Eltrombopag: Difference between revisions
Matt Pijoan (talk | contribs) m Protected "Eltrombopag": Protecting pages from unwanted edits ([edit=sysop] (indefinite) [move=sysop] (indefinite)) |
No edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{DrugProjectFormSinglePage | ||
| | |authorTag={{AV}} | ||
| image | |genericName=Eltrombopag olamine | ||
| width | |aOrAn=a | ||
| image2 | |drugClass=[[thrombopoietin receptor agonist]] | ||
| width2 | |indicationType=treatment | ||
| CAS_number | |indication=[[thrombocytopenia]] in patients with chronic immune (idiopathic) [[thrombocytopenia]] (ITP) who have had an insufficient response to [[corticosteroids]], [[immunoglobulins]], or [[splenectomy]] | ||
| CAS_supplemental | |hasBlackBoxWarning=Yes | ||
| ATC_prefix | |adverseReactions=[[thrombocytopenia]], [[aplastic anemia]], [[hyperbilirubinemia]], [[fatigue]], [[cough]], [[epistaxis]], [[fever]], [[diarrhea]] <!--Black Box Warning--> | ||
| ATC_suffix | |blackBoxWarningTitle=WARNING | ||
| ATC_supplemental | |blackBoxWarningBody=<i><span style="color:#FF0000;">RISK FOR HEPATIC DECOMPENSATION IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC HEPATITIS C: </span></i> | ||
| PubChem | |||
| DrugBank | *In patients with chronic hepatitis C, Eltrombopag olamine® in combination with interferon and ribavirin may increase the risk of hepatic decompensation | ||
<!--Adult Indications and Dosage--> | |||
<!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)--> | |||
|fdaLIADAdult= | |||
=====Idiopathic Thrombocytopenia===== | |||
*Eltrombopag olamine is indicated for the treatment of [[thrombocytopenia]] in patients with chronic immune (idiopathic) [[thrombocytopenia]] (ITP) who have had an insufficient response to [[corticosteroids]], [[immunoglobulins]], or [[splenectomy]]. | |||
======Treatment of Thrombocytopenia in Patients with Hepatitis C Infection====== | |||
*Eltrombopag olamine is indicated for the treatment of [[thrombocytopenia]] in patients with chronic [[hepatitis C]] to allow the initiation and maintenance of [[interferon]]-based therapy. | |||
======Treatment of Severe Aplastic Anemia====== | |||
*Eltrombopag olamine is indicated for the treatment of patients with severe [[aplastic anemia]] who have had an insufficient response to immunosuppressive therapy. | |||
======Limitations of Use====== | |||
*Eltrombopag olamine should be used only in patients with ITP whose degree of [[thrombocytopenia]] and clinical condition increase the risk for [[bleeding]]. | |||
*Eltrombopag olamine should be used only in patients with chronic [[hepatitis]] C whose degree of [[thrombocytopenia]] prevents the initiation of [[interferon]]-based therapy or limits the ability to maintain [[interferon]]-based therapy. | |||
*Safety and efficacy have not been established in combination with direct-acting antiviral agents used without interferon for treatment of chronic [[hepatitis]] C infection. | |||
=====Dosing Information===== | |||
======Chronic Immune (Idiopathic) Thrombocytopenia====== | |||
*Use the lowest dose of Eltrombopag olamine to achieve and maintain a [[platelet count]] greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L as necessary to reduce the risk for [[bleeding]]. Dose adjustments are based upon the [[platelet count]] response. Do not use Eltrombopag olamine to normalize [[platelet counts]] . In clinical trials, [[platelet counts]] generally increased within 1 to 2 weeks after starting Eltrombopag olamine and decreased within 1 to 2 weeks after discontinuing Eltrombopag olamine . | |||
*Initial Dose Regimen: Initiate Eltrombopag olamine at a dose of 50 mg once daily, except in patients who are of East Asian ancestry (such as Chinese, Japanese, Taiwanese, or Korean) or who have mild to severe [[hepatic impairment]] ([[Child-Pugh Class]] A, B, C). | |||
*For [[ITP]] patients of East Asian ancestry, initiate Eltrombopag olamine at a reduced dose of 25 mg once daily . | |||
*For [[ITP]] patients with mild, moderate, or severe [[hepatic impairment]] ([[Child-Pugh Class]] A, B, C), initiate Eltrombopag olamine at a reduced dose of 25 mg once daily | |||
*For [[ITP]] patients of East Asian ancestry with [[hepatic impairment]] ([[Child-Pugh Class]] A, B, C), consider initiating Eltrombopag olamine at a reduced dose of 12.5 mg once daily | |||
*Monitoring and Dose Adjustment: After initiating Eltrombopag olamine, adjust the dose to achieve and maintain a platelet count greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L as necessary to reduce the risk for [[bleeding]]. Do not exceed a dose of 75 mg daily. Monitor clinical [[hematology]] and liver tests regularly throughout therapy with Eltrombopag olamine and modify the dosage regimen of Eltrombopag olamine based on platelet counts as outlined in Table 1. During therapy with Eltrombopag olamine, assess CBCs with differentials, including [[platelet counts]], weekly until a stable [[platelet count]] has been achieved. Obtain CBCs with differentials, including [[platelet counts]], monthly thereafter. | |||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}01.png|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
*In ITP patients with [[hepatic impairment]] ([[Child-Pugh Class]] A, B, C), after initiating Eltrombopag olamine or after any subsequent dosing increase, wait 3 weeks before increasing the dose. | |||
*Modify the dosage regimen of concomitant [[ITP]] medications, as medically appropriate, to avoid excessive increases in [[platelet counts]] during therapy with Eltrombopag olamine. Do not administer more than one dose of Eltrombopag olamine within any 24-hour period. | |||
*Discontinuation: Discontinue Eltrombopag olamine if the [[platelet count]] does not increase to a level sufficient to avoid clinically important [[bleeding]] after 4 weeks of therapy with Eltrombopag olamine at the maximum daily dose of 75 mg. Excessive [[platelet count]] responses, as outlined in Table 1, or important liver test abnormalities also necessitate discontinuation of Eltrombopag olamine . Obtain [[CBCs]] with differentials, including [[platelet counts]], weekly for at least 4 weeks following discontinuation of Eltrombopag olamine. | |||
====== Chronic Hepatitis C-associated Thrombocytopenia====== | |||
*Use the lowest dose of Eltrombopag olamine to achieve and maintain a [[platelet count]] necessary to initiate and maintain [[antiviral]] therapy with pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Dose adjustments are based upon the [[platelet count]] response. Do not use Eltrombopag olamine to normalize platelet counts . In clinical trials, [[platelet counts]] generally began to rise within the first week of treatment with Eltrombopag olamine . | |||
*Initial Dose Regimen: Initiate Eltrombopag olamine at a dose of 25 mg once daily. | |||
*Monitoring and Dose Adjustment: Adjust the dose of Eltrombopag olamine in 25-mg increments every 2 weeks as necessary to achieve the target [[platelet count]] required to initiate antiviral therapy. Monitor [[platelet counts]] every week prior to starting [[antiviral]] therapy. | |||
*During antiviral therapy, adjust the dose of Eltrombopag olamine to avoid dose reductions of [[peginterferon]]. Monitor CBCs with differentials, including [[platelet counts]], weekly during antiviral therapy until a stable [[platelet count]] is achieved. Monitor [[platelet counts]] monthly thereafter. Do not exceed a dose of 100 mg daily. Monitor clinical hematology and liver tests regularly throughout therapy with Eltrombopag olamine. | |||
*For specific dosage instructions for [[peginterferon]] or [[ribavirin]], refer to their respective prescribing information. | |||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}02.png|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
*Discontinuation: The prescribing information for [[pegylated interferon]] and [[ribavirin]] include recommendations for [[antiviral]] treatment discontinuation for treatment futility. Refer to pegylated [[interferon]] and [[ribavirin]] prescribing information for discontinuation recommendations for antiviral treatment futility. | |||
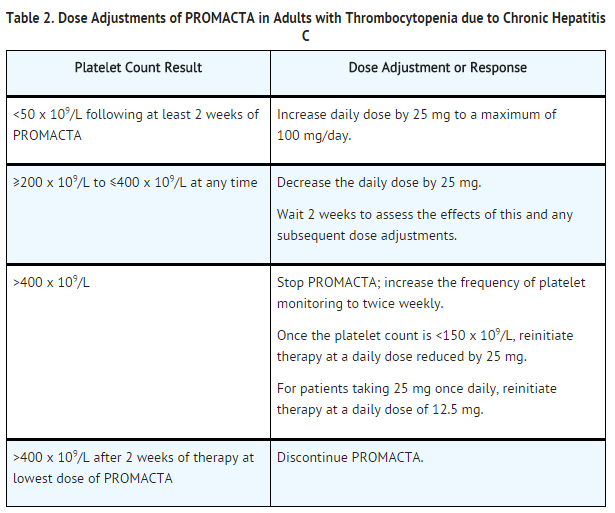
*Eltrombopag olamine should be discontinued when antiviral therapy is discontinued. Excessive [[platelet count]] responses, as outlined in Table 2, or important liver test abnormalities also necessitate discontinuation of Eltrombopag olamine. | |||
====== Severe Aplastic Anemia====== | |||
*Use the lowest dose of Eltrombopag olamine to achieve and maintain a hematologic response. Dose adjustments are based upon the [[platelet count]]. Hematologic response requires dose titration, generally up to 150 mg, and may take up to 16 weeks after starting Eltrombopag olamine. | |||
*Initial Dose Regimen: Initiate Eltrombopag olamine at a dose of 50 mg once daily. | |||
*For severe [[aplastic anemia]] in patients of East Asian ancestry or those with mild, moderate, or severe [[hepatic impairment]] ([[Child-Pugh Class]] A, B, C), initiate Eltrombopag olamine at a reduced dose of 25 mg once daily | |||
*Monitoring and Dose Adjustment: Adjust the dose of Eltrombopag olamine in 50-mg increments every 2 weeks as necessary to achieve the target [[platelet count]] greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L as necessary. Do not exceed a dose of 150 mg daily. Monitor clinical [[hematology]] and liver tests regularly throughout therapy with Eltrombopag olamine and modify the dosage regimen of Eltrombopag olamine based on platelet counts as outlined in Table 3. | |||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}03.png|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
*For patients who achieve tri-lineage response, including transfusion independence, lasting at least 8 weeks: the dose of Eltrombopag olamine may be reduced by 50% . If counts remain stable after 8 weeks at the reduced dose, then discontinue Eltrombopag olamine and monitor blood counts. If platelet counts drop to less than 30 x 109/L, hemoglobin to less than 9 g/dL, or ANC to less than 0.5 x 109/L, Eltrombopag olamine may be reinitiated at the previous effective dose. | |||
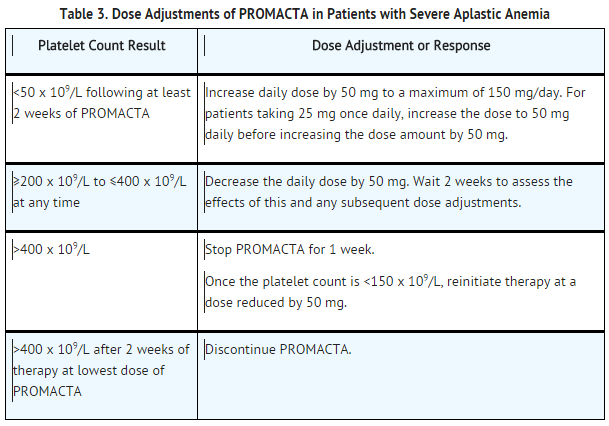
*Discontinuation: If no hematologic response has occurred after 16 weeks of therapy with Eltrombopag olamine, discontinue therapy. If new cytogenetic abnormalities are observed, consider discontinuation of Eltrombopag olamine. Excessive platelet count responses (as outlined in Table 3) or important liver test abnormalities also necessitate discontinuation of Eltrombopag olamine . | |||
======Administration====== | |||
*Take Eltrombopag olamine on an empty stomach (1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal) | |||
*Allow at least a 4-hour interval between Eltrombopag olamine and other medications (e.g., [[antacids]]), calcium-rich foods (e.g., dairy products and calcium fortified juices), or supplements containing polyvalent cations such as [[iron]], [[calcium]], [[aluminum]], [[magnesium]], [[selenium]], and [[zinc]] | |||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | |||
<!--Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | |||
|offLabelAdultGuideSupport= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in adult patients. | |||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Adult)--> | |||
|offLabelAdultNoGuideSupport= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in adult patients. | |||
<!--Pediatric Indications and Dosage--> | |||
<!--FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | |||
|fdaLIADPed= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>FDA-Labeled Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | |||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)--> | |||
<!--Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | |||
|offLabelPedGuideSupport= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | |||
<!--Non–Guideline-Supported Use (Pediatric)--> | |||
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport= | |||
There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in pediatric patients. | |||
<!--Contraindications--> | |||
|contraindications=*None. | |||
<!--Warnings--> | |||
|warnings= | |||
======Hepatic Decompensation in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C====== | |||
*In patients with chronic [[hepatitis C]], Eltrombopag olamine in combination with [[interferon]] and [[ribavirin]] may increase the risk of hepatic decompensation. In two controlled clinical trials in patients with chronic [[hepatitis C]] and [[thrombocytopenia]], [[ascites]] and [[encephalopathy]] occurred more frequently on the arm receiving treatment with Eltrombopag olamine plus antivirals (7%) than the placebo plus antivirals arm (4%). Patients with low albumin levels (less than 3.5 g/dL) or Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score greater than or equal to 10 at baseline had a greater risk for hepatic decompensation on the arm receiving treatment with Eltrombopag olamine plus antivirals. Discontinue Eltrombopag olamine if antiviral therapy is discontinued. | |||
======Hepatotoxicity====== | |||
*Eltrombopag olamine can cause liver enzyme elevations . Measure serum [[ALT]], [[AST]], and [[bilirubin]] prior to initiation of Eltrombopag olamine, every 2 weeks during the dose adjustment phase, and monthly following establishment of a stable dose. Eltrombopag olamine inhibits UGT1A1 and OATP1B1, which may lead to indirect [[hyperbilirubinemia]]. If bilirubin is elevated, perform fractionation. Evaluate abnormal serum liver tests with repeat testing within 3 to 5 days. If the abnormalities are confirmed, monitor serum liver tests weekly until resolved or stabilized. Discontinue Eltrombopag olamine if [[ALT]] levels increase to greater than or equal to 3X ULN in patients with normal liver function or greater than or equal to 3X baseline in patients with pre-treatment elevations in [[transaminases]] and are: | |||
