Obturator internus muscle: Difference between revisions
Brian Blank (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
m Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{SIB}} +, -{{EH}} +, -{{EJ}} +, -{{Editor Help}} +, -{{Editor Join}} +) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
{{SI}} | {{SI}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
The '''obturator internus''' muscle originates on the medial surface of the [[obturator membrane]], the [[ischium]] near the membrane, and the rim of the [[pubis]]. | The '''obturator internus''' muscle originates on the medial surface of the [[obturator membrane]], the [[ischium]] near the membrane, and the rim of the [[pubis]]. | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
[[Category:Hip muscles]] | [[Category:Hip muscles]] | ||
[[de:Musculus obturator internus]] | [[de:Musculus obturator internus]] | ||
[[es:Obturador interno]] | [[es:Obturador interno]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:27, 20 August 2012
Overview
The obturator internus muscle originates on the medial surface of the obturator membrane, the ischium near the membrane, and the rim of the pubis.
It exits the pelvic cavity through the lesser sciatic foramen.
The Obturator internus is situated partly within the lesser pelvis, and partly at the back of the hip-joint.
Origin and insertion
It arises from the inner surface of the antero-lateral wall of the pelvis, where it surrounds the greater part of the obturator foramen, being attached to the inferior rami of the pubis and ischium, and at the side to the inner surface of the hip bone below and behind the pelvic brim, reaching from the upper part of the greater sciatic foramen above and behind to the obturator foramen below and in front.
It also arises from the pelvic surface of the obturator membrane except in the posterior part, from the tendinous arch which completes the canal for the passage of the obturator vessels and nerve, and to a slight extent from the obturator fascia, which covers the muscle.
The fibers converge rapidly toward the lesser sciatic foramen, and end in four or five tendinous bands, which are found on the deep surface of the muscle; these bands are reflected at a right angle over the grooved surface of the ischium between its spine and tuberosity.
Bursa/bands
This bony surface is covered by smooth cartilage, which is separated from the tendon by a bursa, and presents one or more ridges corresponding with the furrows between the tendinous bands.
These bands leave the pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen and unite into a single flattened tendon, which passes horizontally across the capsule of the hip-joint, and, after receiving the attachments of the gemelli, is inserted into the forepart of the medial surface of the greater trochanter above the trochanteric fossa.
A bursa, narrow and elongated in form, is usually found between the tendon and the capsule of the hip-joint; it occasionally communicates with the bursa between the tendon and the ischium.
Additional images
-
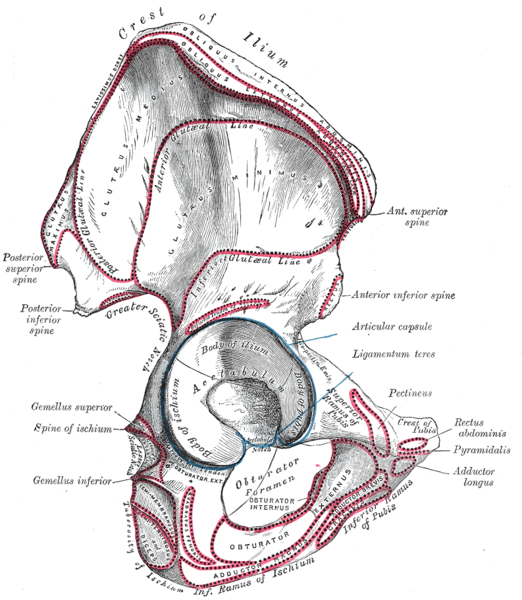
Right hip bone. External surface.
-
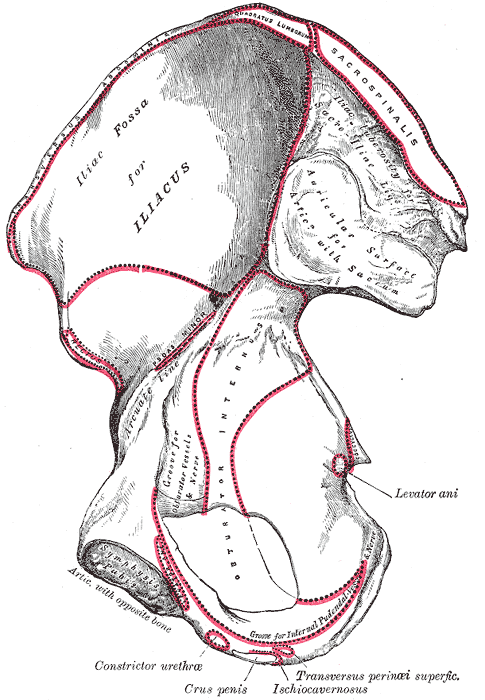
Right hip bone. Internal surface.
-
Right femur. Anterior surface.
-
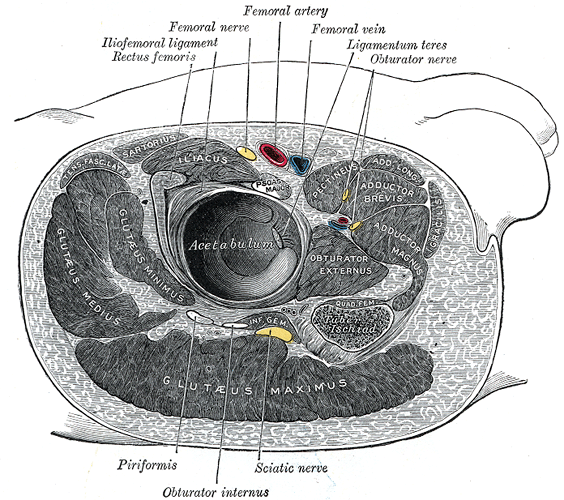
Structures surrounding right hip-joint.
-
Muscles of the gluteal and posterior femoral regions.
-
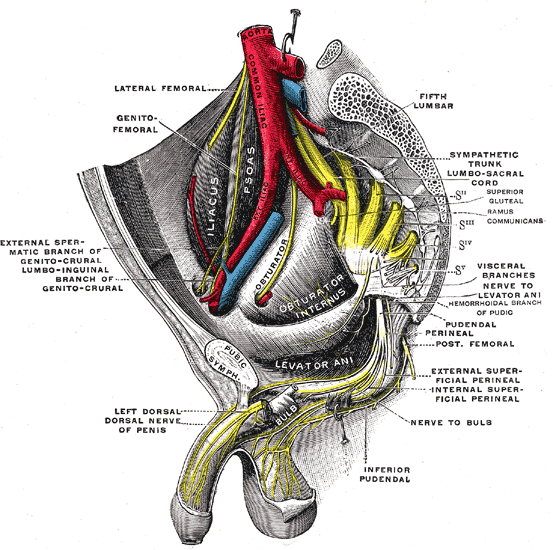
Sacral plexus of the right side.
External links
- Template:GPnotebook
- Template:MuscleLoyola
- Template:SUNYAnatomyLabs - "Gluteal Region: Muscles"
- Template:SUNYAnatomyLabs - "The Female Pelvis: Muscles"
- Template:ViennaCrossSection
- Template:NormanAnatomy (Template:NormanAnatomyFig, Template:NormanAnatomyFig)
- Template:NormanAnatomy (Template:NormanAnatomyFig)
Template:Gray's
Template:Muscles of lower limb