Sandbox ap: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Widget) |
(→Widget) |
||
| Line 176: | Line 176: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
[https://twitter.com/NEJM?ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw Tweets by NEJM] | |||
==Bulllets== | ==Bulllets== | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 15:34, 16 May 2018
==Classification Gastritis
| Gastritis | Etiology | Gasstritis synonyms | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-atrophic |
|
Superficial Diffuse antral gastritis (DAG) Chronic antral gastritis (CAG) Interstitial - follicular Hypersecretory Type B* | |
| Atrophic | Autoimmune |
|
Type A* Diffuse corporal Pernicious anemia-associated |
| Multifocal atrophic | Helicobacter pylori | Type B*, type AB* | |
| Dietary | Environmental | ||
| Environmental factors | Metaplastic | ||
| Special form | Chemical | Chemical irritation | Reactive |
|
| ||
|
| ||
|
| ||
| Radiation | Radiation injury | ||
Risk assessment table
| Scoring criteria for risk assessment* | ||
|---|---|---|
| Scoring system | Score | Risk |
| IMPROVEDD Score[1] | Predicted % VTE risk through 42 days | |
| 0 | 0.4% | |
| 1 | 0.6% | |
| 2 | 0.8% | |
| 3 | 1.2% | |
| 4 | 1.6% | |
| 5-10 | 2.2% | |
| Predicted % VTE risk through 77 days | ||
| 0 | 0.5% | |
| 1 | 0.7% | |
| 2 | 1.0% | |
| 3 | 1.4% | |
| 4 | 1.9% | |
| 5-10 | 2.75 | |
| IMPROVE score[2] | Predicted % VTE risk through 3 months | |
| 0 | 0.5% | |
| 1 | 1.0% | |
| 2 | 1.7% | |
| 3 | 3.1% | |
| 4 | 4% | |
| 5-8 | 11% | |
| Padua Score[3] | < 4 | Low risk for VTE |
| ≥ 4 | High risk for VTE | |
| Caprini score[4] | 0-1 | Low risk of VTE |
| 2 | Moderate of VTE | |
| 3-4 | High risk of VTE | |
| ≥ 5 | Highest risk for VTE | |
Images ILD
-
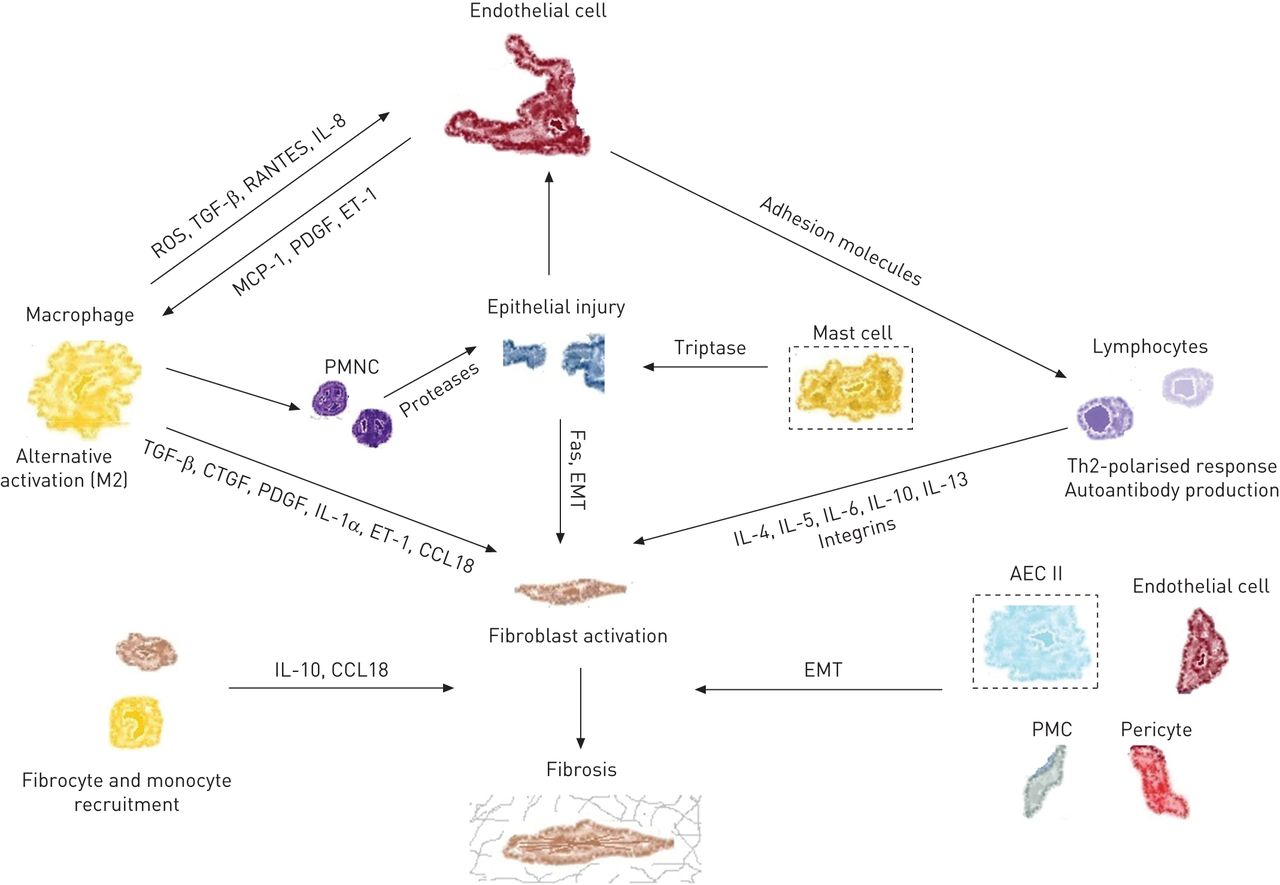
Cellular Players and Molecules in IPF
Adapted from European Respiratory Review
-
Flow Chart for Lung Fibrosis Evaluation in ILD
Adapted from Clinics in Chest Medicine
Widget
News from WikiDoc
Bulllets
References
- ↑ . doi:10.1055/s-0037-160392910.1055/s-0037-1603929. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Spyropoulos AC, Anderson FA, Fitzgerald G, Decousus H, Pini M, Chong BH; et al. (2011). "Predictive and associative models to identify hospitalized medical patients at risk for VTE". Chest. 140 (3): 706–14. doi:10.1378/chest.10-1944. PMID 21436241.
- ↑ Barbar S, Noventa F, Rossetto V, Ferrari A, Brandolin B, Perlati M; et al. (2010). "A risk assessment model for the identification of hospitalized medical patients at risk for venous thromboembolism: the Padua Prediction Score". J Thromb Haemost. 8 (11): 2450–7. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.04044.x. PMID 20738765.
- ↑ Caprini JA, Arcelus JI, Hasty JH, Tamhane AC, Fabrega F (1991). "Clinical assessment of venous thromboembolic risk in surgical patients". Semin Thromb Hemost. 17 Suppl 3: 304–12. PMID 1754886.