:*progressively increasing, or | |||
:*persistent for greater than or equal to 4 weeks, or | |||
:*accompanied by increased direct [[bilirubin]], or | |||
:*accompanied by clinical symptoms of [[liver injury]] or evidence for hepatic decompensation. | |||
*If the potential benefit for reinitiating treatment with Eltrombopag olamine is considered to outweigh the risk for hepatotoxicity, then consider cautiously reintroducing Eltrombopag olamine and measure serum liver tests weekly during the dose adjustment phase. [[Hepatotoxicity]] may reoccur if Eltrombopag olamine is reinitiated. If liver tests abnormalities persist, worsen or recur, then permanently discontinue Eltrombopag olamine. | |||
======Thrombotic/Thromboembolic Complications====== | |||
*In 2 controlled clinical trials in patients with chronic [[hepatitis C]] and [[thrombocytopenia]], 3% (31/955) treated with Eltrombopag olamine experienced a thrombotic event compared with 1% (5/484) on placebo. The majority of events were of the portal venous system (1% in patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine versus less than 1% for placebo). | |||
*[[Thrombotic]]/[[thromboembolic]] complications may result from increases in [[platelet counts]] with Eltrombopag olamine. Reported [[thrombotic]]/[[thromboembolic]] complications included both venous and arterial events and were observed at low and at normal platelet counts. | |||
*Consider the potential for an increased risk of [[thromboembolism]] when administering Eltrombopag olamine to patients with known risk factors for [[thromboembolism]] (e.g., Factor V Leiden, [[ATIII deficiency]], [[antiphospholipid syndrome]], chronic liver disease). To minimize the risk for [[thrombotic]]/[[thromboembolic]] complications, do not use Eltrombopag olamine in an attempt to normalize [[platelet counts]]. Follow the dose adjustment guidelines to achieve and maintain target [[platelet counts]] . | |||
*In a controlled trial in non-ITP [[thrombocytopenic]] patients with chronic liver disease undergoing elective invasive procedures (N = 292), the risk of [[thrombotic]] events was increased in patients treated with 75 mg of Eltrombopag olamine once daily. Seven [[thrombotic]] complications (six patients) were reported in the group that received Eltrombopag olamine and three [[thrombotic]] complications were reported in the placebo group (two patients). All of the thrombotic complications reported in the group that received Eltrombopag olamine were [[portal vein thrombosis]] (PVT). Symptoms of PVT included abdominal pain, [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], and [[diarrhea]]. Five of the six patients in the group that received Eltrombopag olamine experienced a [[thrombotic]] complication within 30 days of completing treatment with Eltrombopag olamine and at a platelet count above 200 x 109/L. The risk of [[portal venous thrombosis]] was increased in [[thrombocytopenic]] patients with chronic liver disease treated with 75 mg of Eltrombopag olamine once daily for 2 weeks in preparation for invasive procedures. | |||
======Cataracts====== | |||
*In the 3 controlled clinical trials in chronic [[ITP]], cataracts developed or worsened in 15 (7%) patients who received 50 mg of Eltrombopag olamine daily and 8 (7%) placebo-group patients. In the extension trial, [[cataracts]] developed or worsened in 4% of patients who underwent ocular examination prior to therapy with Eltrombopag olamine. In the 2 controlled clinical trials in patients with chronic [[hepatitis C]] and [[thrombocytopenia]], cataracts developed or worsened in 8% patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine and 5% patients treated with placebo. | |||
*[[Cataracts]] were observed in toxicology studies of eltrombopag in rodents . Perform a baseline ocular examination prior to administration of Eltrombopag olamine and, during therapy with Eltrombopag olamine, regularly monitor patients for signs and symptoms of cataracts. | |||
<!--Adverse Reactions--> | |||
<!--Clinical Trials Experience--> | |||
|clinicalTrials= | |||
*The following serious adverse reactions associated with Eltrombopag olamine are described in other sections. | |||
:*Hepatic Decompensation in Patients with Chronic [[Hepatitis C]] | |||
:*[[Hepatotoxicity]] | |||
:*[[Thrombotic]]/[[Thromboembolic]] Complications | |||
:*[[Cataracts]] | |||
====== Clinical Trials Experience====== | |||
*Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. | |||
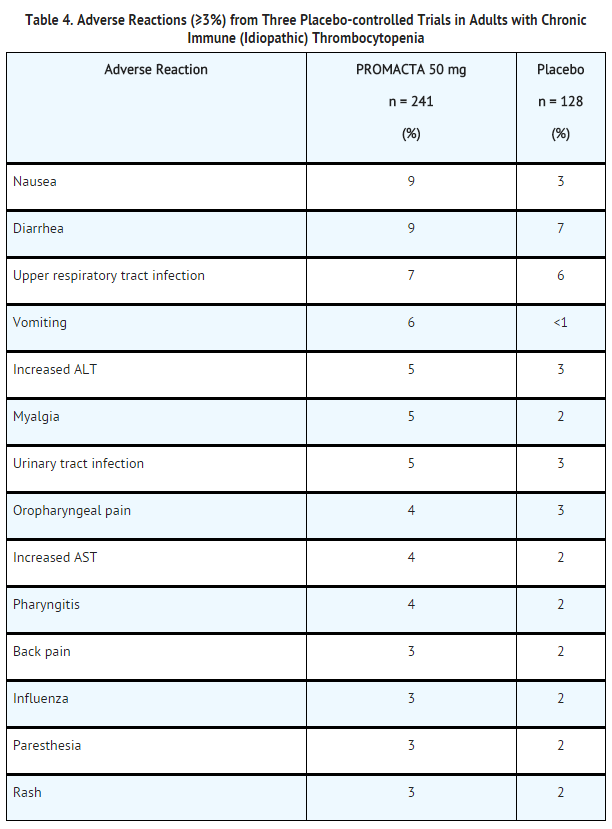
*Chronic Immune (Idiopathic) Thrombocytopenia: In clinical trials, hemorrhage was the most common serious adverse reaction and most hemorrhagic reactions followed discontinuation of Eltrombopag olamine. Other serious adverse reactions included [[thrombotic]]/[[thromboembolic]] complications . | |||
*The data described below reflect exposure of Eltrombopag olamine to 446 patients with chronic [[ITP]] aged 18 to 85, of whom 65% were female across the ITP clinical development program including 3 placebo-controlled trials. Eltrombopag olamine was administered to 277 patients for at least 6 months and 202 patients for at least 1 year. | |||
*Table 4 presents the most common adverse drug reactions (experienced by greater than or equal to 3% of patients receiving Eltrombopag olamine) from the 3 placebo-controlled trials, with a higher incidence in Eltrombopag olamine versus placebo. | |||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}04.png|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
*In the 3 controlled clinical chronic [[ITP]] trials, [[alopecia]], musculoskeletal pain, blood [[alkaline phosphatase]] increased, and dry mouth were the adverse reactions reported in 2% of patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine and in no patients who received placebo. | |||
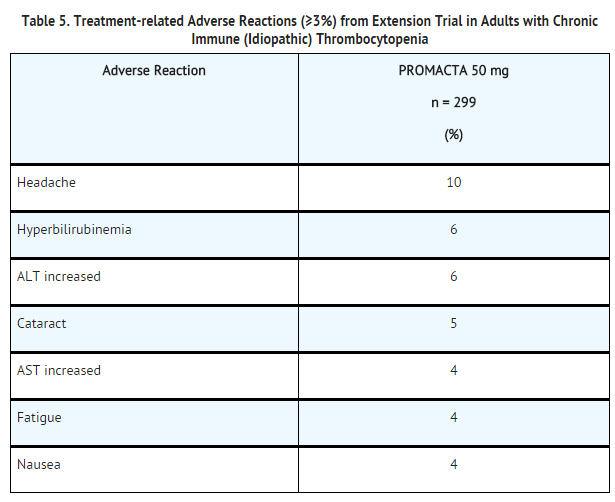
*Among 299 patients with chronic [[ITP]] who received Eltrombopag olamine in the single-arm extension trial, the adverse reactions occurred in a pattern similar to that seen in the placebo-controlled trials. Table 5 presents the most common treatment-related adverse reactions (experienced by greater than or equal to 3% of patients receiving Eltrombopag olamine) from the extension trial. | |||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}05.png|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
*In the 3 controlled chronic ITP trials, serum liver test abnormalities (predominantly Grade 2 or less in severity) were reported in 11% and 7% of patients for Eltrombopag olamine and placebo, respectively. Four patients (1%) treated with Eltrombopag olamine and three patients in the placebo group (2%) discontinued treatment due to hepatobiliary laboratory abnormalities. Seven of the patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine in the controlled trials with hepatobiliary laboratory abnormalities were re-exposed to Eltrombopag olamine in the extension trial. Six of these patients again experienced liver test abnormalities (predominantly Grade 1) resulting in discontinuation of Eltrombopag olamine in one patient. In the extension chronic ITP trial, one additional patient had Eltrombopag olamine discontinued due to liver test abnormalities (less than or equal to Grade 3). | |||
*In a placebo-controlled trial of Eltrombopag olamine in non-ITP thrombocytopenic patients with [[chronic liver disease]], six patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine and one patient in the placebo group developed [[portal vein thromboses]]. | |||
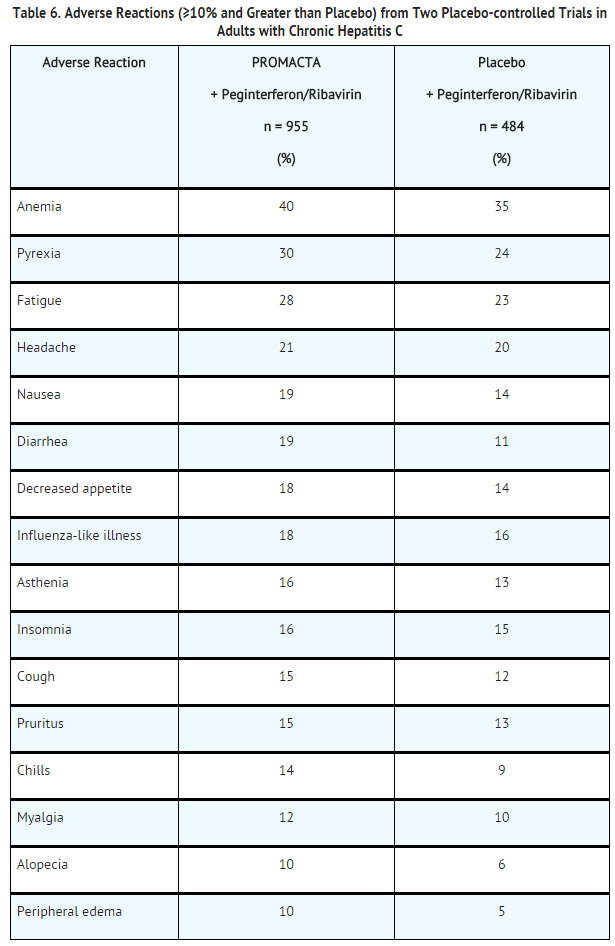
*Chronic [[Hepatitis C]]-associated [[Thrombocytopenia]]: In the 2 placebo-controlled trials, 955 patients with chronic hepatitis C-associated [[thrombocytopenia]] received Eltrombopag olamine. Table 6 presents the most common adverse drug reactions (experienced by greater than or equal to 10% of patients receiving Eltrombopag olamine compared with placebo). | |||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}06.png|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]]*In the 2 | |||
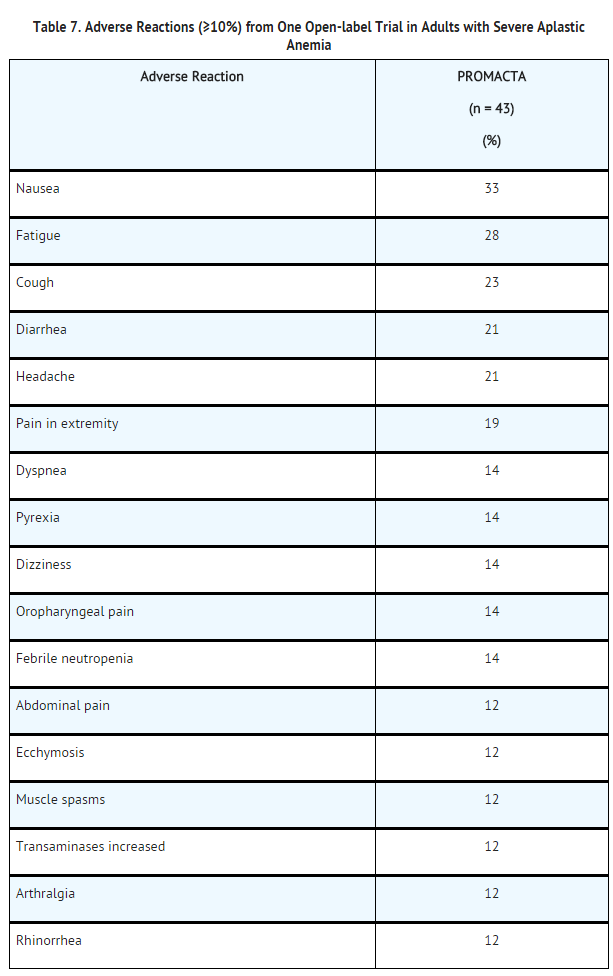
*Severe Aplastic Anemia: In the single-arm, open-label trial, 43 patients with severe [[aplastic anemia]] received Eltrombopag olamine. Eleven patients (26%) were treated for greater than 6 months and 7 patients (16%) were treated for greater than 1 year. The most common adverse reactions (greater than or equal to 20%) were [[nausea]], [[fatigue]], [[cough]], [[diarrhea]], and [[headache]]. | |||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}07.png|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]]*In this tri | |||
<!--Postmarketing Experience--> | |||
|postmarketing= | |||
*There is limited information regarding <i>Postmarketing Experience</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
*The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of Eltrombopag olamine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size it is not always possible to reliably estimate the frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. | |||
*Vascular Disorders: Thrombotic microangiopathy with acute [[renal failure]]. | |||
<!--Drug Interactions--> | |||
|drugInteractions=*n vitro, CYP1A2, CYP2C8, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT)1A1 and UGT1A3 are involved in the metabolism of eltrombopag. In vitro, eltrombopag inhibits the following metabolic or transporter systems: CYP2C8, CYP2C9, UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A4, UGT1A6, UGT1A9, UGT2B7, UGT2B15, OATP1B1 and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. | |||
=====Polyvalent Cations (Chelation)===== | |||
*Eltrombopag chelates polyvalent cations (such as iron, [[calcium]], [[aluminum]], [[magnesium]], [[selenium]], and [[zinc]]) in foods, mineral supplements, and antacids. In a clinical trial, administration of Eltrombopag olamine with a polyvalent cation-containing antacid decreased plasma eltrombopag systemic exposure by approximately 70%. | |||
*Eltrombopag olamine must not be taken within 4 hours of any medications or products containing polyvalent cations such as [[antacids]], dairy products, and mineral supplements to avoid significant reduction in absorption of Eltrombopag olamine due to [[chelation]] | |||
=====Transporters===== | |||
*Coadministration of Eltrombopag olamine with the OATP1B1 and BCRP substrate, [[rosuvastatin]], to healthy adult subjects increased plasma rosuvastatin AUC0-∞ by 55% and Cmax by 103% | |||
*Use caution when concomitantly administering Eltrombopag olamine and drugs that are substrates of OATP1B1 (e.g., [[atorvastatin]], [[bosentan]], [[ezetimibe]], [[fluvastatin]], [[glyburide]], [[olmesartan]], [[pitavastatin]], [[pravastatin]], [[rosuvastatin]], [[repaglinide]], [[rifampin]], [[simvastatin]] acid, SN-38 [active metabolite of [[irinotecan]]], [[valsartan]]) or BCRP (e.g., [[imatinib]], [[irinotecan]], [[lapatinib]], [[methotrexate]], [[mitoxantrone]], [[rosuvastatin]], [[sulfasalazine]], topotecan). Monitor patients closely for signs and symptoms of excessive exposure to the drugs that are substrates of OATP1B1 or BCRP and consider reduction of the dose of these drugs, if appropriate. In clinical trials with Eltrombopag olamine, a dose reduction of rosuvastatin by 50% was recommended. | |||
=====Protease Inhibitors===== | |||
*HIV Protease Inhibitors: In a drug interaction trial, coadministration of Eltrombopag olamine with lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/RTV) decreased plasma eltrombopag exposure by 17% adjustment is recommended when Eltrombopag olamine is coadministered with LPV/RTV. Drug interactions with other HIV protease inhibitors have not been evaluated. | |||
*[[Hepatitis C]] Virus (HCV) Protease Inhibitors: Coadministration of Eltrombopag olamine with either [[boceprevir]] or [[telaprevir]] did not affect eltrombopag or [[protease inhibitor]] exposure significantly . No dose adjustments are recommended. Drug interactions with other HCV protease inhibitors have not been evaluated. | |||
=====Peginterferon Alfa 2a/b Therapy===== | |||
*Coadministration of peginterferon alfa 2a (PEGASYS®) or 2b (PEGINTRON®) did not affect eltrombopag exposure in 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials with adult patients with chronic [[hepatitis C]] | |||
<!--Use in Specific Populations--> | |||
|useInPregnancyFDA=*Pregnancy Category C | |||
*There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of eltrombopag use in pregnancy. In animal reproduction and developmental toxicity studies, there was evidence of embryolethality and reduced fetal weights at maternally toxic doses. Eltrombopag olamine should be used in pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the mother justifies the potential risk to the fetus. | |||
*In an early embryonic development study, female rats received oral eltrombopag at doses of 10, 20, or 60 mg/kg/day (0.8, 2, and 6 times, respectively, the human clinical exposure based on [[AUC]] in [[ITP]] patients at 75 mg/day and 0.3, 1, and 3 times, respectively, the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic [[hepatitis C]] patients at 100 mg/day). Increased pre- and post-implantation loss and reduced fetal weight were observed at the highest dose which also caused maternal toxicity. | |||
