WBR0613: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Sergekorjian (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Sergekorjian (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{WBRQuestion | {{WBRQuestion | ||
|QuestionAuthor={{Rim}} | |QuestionAuthor={{Rim}} (Reviewed by {{YD}}) | ||
|ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | ||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |MainCategory=Pathology | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |MainCategory=Pathology | ||
|SubCategory=Neurology | |SubCategory=Neurology | ||
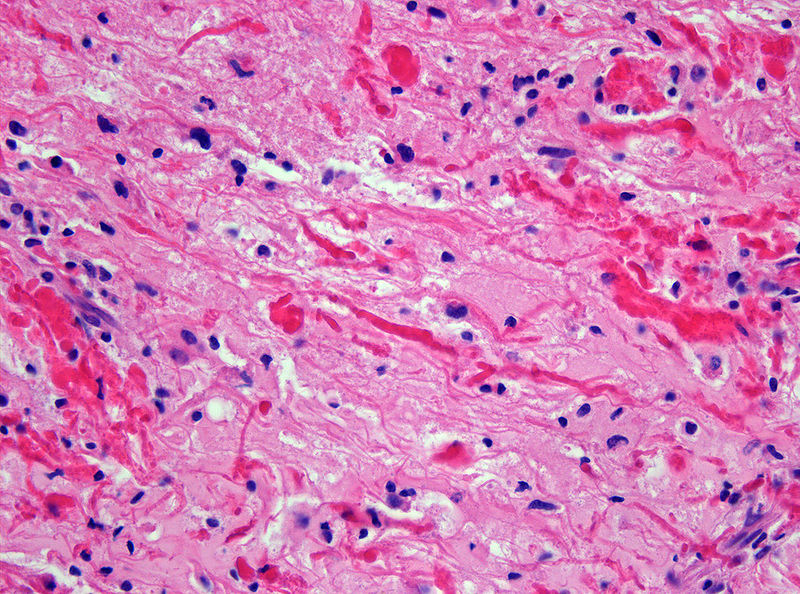
|Prompt=A 10-year-old child is brought to the neurology clinic for worsening chronic headache and gait disturbance. CT scan demonstrates a well-circumscribed mass in the cerebellum with both solid and cystic components. The tumor is successfully resected and treatment is initiated based on | |Prompt=A 10-year-old child is brought to the neurology clinic for worsening chronic headache and gait disturbance. CT scan demonstrates a well-circumscribed mass in the cerebellum with both solid and cystic components. The tumor is successfully resected and treatment is initiated based on the histopathological findings (shown below). What is the most likely function of the cells from which this tumor arises? | ||
[[Image:Rosenthal fibers.jpeg|350px]] | [[Image:Rosenthal fibers.jpeg|350px]] | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
|AnswerEExp=[[Ependymal cells]] in the inner lining of the ventricles produce [[CSF]]. | |AnswerEExp=[[Ependymal cells]] in the inner lining of the ventricles produce [[CSF]]. | ||
|EducationalObjectives=Pilocytic astrocytoma is a tumor arising from astrocytes and usually affects children. It is commonly located in the posterior fossa, but can be found in the supratentorial area. It is pathologically characterized by the presence of [[Rosenthal fibers]] which are eosinophilic corkscrew fibers. [[Astrocytes]] play a role in the maintenance of the [[blood brain barrier]], regulation of potassium metabolism and [[reactive gliosis]]. | |EducationalObjectives=Pilocytic astrocytoma is a tumor arising from astrocytes and usually affects children. It is commonly located in the posterior fossa, but can be found in the supratentorial area. It is pathologically characterized by the presence of [[Rosenthal fibers]] which are eosinophilic corkscrew fibers. [[Astrocytes]] play a role in the maintenance of the [[blood brain barrier]], regulation of potassium metabolism and [[reactive gliosis]]. | ||
|References=First Aid | |References=First Aid 2015 page 492 | ||
|RightAnswer=A | |RightAnswer=A | ||
|WBRKeyword=Pilocytic astrocytoma, | |WBRKeyword=Pilocytic astrocytoma, Brain tumor, Astrocytes, Reactive glioma | ||
|Approved=No | |Approved=No | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 20:58, 15 August 2015
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Rim Halaby, M.D. [1] (Reviewed by Yazan Daaboul, M.D.)]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Pathology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Neurology |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 10-year-old child is brought to the neurology clinic for worsening chronic headache and gait disturbance. CT scan demonstrates a well-circumscribed mass in the cerebellum with both solid and cystic components. The tumor is successfully resected and treatment is initiated based on the histopathological findings (shown below). What is the most likely function of the cells from which this tumor arises? |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Reactive gliosis |
| Answer A Explanation | [[AnswerAExp::Astrocytes play a role in reactive gliosis.]] |
| Answer B | AnswerB::Phagocytosis |
| Answer B Explanation | [[AnswerBExp::Microglia play a role in phagocytosis.]] |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Myelin production |
| Answer C Explanation | [[AnswerCExp::Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes produce myelin.]] |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Action potential generation |
| Answer D Explanation | [[AnswerDExp::Neurons are responsible for the generation and propagation of action potentials.]] |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Production of CSF |
| Answer E Explanation | [[AnswerEExp::Ependymal cells in the inner lining of the ventricles produce CSF.]] |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::A |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::Given the age of the patient, the subtentorial location of the mass, and the cystic and solid features, pilocytic astrocytoma is the most likely diagnosis. Pathology of the tumor reveals Rosenthal fibers which are eosinophilic corkscrew fibers classically observed in pilocytic astrocytoma tumors. The diagnosis can usually be confirmed with GFAP staining. Astrocytes play a role in the maintenance of the blood brain barrier, regulation of potassium metabolism and reactive gliosis.
Shown below is an image depicting Rosenthal fibers.
|
| Approved | Approved::No |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Pilocytic astrocytoma, WBRKeyword::Brain tumor, WBRKeyword::Astrocytes, WBRKeyword::Reactive glioma |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |