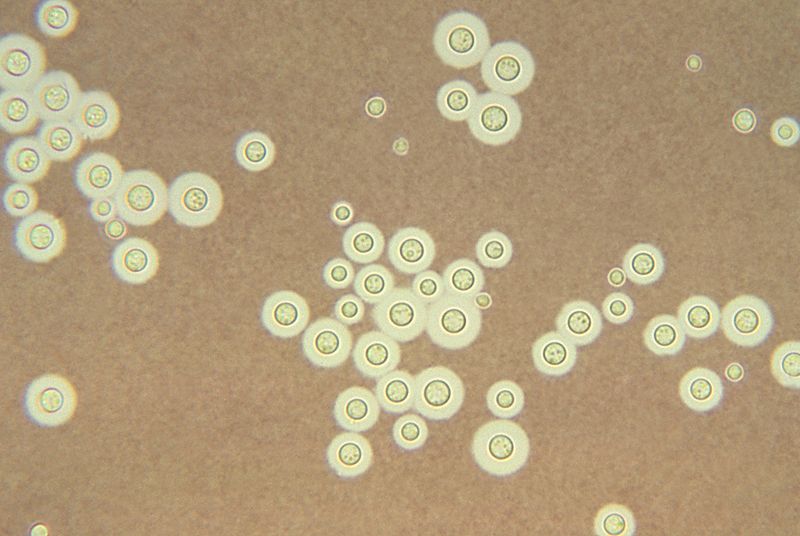
Cryptococcus_neoformans_India_ink_staining.jpg|Cryptococcus: clear halo visualized by the india ink stain | Cryptococcus_neoformans_India_ink_staining.jpg|Cryptococcus: clear halo visualized by the india ink stain | ||
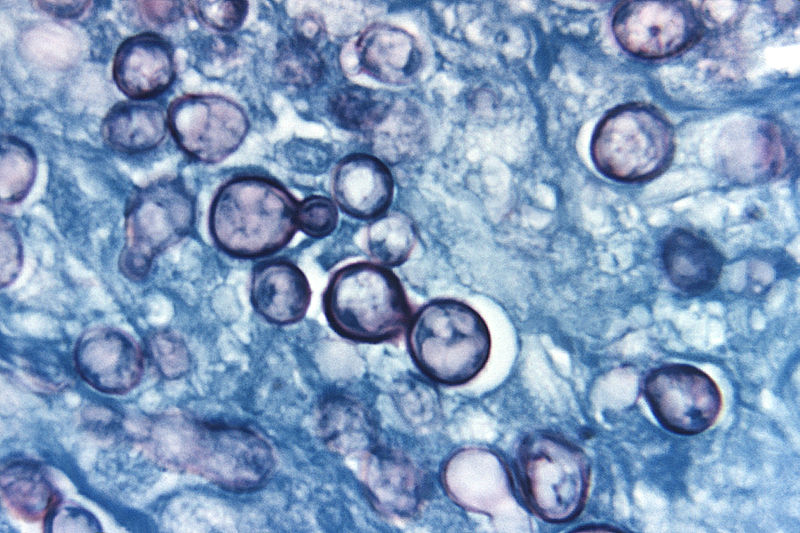
Histoplasma_capsulatum.jpg|Histoplama capsulatum | Histoplasma_capsulatum.jpg|Histoplama capsulatum | ||
Revision as of 18:13, 22 October 2012
|
Fungal meningitis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Fungal meningitis laboratory findings On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Fungal meningitis laboratory findings |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Fungal meningitis laboratory findings |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Assistant Editor(s)-in-Chief: Rim Halaby
Overview
A lumbar puncture is essential for the diagnosis of fungal meningitis and initiation of the appropriate treatment. The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of a patient having bacterial meningitis is distinguished by the presence of lymphocytosis, low glucose level and high proteins level. Specific CSF stains and cultures as well as serologies help in determining the specific nature of the causative fungi.
Laboratory Findings
The General Characteristic CSF Findings in Fungal Meningitis:
- Mononuclear or lymphocytic pleocytosis
- An elevated protein concentration
- A decreased glucose concentration
Other CSF Findings and Serology Tests Specific to Each Particular Fungi
- Aspergillus sp.
- CSF culture
- Blastomyces dermatitidis
- Fungal stain and culture of CSF
- Biopsy and culture of skin and lung lesions
- Antibody detection in serum
- Cryptococcus neoformans
- India ink or fungal wet mount of CSF (budding yeast)
- Mucicarmine stain provides specific staining of the polysaccharide cell wall
- Blood and urine cultures
- Antigen detection in CSF
- Coccidioides immitis
- Antibody detection in CSF and serum
- Candida sp.
- Fungal stain and culture of CSF
- Histoplasma capsulatum
- Fungal stain and culture of large volumes of CSF
- Antigen detection in CSF, serum, and urine
- Antibody detection in serum and CSF
- Sporothrix schenckii
- Antibody detection in CSF and serum
- CSF culture[1]
Fungal Stains
-
Blastomyces: Broad based budding
-
Cryptococcus: clear halo visualized by the india ink stain
-
Histoplama capsulatum
References
- ↑ Koroshetz WJ. Chapter 382. Chronic and Recurrent Meningitis. In: Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J, eds. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 18th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2012.