*Eltrombopag was administered orally to pregnant rats at 10, 20, or 60 mg/kg/day (0.8, 2, and 6 times, respectively, the human clinical exposure based on AUC in [[ITP]] patients at 75 mg/day and 0.3, 1, and 3 times, respectively, the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic [[hepatitis C]] patients at 100 mg/day). Decreased fetal weights (6% to 7%) and a slight increase in the presence of cervical ribs were observed at the highest dose which also caused maternal toxicity. However, no evidence of major structural malformations was observed. | |||
*Pregnant rabbits were treated with oral eltrombopag doses of 30, 80, or 150 mg/kg/day (0.04, 0.3, and 0.5 times, respectively, the human clinical exposure based on AUC in [[ITP]] patients at 75 mg/day and 0.02, 0.1, and 0.3 times, respectively, the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic [[hepatitis C]] patients at 100 mg/day). No evidence of fetotoxicity, embryolethality, or teratogenicity was observed. | |||
*In a pre- and post-natal developmental toxicity study in pregnant rats (F0), no adverse effects on maternal reproductive function or on the development of the offspring (F1) were observed at doses up to 20 mg/kg/day (2 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in [[ITP]] patients at 75 mg/day and similar to the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic [[hepatitis C]] patients at 100 mg/day). Eltrombopag was detected in the plasma of offspring (F1). The plasma concentrations in pups increased with dose following administration of drug to the F0 dams. | |||
|useInPregnancyAUS=* '''Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category''' | |||
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of {{PAGENAME}} in women who are pregnant. | |||
|useInLaborDelivery=There is no FDA guidance on use of {{PAGENAME}} during labor and delivery. | |||
|useInNursing=*It is not known whether eltrombopag is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Eltrombopag olamine, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue Eltrombopag olamine taking into account the importance of Eltrombopag olamine to the mother. | |||
|useInPed=*The safety and efficacy of Eltrombopag olamine in pediatric patients have not been established. | |||
|useInGeri=*Of the 106 patients in 2 randomized clinical trials of Eltrombopag olamine 50 mg in chronic [[ITP]], 22% were 65 years of age and over, while 9% were 75 years of age and over. In the 2 randomized clinical trials of Eltrombopag olamine in patients with chronic [[hepatitis C]] and [[thrombocytopenia]], 7% were 65 years of age and over, while fewer than 1% were 75 years of age and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients in the placebo-controlled trials, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. | |||
|useInGender=There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} with respect to specific gender populations. | |||
|useInRace=*Patients of East Asian ethnicity (i.e., Japanese, Chinese, Taiwanese, and Korean) exhibit higher eltrombopag exposures. A reduction in the initial dose of Eltrombopag olamine is recommended for ITP or severe [[aplastic anemia]] patients of East Asian ancestry and patients of East Asian ancestry with [[hepatic impairment]] ([[Child-Pugh Class]] A, B, C) [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.3)]. No dose reduction is needed in patients of East Asian ethnicity with chronic [[hepatitis C]] | |||
|useInRenalImpair=*No adjustment in the initial dose of Eltrombopag olamine is needed for patients with [[renal impairment]] . Closely monitor patients with impaired renal function when administering Eltrombopag olamine. | |||
|useInHepaticImpair=*[[Hepatic impairment]] influences the exposure of Eltrombopag olamine .Reduce the initial dose of Eltrombopag olamine in patients with chronic [[ITP]] or severe [[aplastic anemia]] who also have [[hepatic impairment]] ([[Child-Pugh Class]] A, B, C) . No dosage adjustment is necessary for [[HCV]] patients with [[hepatic impairment]] | |||
|useInReproPotential=There is no FDA guidance on the use of {{PAGENAME}} in women of reproductive potentials and males. | |||
|useInImmunocomp=There is no FDA guidance one the use of {{PAGENAME}} in patients who are [[immunocompromised]]. | |||
<!--Administration and Monitoring--> | |||
|administration=* Oral | |||
|monitoring=There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--IV Compatibility--> | |||
|IVCompat=There is limited information regarding <i>IV Compatibility</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Overdosage--> | |||
|overdose= | |||
*In the event of overdose, platelet counts may increase excessively and result in [[thrombotic]]/thromboembolic complications. | |||
*In one report, a subject who ingested 5,000 mg of Eltrombopag olamine had a [[platelet count]] increase to a maximum of 929 x 109/L at 13 days following the ingestion. The patient also experienced [[rash]], [[bradycardia]], [[ALT]]/[[AST]] elevations, and [[fatigue]]. The patient was treated with [[gastric lavage]], oral [[lactulose]], intravenous fluids, [[omeprazole]], [[atropine]], [[furosemide]], [[calcium]], [[dexamethasone]], and [[plasmapheresis]]; however, the abnormal platelet count and liver test abnormalities persisted for 3 weeks. After 2 months follow-up, all events had resolved without sequelae. | |||
*In case of an overdose, consider oral administration of a metal cation-containing preparation, such as [[calcium]], [[aluminum]], or [[magnesium]] preparations to chelate eltrombopag and thus limit absorption. Closely monitor platelet counts. Reinitiate treatment with Eltrombopag olamine in accordance with dosing and administration recommendations | |||
<!--Pharmacology--> | |||
<!--Drug box 2--> | |||
|drugBox={{Drugbox2 | |||
| Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| verifiedrevid = 461093150 | |||
| IUPAC_name = 3'-{(2Z)-2-[1-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-3-methyl-5-oxo-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazol-4-ylidene]hydrazino}-2'-hydroxy-3-biphenylcarboxylic acid | |||
| image = eltrombopag.png | |||
| width = 200 | |||
| image2 = | |||
| width2 = | |||
<!--Clinical data--> | |||
| tradename = | |||
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|monograph|eltrombopag}} | |||
| MedlinePlus = a609011 | |||
| licence_EU = <!-- EMEA requires brand name --> | |||
| licence_US = Eltrombopag | |||
| pregnancy_AU = B3 | |||
| pregnancy_US = C | |||
| pregnancy_category = | |||
| legal_AU = <!-- Unscheduled / S2 / S3 / S4 / S5 / S6 / S7 / S8 / S9 --> | |||
| legal_CA = <!-- / Schedule I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII --> | |||
| legal_UK = <!-- GSL / P / POM / CD / Class A, B, C --> | |||
| legal_US = <!-- OTC / Rx-only / Schedule I, II, III, IV, V --> | |||
| legal_status = | |||
| dependency_liability = | |||
| routes_of_administration = Oral | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | |||
| bioavailability = | |||
| protein_bound = | |||
| metabolism = | |||
| elimination_half-life = | |||
| excretion = | |||
<!--Identifiers--> | |||
| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|changed|??}} | |||
| CAS_number = 496775-61-2 | |||
| CAS_supplemental = <br />{{CAS|496775-62-3}} ([[olamine]]) | |||
| ATC_prefix = B02 | |||
| ATC_suffix = BX05 | |||
| ATC_supplemental = | |||
| PubChem = 9846180 | |||
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | |||
| DrugBank = | |||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| ChemSpiderID = 21106301 | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| UNII = S56D65XJ9G | |||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|changed|EBI}} | |||
| ChEMBL = 461101 | |||
<!--Chemical data--> | |||
| C=25 | H=22 | N=4 | O=4 | | C=25 | H=22 | N=4 | O=4 | ||
| molecular_weight | | molecular_weight = 442.467 g/mol | ||
| smiles | | smiles = CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)N2C(=O)C(=C(N2)C)NN=C3C=CC=C(C3=O)C4=CC(=CC=C4)C(=O)O)C | ||
| | | InChI = 1/C25H22N4O4/c1-14-10-11-19(12-15(14)2)29-24(31)22(16(3)28-29)27-26-21-9-5-8-20(23(21)30)17-6-4-7-18(13-17)25(32)33/h4-13,26,30H,1-3H3,(H,32,33)/b27-22+ | ||
| InChIKey = XDXWLKQMMKQXPV-HPNDGRJYBX | |||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChI = 1S/C25H22N4O4/c1-14-10-11-19(12-15(14)2)29-24(31)22(16(3)28-29)27-26-21-9-5-8-20(23(21)30)17-6-4-7-18(13-17)25(32)33/h4-13,26,30H,1-3H3,(H,32,33)/b27-22+ | |||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChIKey = XDXWLKQMMKQXPV-HPNDGRJYSA-N | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
}} | }} | ||
<!--Mechanism of Action--> | |||
|mechAction=*Eltrombopag is an orally [[bioavailable]], small-molecule TPO-receptor agonist that interacts with the transmembrane domain of the human TPO-receptor and initiates signaling cascades that induce proliferation and differentiation from bone marrow progenitor cells. | |||
<!--Structure--> | |||
|structure=* Eltrombopag olamine (eltrombopag) tablets contain eltrombopag olamine, a small molecule thrombopoietin (TPO) receptor agonist for oral administration. Eltrombopag interacts with the transmembrane domain of the TPO receptor (also known as cMpl) leading to increased platelet production. Each tablet contains eltrombopag olamine in the amount equivalent to 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, or 100 mg of eltrombopag free acid. | |||
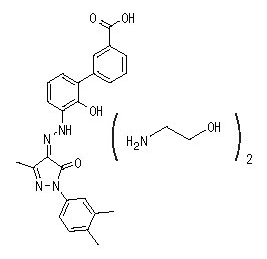
Eltrombopag olamine is a biphenyl hydrazone. The chemical name for eltrombopag olamine is 3'-{(2Z)-2-[1-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-3-methyl-5-oxo-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazol-4-ylidene]hydrazino}-2'-hydroxy-3-biphenylcarboxylic acid - 2-aminoethanol (1:2). It has the molecular formula C25H22N4O4●2(C2H7NO). The molecular weight is 564.65 for eltrombopag olamine and 442.5 for eltrombopag free acid. Eltrombopag olamine has the following structural formula: | |||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}08.png|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
*Eltrombopag olamine is practically insoluble in aqueous buffer across a pH range of 1 to 7.4, and is sparingly soluble in water. | |||
*The inactive ingredients of Eltrombopag olamine are: Tablet Core: magnesium stearate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, and sodium starch glycolate. Coating: hypromellose (12.5-mg, 25-mg, 50-mg, and 75-mg tablets) or polyvinyl alcohol and talc (100-mg tablet), polyethylene glycol 400, titanium dioxide, polysorbate 80 (12.5-mg tablet), FD&C Yellow No. 6 aluminum lake (25-mg tablet), FD&C Blue No. 2 aluminum lake (50-mg tablet), Iron Oxide Red and Iron Oxide Black (75-mg tablet), or Iron Oxide Yellow and Iron Oxide Black (100-mg tablet). | |||
<!--Pharmacodynamics--> | |||
|PD=There is limited information regarding <i>Pharmacodynamics</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetics--> | |||
|PK=*Absorption: Eltrombopag is absorbed with a peak concentration occurring 2 to 6 hours after oral administration. Based on urinary excretion and [[biotransformation]] products eliminated in feces, the oral absorption of drug-related material following administration of a single 75-mg solution dose was estimated to be at least 52%. | |||
*An open-label, randomized, crossover trial was conducted to assess the effect of food on the [[bioavailability]] of eltrombopag. A standard high-fat breakfast significantly decreased plasma eltrombopag AUC0-∞ by approximately 59% and Cmax by 65% and delayed Tmax by 1 hour. The [[calcium]] content of this meal may have also contributed to this decrease in exposure. | |||
*Distribution: The concentration of eltrombopag in blood cells is approximately 50% to 79% of plasma concentrations based on a radiolabel study. In vitro studies suggest that eltrombopag is highly bound to human [[plasma proteins]] (greater than 99%). Eltrombopag is a substrate of BCRP, but is not a substrate for [[P-glycoprotein]] (P-gp) or OATP1B1. | |||
*Metabolism: Absorbed eltrombopag is extensively metabolized, predominantly through pathways including cleavage, oxidation, and conjugation with glucuronic acid, glutathione, or cysteine. In vitrostudies suggest that CYP1A2 and CYP2C8 are responsible for the oxidative metabolism of eltrombopag. UGT1A1 and UGT1A3 are responsible for the glucuronidation of eltrombopag. | |||
*Elimination: The predominant route of eltrombopag excretion is via feces (59%), and 31% of the dose is found in the [[urine]]. Unchanged eltrombopag in feces accounts for approximately 20% of the dose; unchanged eltrombopag is not detectable in urine. The plasma elimination half-life of eltrombopag is approximately 21 to 32 hours in healthy subjects and 26 to 35 hours in ITP patients. | |||
*Drug Interactions: Polyvalent Cation-containing Antacids: In a clinical trial, coadministration of 75 mg of Eltrombopag olamine with a polyvalent cation-containing antacid (1,524 mg aluminum hydroxide, 1,425 mg [[magnesium]] carbonate, and sodium [[alginate]]) to 26 healthy adult subjects decreased plasma eltrombopag AUC0-∞ and Cmax by approximately 70%. The contribution of sodium alginate to this interaction is not known. | |||
*[[Cytochrome P450 Enzymes]] (CYPs): In a clinical trial, Eltrombopag olamine 75 mg once daily was administered for 7 days to 24 healthy male subjects did not show inhibition or induction of the metabolism of a combination of probe substrates for CYP1A2 ([[caffeine]]), CYP2C19 ([[omeprazole]]), CYP2C9 ([[flurbiprofen]]), or CYP3A4 ([[midazolam]]) in humans. Probe substrates for CYP2C8 were not evaluated in this trial. | |||
*Rosuvastatin: In a clinical trial, coadministration of 75 mg of Eltrombopag olamine once daily for 5 days with a single 10-mg dose of the OATP1B1 and BCRP substrate, rosuvastatin to 39 healthy adult subjects increased plasma rosuvastatin AUC0-∞ by 55% and Cmax by 103%. | |||
*Protease Inhibitors: HIV Protease Inhibitors: In a clinical trial, coadministration of repeat-dose lopinavir 400 mg/ritonavir 100 mg twice daily with a single dose of Eltrombopag olamine 100 mg to 40 healthy adult subjects decreased plasma eltrombopag AUC0-∞ by 17%. | |||
*HCV [[Protease Inhibitors]]: In a clinical trial, coadministration of repeat-dose [[telaprevir]] 750 mg every 8 hours or boceprevir 800 mg every 8 hours with a single dose of Eltrombopag olamine 200 mg to healthy adult subjects did not alter plasma [[telaprevir]], [[boceprevir]], or eltrombopag AUC0-∞ or Cmax to a significant extent. | |||
*Pegylated Interferon alfa-2a + [[Ribavirin]] and Pegylated [[Interferon]] alfa-2b + Ribavirin: The pharmacokinetics of eltrombopag in both the presence and absence of pegylated interferon alfa 2a and 2b therapy were evaluated using a population pharmacokinetic analysis in 635 patients with chronic [[hepatitis C]]. The population PK model estimates of clearance indicate no significant difference in eltrombopag clearance in the presence of pegylated interferon alfa plus ribavirin therapy. | |||
*In vitro Studies: Eltrombopag is an inhibitor of CYP2C8 and CYP2C9 in vitro. Eltrombopag is an inhibitor of UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A4, UGT1A6, UGT1A9, UGT2B7, and UGT2B15 in vitro. Eltrombopag is an inhibitor of the organic anion transporting polypeptide OATP1B1 and BCRP in vitro. | |||
*Specific Populations: Ethnicity: Based on two population PK analyses of eltrombopag concentrations in ITP and chronic [[hepatitis C]] patients, East Asian (i.e., Japanese, Chinese, Taiwanese, and Korean) subjects exhibited 50% to 55% higher eltrombopag plasma concentrations compared with non-East Asian subjects . | |||
*An approximately 40% higher systemic eltrombopag exposure in healthy African-American subjects was noted in at least one clinical pharmacology trial. The effect of African-American ethnicity on exposure and related safety and efficacy of eltrombopag has not been established. | |||
*Hepatic Impairment: In a pharmacokinetic trial, the disposition of a single 50-mg dose of Eltrombopag olamine in patients with mild, moderate, and severe [[hepatic impairment]] was compared with subjects with normal hepatic function. The degree of hepatic impairment was based on [[Child-Pugh score]]. Plasma eltrombopag AUC0-∞ was 41% higher in patients with mild [[hepatic impairment]] ([[Child-Pugh Class]] A) compared with subjects with normal hepatic function. Plasma eltrombopag AUC0-∞ was approximately 2-fold higher in patients with moderate ([[Child-Pugh Class]] B) and [[severe hepatic impairment]] ([[Child-Pugh Class]] C). The half-life of eltrombopag was prolonged 2-fold in these patients. This clinical trial did not evaluate protein binding effects. | |||
*Chronic Liver Disease: A population PK analysis in thrombocytopenic patients with chronic liver disease following repeat doses of eltrombopag demonstrated that mild hepatic impairment resulted in an 87% to 110% higher plasma eltrombopag AUC(0-τ) and patients with moderate [[hepatic impairment]] had approximately 141% to 240% higher plasma eltrombopag AUC(0-τ) values compared with patients with normal hepatic function. The half-life of eltrombopag was prolonged 3-fold in patients with mild hepatic impairment and 4-fold in patients with moderate [[hepatic impairment]]. This clinical trial did not evaluate protein binding effects. | |||
*Chronic Hepatitis C: A population PK in 28 healthy adults and 635 patients with chronic [[hepatitis C]] demonstrated that patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with Eltrombopag olamine had higher plasma AUC(0-τ) values as compared with healthy subjects, and AUC(0-τ) increased with increasing Child-Pugh score. Patients with chronic hepatitis C and mild hepatic impairment had approximately 100% to 144% higher plasma AUC(0-τ) compared with healthy subjects. This clinical trial did not evaluate protein binding effects. | |||
*Renal Impairment: The disposition of a single 50-mg dose of Eltrombopag olamine in patients with mild ([[creatinine clearance]] [CrCl] of 50 to 80 mL/min), moderate (CrCl of 30 to 49 mL/min), and severe ([[CrCl]] less than 30 mL/min) [[renal impairment]] was compared with subjects with normal renal function. Average total plasma eltrombopag AUC0-∞ was 32% to 36% lower in subjects with mild to moderate renal impairment and 60% lower in subjects with severe [[renal impairment]] compared with healthy subjects. The effect of renal impairment on unbound (active) eltrombopag exposure has not been assessed. | |||
=====Assessment of Risk of QT/QTc Prolongation===== | |||
*There is no indication of a QT/QTc prolonging effect of Eltrombopag olamine at doses up to 150 mg daily for 5 days. The effects of Eltrombopag olamine at doses up to 150 mg daily for 5 days (supratherapeutic doses) on the QT/QTc interval was evaluated in a double-blind, randomized, placebo- and positive-controlled ([[moxifloxacin]] 400 mg, single oral dose) crossover trial in healthy adult subjects. Assay sensitivity was confirmed by significant QTc prolongation by moxifloxacin.<!--Nonclinical Toxicology--> | |||
|nonClinToxic= | |||
======Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility====== | |||
*Eltrombopag does not stimulate platelet production in rats, mice, or dogs because of unique TPO receptor specificity. Data from these animals do not fully model effects in humans. | |||
*Eltrombopag was not carcinogenic in mice at doses up to 75 mg/kg/day or in rats at doses up to 40 mg/kg/day (exposures up to 4 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and 2 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day). | |||
*Eltrombopag was not mutagenic or clastogenic in a bacterial mutation assay or in 2 in vivo assays in rats (micronucleus and unscheduled DNA synthesis, 10 times the human clinical exposure based on [[Cmax]] in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and 7 times the human clinical exposure based on Cmax in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day). In the in vitro mouse lymphoma assay, eltrombopag was marginally positive (less than 3-fold increase in mutation frequency). | |||
*Eltrombopag did not affect female fertility in rats at doses up to 20 mg/kg/day (2 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in [[ITP]] patients at 75 mg/day and similar to the human clinical exposure based on [[AUC]] in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day). Eltrombopag did not affect male [[fertility]] in rats at doses up to 40 mg/kg/day, the highest dose tested (3 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and 2 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day). | |||
======Animal Pharmacology and/or Toxicology====== | |||
*Eltrombopag is phototoxic in vitro. There was no evidence of in vivo cutaneous or ocular phototoxicity in rodents. | |||
*Treatment-related cataracts were detected in rodents in a dose- and time-dependent manner. At greater than or equal to 6 times the human clinical exposure based on [[AUC]] in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and 3 times the human clinical exposure based on [[AUC]] in chronic [[hepatitis C]] patients at 100 mg/day, cataracts were observed in mice after 6 weeks and in rats after 28 weeks of dosing. At greater than or equal to 4 times the human clinical exposure based on [[AUC]] in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and 2 times the human clinical exposure based on [[AUC]] in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day, cataracts were observed in mice after 13 weeks and in rats after 39 weeks of dosing . | |||
*Renal tubular toxicity was observed in studies up to 14 days in duration in mice and rats at exposures that were generally associated with morbidity and mortality. Tubular toxicity was also observed in a 2-year oral [[carcinogenicity]] study in mice at doses of 25, 75, and 150 mg/kg/day. The exposure at the lowest dose was 1.2 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and 0.6 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day. No similar effects were observed in mice after 13 weeks at exposures greater than those associated with renal changes in the 2-year study, suggesting that this effect is both dose- and time-dependent. | |||
<!--Clinical Studies--> | |||
|clinicalStudies= | |||
======Chronic ITP====== | |||
*The efficacy and safety of Eltrombopag olamine in adult patients with chronic ITP were evaluated in 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials and in an open-label extension trial. | |||
*Trials 1 and 2: In trials 1 and 2, patients who had completed at least one prior ITP therapy and who had a platelet count less than 30 x 109/L were randomized to receive either Eltrombopag olamine or placebo daily for up to 6 weeks, followed by 6 weeks off therapy. During the trials, Eltrombopag olamine or placebo was discontinued if the platelet count exceeded 200 x 109/L. The primary efficacy endpoint was response rate, defined as a shift from a baseline [[platelet count]] of less than 30 x 109/L to greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L at any time during the treatment period. | |||
*The median age of the patients was 50 years and 60% were female. Approximately 70% of the patients had received at least 2 prior [[ITP]] therapies (predominantly [[corticosteroids]], [[immunoglobulins]], [[rituximab]], cytotoxic therapies, [[danazol]], and [[azathioprine]]) and 40% of the patients had undergone [[splenectomy]]. The median baseline [[platelet counts]] (approximately 18 x 109/L) were similar among all treatment groups. | |||
*Trial 1 randomized 114 patients (2:1) to Eltrombopag olamine 50 mg or placebo. Trial 2 randomized 117 patients (1:1:1:1) among placebo or 1 of 3 dose regimens of Eltrombopag olamine, 30 mg, 50 mg, or 75 mg each administered daily. | |||
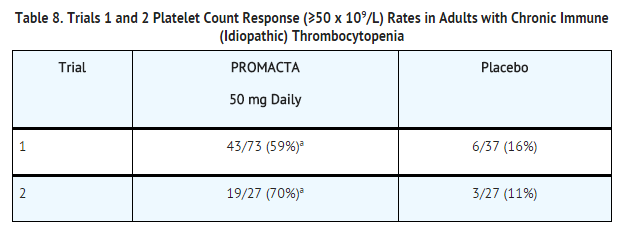
*Table 8 shows for each trial the primary efficacy outcomes for the placebo groups and the patient groups who received the 50-mg daily regimen of Eltrombopag olamine. | |||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}000.png|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
*The platelet count response to Eltrombopag olamine was similar among patients who had or had not undergone [[splenectomy]]. In general, increases in platelet counts were detected 1 week following initiation of Eltrombopag olamine and the maximum response was observed after 2 weeks of therapy. In the placebo and 50-mg–dose groups of Eltrombopag olamine, the trial drug was discontinued due to an increase in [[platelet counts]] to greater than 200 x 109/L in 3% and 27% of the patients, respectively. The median duration of treatment with the 50-mg dose of Eltrombopag olamine was 42 days in Trial 1 and 43 days in Trial 2. | |||
*Of 7 patients who underwent hemostatic challenges, additional ITP medications were required in 3 of 3 placebo group patients and 0 of 4 patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine. Surgical procedures accounted for most of the hemostatic challenges. Hemorrhage requiring transfusion occurred in one placebo group patient and no patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine. | |||
*Trial 3: In this trial, 197 patients were randomized (2:1) to receive either Eltrombopag olamine 50 mg once daily (n = 135) or placebo (n = 62) for 6 months, during which time the dose of Eltrombopag olamine could be adjusted based on individual [[platelet counts]]. Patients were allowed to taper or discontinue concomitant [[ITP]] medications after being treated with Eltrombopag olamine for 6 weeks. Patients were permitted to receive rescue treatments at any time during the trial as clinically indicated. The primary endpoint was the odds of achieving a [[platelet count]] greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L and less than or equal to 400 x 109/L for patients receiving Eltrombopag olamine relative to placebo and was based on patient response profiles throughout the 6-month treatment period. | |||
*The median age of the patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine and placebo was 47 years and 52.5 years, respectively. Approximately half of the patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine and placebo (47% and 50%, respectively) were receiving concomitant [[ITP]] medication (predominantly [[corticosteroids]]) at randomization and had baseline [[platelet counts]] less than or equal to15 x 109/L (50% and 48%, respectively). A similar percentage of patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine and placebo (37% and 34%, respectively) had a prior splenectomy. | |||
*In 134 patients who completed 26 weeks of treatment, a sustained platelet response (platelet count greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L and less than or equal to 400 x 109/L for 6 out of the last 8 weeks of the 26-week treatment period in the absence of rescue medication at any time) was achieved by 60% of patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine, compared with 10% of patients treated with placebo (splenectomized patients: Eltrombopag olamine 51%, placebo 8%; non-splenectomized patients: Eltrombopag olamine 66%, placebo 11%). The proportion of responders in the group of patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine was between 37% and 56% compared with 7% and 19% in the placebo treatment group for all on-therapy visits. Patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine were significantly more likely to achieve a platelet count between 50 x 109/L and 400 x 109/L during the entire 6-month treatment period compared with those patients treated with placebo. | |||
In | |||
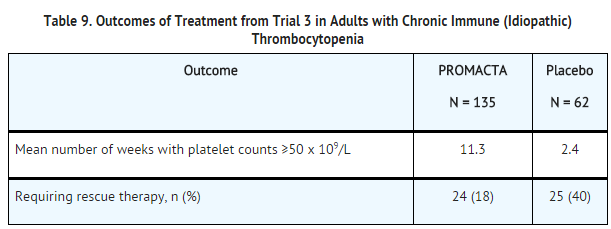
== | *Outcomes of treatment are presented in Table 9 for all patients enrolled in the trial. | ||
Eltrombopag | |||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}09.png|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
*Among 94 patients receiving other [[ITP]] therapy at baseline, 37 (59%) of 63 patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine and 10 (32%) of 31 patients in the placebo group discontinued concomitant therapy at some time during the trial. | |||
*Extension Trial: Patients who completed any prior clinical trial with Eltrombopag olamine were enrolled in an open-label, single-arm trial in which attempts were made to decrease the dose or eliminate the need for any concomitant [[ITP]] medications. Eltrombopag olamine was administered to 299 patients; 249 completed 6 months, 210 patients completed 12 months, and 138 patients completed 24 months of therapy. The median baseline platelet count was 19 x 109/L prior to administration of Eltrombopag olamine. | |||
======Chronic Hepatitis C-associated Thrombocytopenia====== | |||
*The efficacy and safety of Eltrombopag olamine for the treatment of [[thrombocytopenia]] in adult patients with chronic [[hepatitis C]] were evaluated in 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Trial 1 utilized [[peginterferon]] alfa-2a (PEGASYS®) plus [[ribavirin]] for antiviral treatment and Trial 2 utilized [[peginterferon alfa-2b]] (PEGINTRON®) plus ribavirin. In both trials, patients with a platelet count of less than 75 x 109/L were enrolled and stratified by platelet count, screening [[HCV]] [[RNA]], and [[HCV]] genotype. Patients were excluded if they had evidence of [[decompensated liver disease]] with [[Child-Pugh score]] greater than 6 (class B and C), history of [[ascites]], or [[hepatic encephalopathy]]. The median age of the patients in both trials was 52 years, 63% were male, and 74% were Caucasian. Sixty-nine percent of patients had HCV genotypes 1, 4, 6 with the remainder genotypes 2 and 3. Approximately 30% of patients had been previously treated with [[interferon]] and [[ribavirin]]. The majority of patients (90%) had bridging fibrosis and cirrhosis, as indicated by noninvasive testing. A similar proportion (95%) of patients in both treatment groups had Child-Pugh level A (score 5-6) at baseline. A similar proportion of patients (2%) in both treatment groups had baseline international normalized ratio (INR) greater than 1.7. Median baseline platelet counts (approximately 60 x 109/L) were similar in both treatment groups. The trials consisted of two phases – a pre-antiviral treatment phase and an antiviral treatment phase. In the pre-antiviral treatment phase, patients received open-label Eltrombopag olamine to increase the platelet count to a threshold of greater than or equal to 90 x 109/L for Trial 1 and greater than or equal to 100 x 109/L for Trial 2. Eltrombopag olamine was administered at an initial dose of 25 mg once daily for 2 weeks and increased in 25-mg increments over 2- to 3-week periods to achieve the optimal platelet count to initiate antiviral therapy. The maximal time patients could receive open-label Eltrombopag olamine was 9 weeks. If threshold platelet counts were achieved, patients were randomized (2:1) to the same dose of Eltrombopag olamine at the end of the pre-treatment phase or to placebo. Eltrombopag olamine was administered in combination with pegylated interferon and ribavirin per their respective prescribing information for up to 48 weeks. | |||
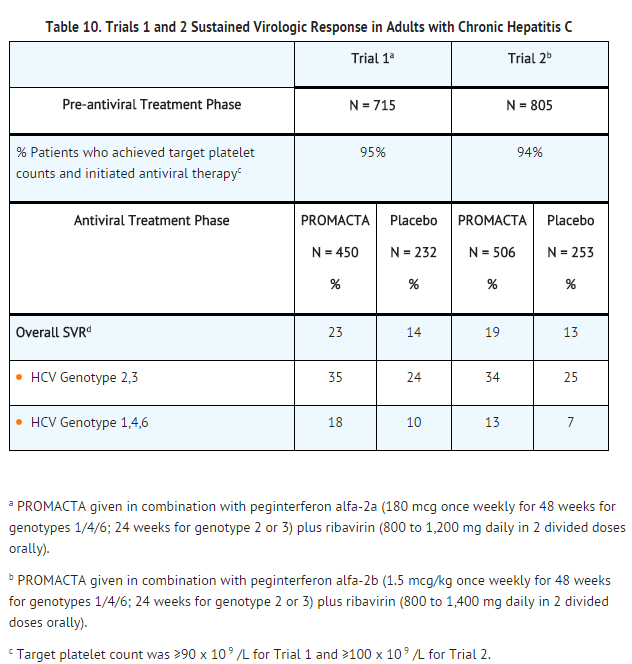
*The primary efficacy endpoint for both trials was sustained virologic response (SVR) defined as the percentage of patients with undetectable HCV-RNA at 24 weeks after completion of antiviral treatment. The median time to achieve the target platelet count greater than or equal to 90 x 109/L was approximately 2 weeks. Ninety-five percent of patients were able to initiate antiviral therapy. | |||
*In both trials, a significantly greater proportion of patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine achieved SVR (see Table 10). The improvement in the proportion of patients who achieved SVR was consistent across subgroups based on baseline platelet count (less than 50 x 109/L versus greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L). In patients with high baseline viral loads (greater than or equal to 800,000), the SVR rate was 18% (82/452) for Eltrombopag olamine versus 8% (20/239) for placebo. | |||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}10.png|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
*The majority of patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine (76%) maintained a [[platelet count]] greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L compared with 19% for placebo. A greater proportion of patients on Eltrombopag olamine did not require any antiviral dose reduction as compared with placebo (45% versus 27%). | |||
======Severe Aplastic Anemia====== | |||
*Eltrombopag olamine was studied in a single-arm, single-center, open-label trial in 43 patients with severe [[aplastic anemia]] who had an insufficient response to at least one prior immunosuppressive therapy and who had a [[platelet count]] less than or equal to 30 x 109/L. Eltrombopag olamine was administered at an initial dose of 50 mg once daily for 2 weeks and increased over 2 week periods up to a maximum dose of 150 mg once daily. The primary endpoint was hematologic response assessed after 12 weeks of treatment with Eltrombopag olamine. Hematologic response was defined as meeting 1 or more of the following criteria: 1) [[platelet count]] increases to 20 x 109/L above baseline, or stable platelet counts with transfusion independence for a minimum of 8 weeks; 2) [[hemoglobin]] increase by greater than 1.5 g/dL, or a reduction in greater than or equal to 4 units of RBC transfusions for 8 consecutive weeks; 3) [[ANC]] increase of 100% or an [[ANC]] increase greater than 0.5 x 109/L. Eltrombopag olamine was discontinued after 16 weeks if no hematologic response was observed. Patients who responded continued therapy in an extension phase of the trial. | |||
*The treated population had median age of 45 years (range 17 to 77 years) and 56% were male. At baseline, the median platelet count was 20 x 109/L, hemoglobin was 8.4 g/dL, ANC was 0.58 x 109/L and absolute reticulocyte count was 24.3 x109/L. Eighty-six percent of patients were RBC transfusion dependent and 91% were [[platelet transfusion]] dependent. The majority of patients (84%) received at least 2 prior immunosuppressive therapies. Three patients had cytogenetic abnormalities at baseline. | |||
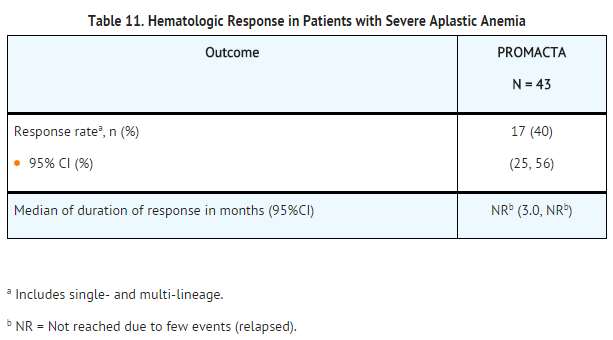
*Table 11 presents the primary efficacy results. | |||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}11.png|thumb|none|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
*In the 17 responders, the [[platelet transfusion]]-free period ranged from 8 to 1,096 days with a median of 200 days, and the RBC transfusion-free period ranged from 15 to 1,082 days with a median of 208 days. | |||
*In the extension phase, 8 patients achieved a multi-lineage response; 4 of these patients subsequently tapered off treatment with Eltrombopag olamine and maintained the response(median follow up: 8.1 months, range: 7.2 to 10.6 months). | |||
<!--How Supplied--> | |||
|howSupplied=:*The 12.5-mg tablets are round, biconvex, white, film-coated tablets debossed with GS MZ1 and 12.5 on one side and are available in bottles of 30: NDC 0007-4643-13. | |||
:*The 25-mg tablets are round, biconvex, orange, film-coated tablets debossed with GS NX3 and 25 on one side and are available in bottles of 30: NDC 0007-4640-13. | |||
:*The 50-mg tablets are round, biconvex, blue, film-coated tablets debossed with GS UFU and 50 on one side and are available in bottles of 30: NDC 0007-4641-13. | |||
:*The 75-mg tablets are round, biconvex, pink, film-coated tablets debossed with GS FFS and 75 on one side and are available in bottles of 30: NDC 0007-4642-13. | |||
:*The 100-mg tablets are round, biconvex, green, film-coated tablets debossed with GS 1L5 and are available in bottles of 30: NDC 0007-4646-13. This product contains a desiccant. | |||
*Store at room temperature between 20°C and 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not remove desiccant if present. Dispense in original bottle. | |||
<!--Patient Counseling Information--> | |||
|fdaPatientInfo=*Prior to treatment, patients should fully understand and be informed of the following risks and considerations for Eltrombopag olamine: | |||
*For patients with chronic [[ITP]], therapy with Eltrombopag olamine is administered to achieve and maintain a platelet count greater than or equal to 50 x 10 9/L as necessary to reduce the risk for bleeding. | |||
*For patients with chronic [[hepatitis C]], therapy with Eltrombopag olamine is administered to achieve and maintain a platelet count necessary to initiate and maintain antiviral therapy with [[pegylated interferon]] and [[ribavirin]]. | |||
*Therapy with Eltrombopag olamine may be associated with hepatobiliary laboratory abnormalities. | |||
*Advise patients with chronic [[hepatitis C]] and [[cirrhosis]] that they may be at risk for hepatic decompensation when receiving [[alfa interferon]] therapy. | |||
*Advise patients that they should report any of the following signs and symptoms of liver problems to their healthcare provider right away. | |||
:*yellowing of the skin or the whites of the eyes ([[jaundice]]) | |||
:*unusual darkening of the urine | |||
:*unusual tiredness | |||
:*right upper stomach area pain | |||
:*[[confusion]] | |||
:*swelling of the stomach area (abdomen) | |||
*Advise patients that [[thrombocytopenia]] and risk of bleeding may reoccur upon discontinuing Eltrombopag olamine, particularly if Eltrombopag olamine is discontinued while the patient is on anticoagulants or [[antiplatelet agents]]. | |||
*Advise patients that too much Eltrombopag olamine may result in excessive platelet counts and a risk for [[thrombotic]]/[[thromboembolic]] complications. | |||
*Advise patients that during therapy with Eltrombopag olamine, they should continue to avoid situations or medications that may increase the risk for bleeding. | |||
*Advise patients to have a baseline ocular examination prior to administration of Eltrombopag olamine and be monitored for signs and symptoms of cataracts during therapy. | |||
*Advise patients to keep at least a 4-hour interval between Eltrombopag olamine and foods, mineral supplements, and antacids which contain polyvalent cations such as iron, [[calcium]], [[aluminum]], [[magnesium]], [[selenium]], and [[zinc]]. | |||
<!--Precautions with Alcohol--> | |||
|alcohol=* Alcohol-{{PAGENAME}} interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | |||
<!--Brand Names--> | |||
|brandNames=*Eltrombopag olamine | |||
<!--Look-Alike Drug Names--> | |||
|lookAlike= | |||
<!--Drug Shortage Status--> | |||
|drugShortage= | |||
}} | |||
<!--Pill Image--> | |||
<!--Label Display Image--> | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}}12.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
}} | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}}13.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
}} | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}}14.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
}} | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}}15.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
}} | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}}16.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
}} | |||
{{LabelImage | |||
|fileName={{PAGENAME}}17.png|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine. | |||
}} | |||
<!--Category--> | |||
< | |||
[[Category: | [[Category:Drug]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:35, 17 April 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aparna Vuppala, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
WARNING
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
RISK FOR HEPATIC DECOMPENSATION IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC HEPATITIS C:
|
Overview
Eltrombopag is a thrombopoietin receptor agonist that is FDA approved for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in patients with chronic immune (idiopathic) thrombocytopenia (ITP) who have had an insufficient response to corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, or splenectomy. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include thrombocytopenia, aplastic anemia, hyperbilirubinemia, fatigue, cough, epistaxis, fever, diarrhea.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Idiopathic Thrombocytopenia
- Eltrombopag olamine is indicated for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in patients with chronic immune (idiopathic) thrombocytopenia (ITP) who have had an insufficient response to corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, or splenectomy.
Treatment of Thrombocytopenia in Patients with Hepatitis C Infection
- Eltrombopag olamine is indicated for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in patients with chronic hepatitis C to allow the initiation and maintenance of interferon-based therapy.
Treatment of Severe Aplastic Anemia
- Eltrombopag olamine is indicated for the treatment of patients with severe aplastic anemia who have had an insufficient response to immunosuppressive therapy.
Limitations of Use
- Eltrombopag olamine should be used only in patients with ITP whose degree of thrombocytopenia and clinical condition increase the risk for bleeding.
- Eltrombopag olamine should be used only in patients with chronic hepatitis C whose degree of thrombocytopenia prevents the initiation of interferon-based therapy or limits the ability to maintain interferon-based therapy.
- Safety and efficacy have not been established in combination with direct-acting antiviral agents used without interferon for treatment of chronic hepatitis C infection.
Dosing Information
Chronic Immune (Idiopathic) Thrombocytopenia
- Use the lowest dose of Eltrombopag olamine to achieve and maintain a platelet count greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L as necessary to reduce the risk for bleeding. Dose adjustments are based upon the platelet count response. Do not use Eltrombopag olamine to normalize platelet counts . In clinical trials, platelet counts generally increased within 1 to 2 weeks after starting Eltrombopag olamine and decreased within 1 to 2 weeks after discontinuing Eltrombopag olamine .
- Initial Dose Regimen: Initiate Eltrombopag olamine at a dose of 50 mg once daily, except in patients who are of East Asian ancestry (such as Chinese, Japanese, Taiwanese, or Korean) or who have mild to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, B, C).
- For ITP patients of East Asian ancestry, initiate Eltrombopag olamine at a reduced dose of 25 mg once daily .
- For ITP patients with mild, moderate, or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, B, C), initiate Eltrombopag olamine at a reduced dose of 25 mg once daily
- For ITP patients of East Asian ancestry with hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, B, C), consider initiating Eltrombopag olamine at a reduced dose of 12.5 mg once daily
- Monitoring and Dose Adjustment: After initiating Eltrombopag olamine, adjust the dose to achieve and maintain a platelet count greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L as necessary to reduce the risk for bleeding. Do not exceed a dose of 75 mg daily. Monitor clinical hematology and liver tests regularly throughout therapy with Eltrombopag olamine and modify the dosage regimen of Eltrombopag olamine based on platelet counts as outlined in Table 1. During therapy with Eltrombopag olamine, assess CBCs with differentials, including platelet counts, weekly until a stable platelet count has been achieved. Obtain CBCs with differentials, including platelet counts, monthly thereafter.
- In ITP patients with hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, B, C), after initiating Eltrombopag olamine or after any subsequent dosing increase, wait 3 weeks before increasing the dose.
- Modify the dosage regimen of concomitant ITP medications, as medically appropriate, to avoid excessive increases in platelet counts during therapy with Eltrombopag olamine. Do not administer more than one dose of Eltrombopag olamine within any 24-hour period.
- Discontinuation: Discontinue Eltrombopag olamine if the platelet count does not increase to a level sufficient to avoid clinically important bleeding after 4 weeks of therapy with Eltrombopag olamine at the maximum daily dose of 75 mg. Excessive platelet count responses, as outlined in Table 1, or important liver test abnormalities also necessitate discontinuation of Eltrombopag olamine . Obtain CBCs with differentials, including platelet counts, weekly for at least 4 weeks following discontinuation of Eltrombopag olamine.
Chronic Hepatitis C-associated Thrombocytopenia
- Use the lowest dose of Eltrombopag olamine to achieve and maintain a platelet count necessary to initiate and maintain antiviral therapy with pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Dose adjustments are based upon the platelet count response. Do not use Eltrombopag olamine to normalize platelet counts . In clinical trials, platelet counts generally began to rise within the first week of treatment with Eltrombopag olamine .
- Initial Dose Regimen: Initiate Eltrombopag olamine at a dose of 25 mg once daily.
- Monitoring and Dose Adjustment: Adjust the dose of Eltrombopag olamine in 25-mg increments every 2 weeks as necessary to achieve the target platelet count required to initiate antiviral therapy. Monitor platelet counts every week prior to starting antiviral therapy.
- During antiviral therapy, adjust the dose of Eltrombopag olamine to avoid dose reductions of peginterferon. Monitor CBCs with differentials, including platelet counts, weekly during antiviral therapy until a stable platelet count is achieved. Monitor platelet counts monthly thereafter. Do not exceed a dose of 100 mg daily. Monitor clinical hematology and liver tests regularly throughout therapy with Eltrombopag olamine.
- For specific dosage instructions for peginterferon or ribavirin, refer to their respective prescribing information.
- Discontinuation: The prescribing information for pegylated interferon and ribavirin include recommendations for antiviral treatment discontinuation for treatment futility. Refer to pegylated interferon and ribavirin prescribing information for discontinuation recommendations for antiviral treatment futility.
- Eltrombopag olamine should be discontinued when antiviral therapy is discontinued. Excessive platelet count responses, as outlined in Table 2, or important liver test abnormalities also necessitate discontinuation of Eltrombopag olamine.
Severe Aplastic Anemia
- Use the lowest dose of Eltrombopag olamine to achieve and maintain a hematologic response. Dose adjustments are based upon the platelet count. Hematologic response requires dose titration, generally up to 150 mg, and may take up to 16 weeks after starting Eltrombopag olamine.
- Initial Dose Regimen: Initiate Eltrombopag olamine at a dose of 50 mg once daily.
- For severe aplastic anemia in patients of East Asian ancestry or those with mild, moderate, or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, B, C), initiate Eltrombopag olamine at a reduced dose of 25 mg once daily
- Monitoring and Dose Adjustment: Adjust the dose of Eltrombopag olamine in 50-mg increments every 2 weeks as necessary to achieve the target platelet count greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L as necessary. Do not exceed a dose of 150 mg daily. Monitor clinical hematology and liver tests regularly throughout therapy with Eltrombopag olamine and modify the dosage regimen of Eltrombopag olamine based on platelet counts as outlined in Table 3.
- For patients who achieve tri-lineage response, including transfusion independence, lasting at least 8 weeks: the dose of Eltrombopag olamine may be reduced by 50% . If counts remain stable after 8 weeks at the reduced dose, then discontinue Eltrombopag olamine and monitor blood counts. If platelet counts drop to less than 30 x 109/L, hemoglobin to less than 9 g/dL, or ANC to less than 0.5 x 109/L, Eltrombopag olamine may be reinitiated at the previous effective dose.
- Discontinuation: If no hematologic response has occurred after 16 weeks of therapy with Eltrombopag olamine, discontinue therapy. If new cytogenetic abnormalities are observed, consider discontinuation of Eltrombopag olamine. Excessive platelet count responses (as outlined in Table 3) or important liver test abnormalities also necessitate discontinuation of Eltrombopag olamine .
Administration
- Take Eltrombopag olamine on an empty stomach (1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal)
- Allow at least a 4-hour interval between Eltrombopag olamine and other medications (e.g., antacids), calcium-rich foods (e.g., dairy products and calcium fortified juices), or supplements containing polyvalent cations such as iron, calcium, aluminum, magnesium, selenium, and zinc
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Eltrombopag in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Eltrombopag in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Eltrombopag in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Eltrombopag in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Eltrombopag in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- None.
Warnings
|
WARNING
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
RISK FOR HEPATIC DECOMPENSATION IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC HEPATITIS C:
|
Hepatic Decompensation in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C
- In patients with chronic hepatitis C, Eltrombopag olamine in combination with interferon and ribavirin may increase the risk of hepatic decompensation. In two controlled clinical trials in patients with chronic hepatitis C and thrombocytopenia, ascites and encephalopathy occurred more frequently on the arm receiving treatment with Eltrombopag olamine plus antivirals (7%) than the placebo plus antivirals arm (4%). Patients with low albumin levels (less than 3.5 g/dL) or Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score greater than or equal to 10 at baseline had a greater risk for hepatic decompensation on the arm receiving treatment with Eltrombopag olamine plus antivirals. Discontinue Eltrombopag olamine if antiviral therapy is discontinued.
Hepatotoxicity
- Eltrombopag olamine can cause liver enzyme elevations . Measure serum ALT, AST, and bilirubin prior to initiation of Eltrombopag olamine, every 2 weeks during the dose adjustment phase, and monthly following establishment of a stable dose. Eltrombopag olamine inhibits UGT1A1 and OATP1B1, which may lead to indirect hyperbilirubinemia. If bilirubin is elevated, perform fractionation. Evaluate abnormal serum liver tests with repeat testing within 3 to 5 days. If the abnormalities are confirmed, monitor serum liver tests weekly until resolved or stabilized. Discontinue Eltrombopag olamine if ALT levels increase to greater than or equal to 3X ULN in patients with normal liver function or greater than or equal to 3X baseline in patients with pre-treatment elevations in transaminases and are:
- progressively increasing, or
- persistent for greater than or equal to 4 weeks, or
- accompanied by increased direct bilirubin, or
- accompanied by clinical symptoms of liver injury or evidence for hepatic decompensation.
- If the potential benefit for reinitiating treatment with Eltrombopag olamine is considered to outweigh the risk for hepatotoxicity, then consider cautiously reintroducing Eltrombopag olamine and measure serum liver tests weekly during the dose adjustment phase. Hepatotoxicity may reoccur if Eltrombopag olamine is reinitiated. If liver tests abnormalities persist, worsen or recur, then permanently discontinue Eltrombopag olamine.
Thrombotic/Thromboembolic Complications
- In 2 controlled clinical trials in patients with chronic hepatitis C and thrombocytopenia, 3% (31/955) treated with Eltrombopag olamine experienced a thrombotic event compared with 1% (5/484) on placebo. The majority of events were of the portal venous system (1% in patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine versus less than 1% for placebo).
- Thrombotic/thromboembolic complications may result from increases in platelet counts with Eltrombopag olamine. Reported thrombotic/thromboembolic complications included both venous and arterial events and were observed at low and at normal platelet counts.
- Consider the potential for an increased risk of thromboembolism when administering Eltrombopag olamine to patients with known risk factors for thromboembolism (e.g., Factor V Leiden, ATIII deficiency, antiphospholipid syndrome, chronic liver disease). To minimize the risk for thrombotic/thromboembolic complications, do not use Eltrombopag olamine in an attempt to normalize platelet counts. Follow the dose adjustment guidelines to achieve and maintain target platelet counts .
- In a controlled trial in non-ITP thrombocytopenic patients with chronic liver disease undergoing elective invasive procedures (N = 292), the risk of thrombotic events was increased in patients treated with 75 mg of Eltrombopag olamine once daily. Seven thrombotic complications (six patients) were reported in the group that received Eltrombopag olamine and three thrombotic complications were reported in the placebo group (two patients). All of the thrombotic complications reported in the group that received Eltrombopag olamine were portal vein thrombosis (PVT). Symptoms of PVT included abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Five of the six patients in the group that received Eltrombopag olamine experienced a thrombotic complication within 30 days of completing treatment with Eltrombopag olamine and at a platelet count above 200 x 109/L. The risk of portal venous thrombosis was increased in thrombocytopenic patients with chronic liver disease treated with 75 mg of Eltrombopag olamine once daily for 2 weeks in preparation for invasive procedures.
Cataracts
- In the 3 controlled clinical trials in chronic ITP, cataracts developed or worsened in 15 (7%) patients who received 50 mg of Eltrombopag olamine daily and 8 (7%) placebo-group patients. In the extension trial, cataracts developed or worsened in 4% of patients who underwent ocular examination prior to therapy with Eltrombopag olamine. In the 2 controlled clinical trials in patients with chronic hepatitis C and thrombocytopenia, cataracts developed or worsened in 8% patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine and 5% patients treated with placebo.
- Cataracts were observed in toxicology studies of eltrombopag in rodents . Perform a baseline ocular examination prior to administration of Eltrombopag olamine and, during therapy with Eltrombopag olamine, regularly monitor patients for signs and symptoms of cataracts.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- The following serious adverse reactions associated with Eltrombopag olamine are described in other sections.
- Hepatic Decompensation in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C
- Hepatotoxicity
- Thrombotic/Thromboembolic Complications
- Cataracts
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
- Chronic Immune (Idiopathic) Thrombocytopenia: In clinical trials, hemorrhage was the most common serious adverse reaction and most hemorrhagic reactions followed discontinuation of Eltrombopag olamine. Other serious adverse reactions included thrombotic/thromboembolic complications .
- The data described below reflect exposure of Eltrombopag olamine to 446 patients with chronic ITP aged 18 to 85, of whom 65% were female across the ITP clinical development program including 3 placebo-controlled trials. Eltrombopag olamine was administered to 277 patients for at least 6 months and 202 patients for at least 1 year.
- Table 4 presents the most common adverse drug reactions (experienced by greater than or equal to 3% of patients receiving Eltrombopag olamine) from the 3 placebo-controlled trials, with a higher incidence in Eltrombopag olamine versus placebo.
- In the 3 controlled clinical chronic ITP trials, alopecia, musculoskeletal pain, blood alkaline phosphatase increased, and dry mouth were the adverse reactions reported in 2% of patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine and in no patients who received placebo.
- Among 299 patients with chronic ITP who received Eltrombopag olamine in the single-arm extension trial, the adverse reactions occurred in a pattern similar to that seen in the placebo-controlled trials. Table 5 presents the most common treatment-related adverse reactions (experienced by greater than or equal to 3% of patients receiving Eltrombopag olamine) from the extension trial.
- In the 3 controlled chronic ITP trials, serum liver test abnormalities (predominantly Grade 2 or less in severity) were reported in 11% and 7% of patients for Eltrombopag olamine and placebo, respectively. Four patients (1%) treated with Eltrombopag olamine and three patients in the placebo group (2%) discontinued treatment due to hepatobiliary laboratory abnormalities. Seven of the patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine in the controlled trials with hepatobiliary laboratory abnormalities were re-exposed to Eltrombopag olamine in the extension trial. Six of these patients again experienced liver test abnormalities (predominantly Grade 1) resulting in discontinuation of Eltrombopag olamine in one patient. In the extension chronic ITP trial, one additional patient had Eltrombopag olamine discontinued due to liver test abnormalities (less than or equal to Grade 3).
- In a placebo-controlled trial of Eltrombopag olamine in non-ITP thrombocytopenic patients with chronic liver disease, six patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine and one patient in the placebo group developed portal vein thromboses.
- Chronic Hepatitis C-associated Thrombocytopenia: In the 2 placebo-controlled trials, 955 patients with chronic hepatitis C-associated thrombocytopenia received Eltrombopag olamine. Table 6 presents the most common adverse drug reactions (experienced by greater than or equal to 10% of patients receiving Eltrombopag olamine compared with placebo).
- Severe Aplastic Anemia: In the single-arm, open-label trial, 43 patients with severe aplastic anemia received Eltrombopag olamine. Eleven patients (26%) were treated for greater than 6 months and 7 patients (16%) were treated for greater than 1 year. The most common adverse reactions (greater than or equal to 20%) were nausea, fatigue, cough, diarrhea, and headache.
Postmarketing Experience
- There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Eltrombopag in the drug label.
- The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of Eltrombopag olamine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size it is not always possible to reliably estimate the frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Vascular Disorders: Thrombotic microangiopathy with acute renal failure.
Drug Interactions
- n vitro, CYP1A2, CYP2C8, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT)1A1 and UGT1A3 are involved in the metabolism of eltrombopag. In vitro, eltrombopag inhibits the following metabolic or transporter systems: CYP2C8, CYP2C9, UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A4, UGT1A6, UGT1A9, UGT2B7, UGT2B15, OATP1B1 and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Polyvalent Cations (Chelation)
- Eltrombopag chelates polyvalent cations (such as iron, calcium, aluminum, magnesium, selenium, and zinc) in foods, mineral supplements, and antacids. In a clinical trial, administration of Eltrombopag olamine with a polyvalent cation-containing antacid decreased plasma eltrombopag systemic exposure by approximately 70%.
- Eltrombopag olamine must not be taken within 4 hours of any medications or products containing polyvalent cations such as antacids, dairy products, and mineral supplements to avoid significant reduction in absorption of Eltrombopag olamine due to chelation
Transporters
- Coadministration of Eltrombopag olamine with the OATP1B1 and BCRP substrate, rosuvastatin, to healthy adult subjects increased plasma rosuvastatin AUC0-∞ by 55% and Cmax by 103%
- Use caution when concomitantly administering Eltrombopag olamine and drugs that are substrates of OATP1B1 (e.g., atorvastatin, bosentan, ezetimibe, fluvastatin, glyburide, olmesartan, pitavastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin, repaglinide, rifampin, simvastatin acid, SN-38 [active metabolite of irinotecan], valsartan) or BCRP (e.g., imatinib, irinotecan, lapatinib, methotrexate, mitoxantrone, rosuvastatin, sulfasalazine, topotecan). Monitor patients closely for signs and symptoms of excessive exposure to the drugs that are substrates of OATP1B1 or BCRP and consider reduction of the dose of these drugs, if appropriate. In clinical trials with Eltrombopag olamine, a dose reduction of rosuvastatin by 50% was recommended.
Protease Inhibitors
- HIV Protease Inhibitors: In a drug interaction trial, coadministration of Eltrombopag olamine with lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/RTV) decreased plasma eltrombopag exposure by 17% adjustment is recommended when Eltrombopag olamine is coadministered with LPV/RTV. Drug interactions with other HIV protease inhibitors have not been evaluated.
- Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Protease Inhibitors: Coadministration of Eltrombopag olamine with either boceprevir or telaprevir did not affect eltrombopag or protease inhibitor exposure significantly . No dose adjustments are recommended. Drug interactions with other HCV protease inhibitors have not been evaluated.
Peginterferon Alfa 2a/b Therapy
- Coadministration of peginterferon alfa 2a (PEGASYS®) or 2b (PEGINTRON®) did not affect eltrombopag exposure in 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials with adult patients with chronic hepatitis C
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category C
- There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of eltrombopag use in pregnancy. In animal reproduction and developmental toxicity studies, there was evidence of embryolethality and reduced fetal weights at maternally toxic doses. Eltrombopag olamine should be used in pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the mother justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
- In an early embryonic development study, female rats received oral eltrombopag at doses of 10, 20, or 60 mg/kg/day (0.8, 2, and 6 times, respectively, the human clinical exposure based on AUC in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and 0.3, 1, and 3 times, respectively, the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day). Increased pre- and post-implantation loss and reduced fetal weight were observed at the highest dose which also caused maternal toxicity.
- Eltrombopag was administered orally to pregnant rats at 10, 20, or 60 mg/kg/day (0.8, 2, and 6 times, respectively, the human clinical exposure based on AUC in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and 0.3, 1, and 3 times, respectively, the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day). Decreased fetal weights (6% to 7%) and a slight increase in the presence of cervical ribs were observed at the highest dose which also caused maternal toxicity. However, no evidence of major structural malformations was observed.
- Pregnant rabbits were treated with oral eltrombopag doses of 30, 80, or 150 mg/kg/day (0.04, 0.3, and 0.5 times, respectively, the human clinical exposure based on AUC in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and 0.02, 0.1, and 0.3 times, respectively, the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day). No evidence of fetotoxicity, embryolethality, or teratogenicity was observed.
- In a pre- and post-natal developmental toxicity study in pregnant rats (F0), no adverse effects on maternal reproductive function or on the development of the offspring (F1) were observed at doses up to 20 mg/kg/day (2 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and similar to the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day). Eltrombopag was detected in the plasma of offspring (F1). The plasma concentrations in pups increased with dose following administration of drug to the F0 dams.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Eltrombopag in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Eltrombopag during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether eltrombopag is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Eltrombopag olamine, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue Eltrombopag olamine taking into account the importance of Eltrombopag olamine to the mother.
Pediatric Use
- The safety and efficacy of Eltrombopag olamine in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatic Use
- Of the 106 patients in 2 randomized clinical trials of Eltrombopag olamine 50 mg in chronic ITP, 22% were 65 years of age and over, while 9% were 75 years of age and over. In the 2 randomized clinical trials of Eltrombopag olamine in patients with chronic hepatitis C and thrombocytopenia, 7% were 65 years of age and over, while fewer than 1% were 75 years of age and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients in the placebo-controlled trials, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eltrombopag with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
- Patients of East Asian ethnicity (i.e., Japanese, Chinese, Taiwanese, and Korean) exhibit higher eltrombopag exposures. A reduction in the initial dose of Eltrombopag olamine is recommended for ITP or severe aplastic anemia patients of East Asian ancestry and patients of East Asian ancestry with hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, B, C) [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.3)]. No dose reduction is needed in patients of East Asian ethnicity with chronic hepatitis C
Renal Impairment
- No adjustment in the initial dose of Eltrombopag olamine is needed for patients with renal impairment . Closely monitor patients with impaired renal function when administering Eltrombopag olamine.
Hepatic Impairment
- Hepatic impairment influences the exposure of Eltrombopag olamine .Reduce the initial dose of Eltrombopag olamine in patients with chronic ITP or severe aplastic anemia who also have hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, B, C) . No dosage adjustment is necessary for HCV patients with hepatic impairment
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eltrombopag in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Eltrombopag in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Eltrombopag in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Eltrombopag in the drug label.
Overdosage
- In the event of overdose, platelet counts may increase excessively and result in thrombotic/thromboembolic complications.
- In one report, a subject who ingested 5,000 mg of Eltrombopag olamine had a platelet count increase to a maximum of 929 x 109/L at 13 days following the ingestion. The patient also experienced rash, bradycardia, ALT/AST elevations, and fatigue. The patient was treated with gastric lavage, oral lactulose, intravenous fluids, omeprazole, atropine, furosemide, calcium, dexamethasone, and plasmapheresis; however, the abnormal platelet count and liver test abnormalities persisted for 3 weeks. After 2 months follow-up, all events had resolved without sequelae.
- In case of an overdose, consider oral administration of a metal cation-containing preparation, such as calcium, aluminum, or magnesium preparations to chelate eltrombopag and thus limit absorption. Closely monitor platelet counts. Reinitiate treatment with Eltrombopag olamine in accordance with dosing and administration recommendations
Pharmacology
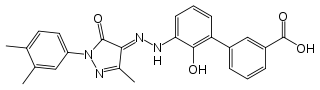
| |
Eltrombopag
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| 3'-{(2Z)-2-[1-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-3-methyl-5-oxo-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazol-4-ylidene]hydrazino}-2'-hydroxy-3-biphenylcarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 496775-62-3 (olamine) |
| ATC code | B02 |
| PubChem | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 442.467 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Licence data |
|
| Pregnancy cat. | |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | Oral |
Mechanism of Action
- Eltrombopag is an orally bioavailable, small-molecule TPO-receptor agonist that interacts with the transmembrane domain of the human TPO-receptor and initiates signaling cascades that induce proliferation and differentiation from bone marrow progenitor cells.
Structure
- Eltrombopag olamine (eltrombopag) tablets contain eltrombopag olamine, a small molecule thrombopoietin (TPO) receptor agonist for oral administration. Eltrombopag interacts with the transmembrane domain of the TPO receptor (also known as cMpl) leading to increased platelet production. Each tablet contains eltrombopag olamine in the amount equivalent to 12.5 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, or 100 mg of eltrombopag free acid.
Eltrombopag olamine is a biphenyl hydrazone. The chemical name for eltrombopag olamine is 3'-{(2Z)-2-[1-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-3-methyl-5-oxo-1,5-dihydro-4H-pyrazol-4-ylidene]hydrazino}-2'-hydroxy-3-biphenylcarboxylic acid - 2-aminoethanol (1:2). It has the molecular formula C25H22N4O4●2(C2H7NO). The molecular weight is 564.65 for eltrombopag olamine and 442.5 for eltrombopag free acid. Eltrombopag olamine has the following structural formula:
- Eltrombopag olamine is practically insoluble in aqueous buffer across a pH range of 1 to 7.4, and is sparingly soluble in water.
- The inactive ingredients of Eltrombopag olamine are: Tablet Core: magnesium stearate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, and sodium starch glycolate. Coating: hypromellose (12.5-mg, 25-mg, 50-mg, and 75-mg tablets) or polyvinyl alcohol and talc (100-mg tablet), polyethylene glycol 400, titanium dioxide, polysorbate 80 (12.5-mg tablet), FD&C Yellow No. 6 aluminum lake (25-mg tablet), FD&C Blue No. 2 aluminum lake (50-mg tablet), Iron Oxide Red and Iron Oxide Black (75-mg tablet), or Iron Oxide Yellow and Iron Oxide Black (100-mg tablet).
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Eltrombopag in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Eltrombopag is absorbed with a peak concentration occurring 2 to 6 hours after oral administration. Based on urinary excretion and biotransformation products eliminated in feces, the oral absorption of drug-related material following administration of a single 75-mg solution dose was estimated to be at least 52%.
- An open-label, randomized, crossover trial was conducted to assess the effect of food on the bioavailability of eltrombopag. A standard high-fat breakfast significantly decreased plasma eltrombopag AUC0-∞ by approximately 59% and Cmax by 65% and delayed Tmax by 1 hour. The calcium content of this meal may have also contributed to this decrease in exposure.
- Distribution: The concentration of eltrombopag in blood cells is approximately 50% to 79% of plasma concentrations based on a radiolabel study. In vitro studies suggest that eltrombopag is highly bound to human plasma proteins (greater than 99%). Eltrombopag is a substrate of BCRP, but is not a substrate for P-glycoprotein (P-gp) or OATP1B1.
- Metabolism: Absorbed eltrombopag is extensively metabolized, predominantly through pathways including cleavage, oxidation, and conjugation with glucuronic acid, glutathione, or cysteine. In vitrostudies suggest that CYP1A2 and CYP2C8 are responsible for the oxidative metabolism of eltrombopag. UGT1A1 and UGT1A3 are responsible for the glucuronidation of eltrombopag.
- Elimination: The predominant route of eltrombopag excretion is via feces (59%), and 31% of the dose is found in the urine. Unchanged eltrombopag in feces accounts for approximately 20% of the dose; unchanged eltrombopag is not detectable in urine. The plasma elimination half-life of eltrombopag is approximately 21 to 32 hours in healthy subjects and 26 to 35 hours in ITP patients.
- Drug Interactions: Polyvalent Cation-containing Antacids: In a clinical trial, coadministration of 75 mg of Eltrombopag olamine with a polyvalent cation-containing antacid (1,524 mg aluminum hydroxide, 1,425 mg magnesium carbonate, and sodium alginate) to 26 healthy adult subjects decreased plasma eltrombopag AUC0-∞ and Cmax by approximately 70%. The contribution of sodium alginate to this interaction is not known.
- Cytochrome P450 Enzymes (CYPs): In a clinical trial, Eltrombopag olamine 75 mg once daily was administered for 7 days to 24 healthy male subjects did not show inhibition or induction of the metabolism of a combination of probe substrates for CYP1A2 (caffeine), CYP2C19 (omeprazole), CYP2C9 (flurbiprofen), or CYP3A4 (midazolam) in humans. Probe substrates for CYP2C8 were not evaluated in this trial.
- Rosuvastatin: In a clinical trial, coadministration of 75 mg of Eltrombopag olamine once daily for 5 days with a single 10-mg dose of the OATP1B1 and BCRP substrate, rosuvastatin to 39 healthy adult subjects increased plasma rosuvastatin AUC0-∞ by 55% and Cmax by 103%.
- Protease Inhibitors: HIV Protease Inhibitors: In a clinical trial, coadministration of repeat-dose lopinavir 400 mg/ritonavir 100 mg twice daily with a single dose of Eltrombopag olamine 100 mg to 40 healthy adult subjects decreased plasma eltrombopag AUC0-∞ by 17%.
- HCV Protease Inhibitors: In a clinical trial, coadministration of repeat-dose telaprevir 750 mg every 8 hours or boceprevir 800 mg every 8 hours with a single dose of Eltrombopag olamine 200 mg to healthy adult subjects did not alter plasma telaprevir, boceprevir, or eltrombopag AUC0-∞ or Cmax to a significant extent.
- Pegylated Interferon alfa-2a + Ribavirin and Pegylated Interferon alfa-2b + Ribavirin: The pharmacokinetics of eltrombopag in both the presence and absence of pegylated interferon alfa 2a and 2b therapy were evaluated using a population pharmacokinetic analysis in 635 patients with chronic hepatitis C. The population PK model estimates of clearance indicate no significant difference in eltrombopag clearance in the presence of pegylated interferon alfa plus ribavirin therapy.
- In vitro Studies: Eltrombopag is an inhibitor of CYP2C8 and CYP2C9 in vitro. Eltrombopag is an inhibitor of UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A4, UGT1A6, UGT1A9, UGT2B7, and UGT2B15 in vitro. Eltrombopag is an inhibitor of the organic anion transporting polypeptide OATP1B1 and BCRP in vitro.
- Specific Populations: Ethnicity: Based on two population PK analyses of eltrombopag concentrations in ITP and chronic hepatitis C patients, East Asian (i.e., Japanese, Chinese, Taiwanese, and Korean) subjects exhibited 50% to 55% higher eltrombopag plasma concentrations compared with non-East Asian subjects .
- An approximately 40% higher systemic eltrombopag exposure in healthy African-American subjects was noted in at least one clinical pharmacology trial. The effect of African-American ethnicity on exposure and related safety and efficacy of eltrombopag has not been established.
- Hepatic Impairment: In a pharmacokinetic trial, the disposition of a single 50-mg dose of Eltrombopag olamine in patients with mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment was compared with subjects with normal hepatic function. The degree of hepatic impairment was based on Child-Pugh score. Plasma eltrombopag AUC0-∞ was 41% higher in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A) compared with subjects with normal hepatic function. Plasma eltrombopag AUC0-∞ was approximately 2-fold higher in patients with moderate (Child-Pugh Class B) and severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C). The half-life of eltrombopag was prolonged 2-fold in these patients. This clinical trial did not evaluate protein binding effects.
- Chronic Liver Disease: A population PK analysis in thrombocytopenic patients with chronic liver disease following repeat doses of eltrombopag demonstrated that mild hepatic impairment resulted in an 87% to 110% higher plasma eltrombopag AUC(0-τ) and patients with moderate hepatic impairment had approximately 141% to 240% higher plasma eltrombopag AUC(0-τ) values compared with patients with normal hepatic function. The half-life of eltrombopag was prolonged 3-fold in patients with mild hepatic impairment and 4-fold in patients with moderate hepatic impairment. This clinical trial did not evaluate protein binding effects.
- Chronic Hepatitis C: A population PK in 28 healthy adults and 635 patients with chronic hepatitis C demonstrated that patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with Eltrombopag olamine had higher plasma AUC(0-τ) values as compared with healthy subjects, and AUC(0-τ) increased with increasing Child-Pugh score. Patients with chronic hepatitis C and mild hepatic impairment had approximately 100% to 144% higher plasma AUC(0-τ) compared with healthy subjects. This clinical trial did not evaluate protein binding effects.
- Renal Impairment: The disposition of a single 50-mg dose of Eltrombopag olamine in patients with mild (creatinine clearance [CrCl] of 50 to 80 mL/min), moderate (CrCl of 30 to 49 mL/min), and severe (CrCl less than 30 mL/min) renal impairment was compared with subjects with normal renal function. Average total plasma eltrombopag AUC0-∞ was 32% to 36% lower in subjects with mild to moderate renal impairment and 60% lower in subjects with severe renal impairment compared with healthy subjects. The effect of renal impairment on unbound (active) eltrombopag exposure has not been assessed.
Assessment of Risk of QT/QTc Prolongation
- There is no indication of a QT/QTc prolonging effect of Eltrombopag olamine at doses up to 150 mg daily for 5 days. The effects of Eltrombopag olamine at doses up to 150 mg daily for 5 days (supratherapeutic doses) on the QT/QTc interval was evaluated in a double-blind, randomized, placebo- and positive-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg, single oral dose) crossover trial in healthy adult subjects. Assay sensitivity was confirmed by significant QTc prolongation by moxifloxacin.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- Eltrombopag does not stimulate platelet production in rats, mice, or dogs because of unique TPO receptor specificity. Data from these animals do not fully model effects in humans.
- Eltrombopag was not carcinogenic in mice at doses up to 75 mg/kg/day or in rats at doses up to 40 mg/kg/day (exposures up to 4 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and 2 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day).
- Eltrombopag was not mutagenic or clastogenic in a bacterial mutation assay or in 2 in vivo assays in rats (micronucleus and unscheduled DNA synthesis, 10 times the human clinical exposure based on Cmax in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and 7 times the human clinical exposure based on Cmax in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day). In the in vitro mouse lymphoma assay, eltrombopag was marginally positive (less than 3-fold increase in mutation frequency).
- Eltrombopag did not affect female fertility in rats at doses up to 20 mg/kg/day (2 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and similar to the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day). Eltrombopag did not affect male fertility in rats at doses up to 40 mg/kg/day, the highest dose tested (3 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and 2 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day).
Animal Pharmacology and/or Toxicology
- Eltrombopag is phototoxic in vitro. There was no evidence of in vivo cutaneous or ocular phototoxicity in rodents.
- Treatment-related cataracts were detected in rodents in a dose- and time-dependent manner. At greater than or equal to 6 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and 3 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day, cataracts were observed in mice after 6 weeks and in rats after 28 weeks of dosing. At greater than or equal to 4 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and 2 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day, cataracts were observed in mice after 13 weeks and in rats after 39 weeks of dosing .
- Renal tubular toxicity was observed in studies up to 14 days in duration in mice and rats at exposures that were generally associated with morbidity and mortality. Tubular toxicity was also observed in a 2-year oral carcinogenicity study in mice at doses of 25, 75, and 150 mg/kg/day. The exposure at the lowest dose was 1.2 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in ITP patients at 75 mg/day and 0.6 times the human clinical exposure based on AUC in chronic hepatitis C patients at 100 mg/day. No similar effects were observed in mice after 13 weeks at exposures greater than those associated with renal changes in the 2-year study, suggesting that this effect is both dose- and time-dependent.
Clinical Studies
Chronic ITP
- The efficacy and safety of Eltrombopag olamine in adult patients with chronic ITP were evaluated in 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials and in an open-label extension trial.
- Trials 1 and 2: In trials 1 and 2, patients who had completed at least one prior ITP therapy and who had a platelet count less than 30 x 109/L were randomized to receive either Eltrombopag olamine or placebo daily for up to 6 weeks, followed by 6 weeks off therapy. During the trials, Eltrombopag olamine or placebo was discontinued if the platelet count exceeded 200 x 109/L. The primary efficacy endpoint was response rate, defined as a shift from a baseline platelet count of less than 30 x 109/L to greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L at any time during the treatment period.
- The median age of the patients was 50 years and 60% were female. Approximately 70% of the patients had received at least 2 prior ITP therapies (predominantly corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, rituximab, cytotoxic therapies, danazol, and azathioprine) and 40% of the patients had undergone splenectomy. The median baseline platelet counts (approximately 18 x 109/L) were similar among all treatment groups.
- Trial 1 randomized 114 patients (2:1) to Eltrombopag olamine 50 mg or placebo. Trial 2 randomized 117 patients (1:1:1:1) among placebo or 1 of 3 dose regimens of Eltrombopag olamine, 30 mg, 50 mg, or 75 mg each administered daily.
- Table 8 shows for each trial the primary efficacy outcomes for the placebo groups and the patient groups who received the 50-mg daily regimen of Eltrombopag olamine.
- The platelet count response to Eltrombopag olamine was similar among patients who had or had not undergone splenectomy. In general, increases in platelet counts were detected 1 week following initiation of Eltrombopag olamine and the maximum response was observed after 2 weeks of therapy. In the placebo and 50-mg–dose groups of Eltrombopag olamine, the trial drug was discontinued due to an increase in platelet counts to greater than 200 x 109/L in 3% and 27% of the patients, respectively. The median duration of treatment with the 50-mg dose of Eltrombopag olamine was 42 days in Trial 1 and 43 days in Trial 2.
- Of 7 patients who underwent hemostatic challenges, additional ITP medications were required in 3 of 3 placebo group patients and 0 of 4 patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine. Surgical procedures accounted for most of the hemostatic challenges. Hemorrhage requiring transfusion occurred in one placebo group patient and no patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine.
- Trial 3: In this trial, 197 patients were randomized (2:1) to receive either Eltrombopag olamine 50 mg once daily (n = 135) or placebo (n = 62) for 6 months, during which time the dose of Eltrombopag olamine could be adjusted based on individual platelet counts. Patients were allowed to taper or discontinue concomitant ITP medications after being treated with Eltrombopag olamine for 6 weeks. Patients were permitted to receive rescue treatments at any time during the trial as clinically indicated. The primary endpoint was the odds of achieving a platelet count greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L and less than or equal to 400 x 109/L for patients receiving Eltrombopag olamine relative to placebo and was based on patient response profiles throughout the 6-month treatment period.
- The median age of the patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine and placebo was 47 years and 52.5 years, respectively. Approximately half of the patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine and placebo (47% and 50%, respectively) were receiving concomitant ITP medication (predominantly corticosteroids) at randomization and had baseline platelet counts less than or equal to15 x 109/L (50% and 48%, respectively). A similar percentage of patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine and placebo (37% and 34%, respectively) had a prior splenectomy.
- In 134 patients who completed 26 weeks of treatment, a sustained platelet response (platelet count greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L and less than or equal to 400 x 109/L for 6 out of the last 8 weeks of the 26-week treatment period in the absence of rescue medication at any time) was achieved by 60% of patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine, compared with 10% of patients treated with placebo (splenectomized patients: Eltrombopag olamine 51%, placebo 8%; non-splenectomized patients: Eltrombopag olamine 66%, placebo 11%). The proportion of responders in the group of patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine was between 37% and 56% compared with 7% and 19% in the placebo treatment group for all on-therapy visits. Patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine were significantly more likely to achieve a platelet count between 50 x 109/L and 400 x 109/L during the entire 6-month treatment period compared with those patients treated with placebo.
- Outcomes of treatment are presented in Table 9 for all patients enrolled in the trial.
- Among 94 patients receiving other ITP therapy at baseline, 37 (59%) of 63 patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine and 10 (32%) of 31 patients in the placebo group discontinued concomitant therapy at some time during the trial.
- Extension Trial: Patients who completed any prior clinical trial with Eltrombopag olamine were enrolled in an open-label, single-arm trial in which attempts were made to decrease the dose or eliminate the need for any concomitant ITP medications. Eltrombopag olamine was administered to 299 patients; 249 completed 6 months, 210 patients completed 12 months, and 138 patients completed 24 months of therapy. The median baseline platelet count was 19 x 109/L prior to administration of Eltrombopag olamine.
Chronic Hepatitis C-associated Thrombocytopenia
- The efficacy and safety of Eltrombopag olamine for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in adult patients with chronic hepatitis C were evaluated in 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Trial 1 utilized peginterferon alfa-2a (PEGASYS®) plus ribavirin for antiviral treatment and Trial 2 utilized peginterferon alfa-2b (PEGINTRON®) plus ribavirin. In both trials, patients with a platelet count of less than 75 x 109/L were enrolled and stratified by platelet count, screening HCV RNA, and HCV genotype. Patients were excluded if they had evidence of decompensated liver disease with Child-Pugh score greater than 6 (class B and C), history of ascites, or hepatic encephalopathy. The median age of the patients in both trials was 52 years, 63% were male, and 74% were Caucasian. Sixty-nine percent of patients had HCV genotypes 1, 4, 6 with the remainder genotypes 2 and 3. Approximately 30% of patients had been previously treated with interferon and ribavirin. The majority of patients (90%) had bridging fibrosis and cirrhosis, as indicated by noninvasive testing. A similar proportion (95%) of patients in both treatment groups had Child-Pugh level A (score 5-6) at baseline. A similar proportion of patients (2%) in both treatment groups had baseline international normalized ratio (INR) greater than 1.7. Median baseline platelet counts (approximately 60 x 109/L) were similar in both treatment groups. The trials consisted of two phases – a pre-antiviral treatment phase and an antiviral treatment phase. In the pre-antiviral treatment phase, patients received open-label Eltrombopag olamine to increase the platelet count to a threshold of greater than or equal to 90 x 109/L for Trial 1 and greater than or equal to 100 x 109/L for Trial 2. Eltrombopag olamine was administered at an initial dose of 25 mg once daily for 2 weeks and increased in 25-mg increments over 2- to 3-week periods to achieve the optimal platelet count to initiate antiviral therapy. The maximal time patients could receive open-label Eltrombopag olamine was 9 weeks. If threshold platelet counts were achieved, patients were randomized (2:1) to the same dose of Eltrombopag olamine at the end of the pre-treatment phase or to placebo. Eltrombopag olamine was administered in combination with pegylated interferon and ribavirin per their respective prescribing information for up to 48 weeks.
- The primary efficacy endpoint for both trials was sustained virologic response (SVR) defined as the percentage of patients with undetectable HCV-RNA at 24 weeks after completion of antiviral treatment. The median time to achieve the target platelet count greater than or equal to 90 x 109/L was approximately 2 weeks. Ninety-five percent of patients were able to initiate antiviral therapy.
- In both trials, a significantly greater proportion of patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine achieved SVR (see Table 10). The improvement in the proportion of patients who achieved SVR was consistent across subgroups based on baseline platelet count (less than 50 x 109/L versus greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L). In patients with high baseline viral loads (greater than or equal to 800,000), the SVR rate was 18% (82/452) for Eltrombopag olamine versus 8% (20/239) for placebo.
- The majority of patients treated with Eltrombopag olamine (76%) maintained a platelet count greater than or equal to 50 x 109/L compared with 19% for placebo. A greater proportion of patients on Eltrombopag olamine did not require any antiviral dose reduction as compared with placebo (45% versus 27%).
Severe Aplastic Anemia
- Eltrombopag olamine was studied in a single-arm, single-center, open-label trial in 43 patients with severe aplastic anemia who had an insufficient response to at least one prior immunosuppressive therapy and who had a platelet count less than or equal to 30 x 109/L. Eltrombopag olamine was administered at an initial dose of 50 mg once daily for 2 weeks and increased over 2 week periods up to a maximum dose of 150 mg once daily. The primary endpoint was hematologic response assessed after 12 weeks of treatment with Eltrombopag olamine. Hematologic response was defined as meeting 1 or more of the following criteria: 1) platelet count increases to 20 x 109/L above baseline, or stable platelet counts with transfusion independence for a minimum of 8 weeks; 2) hemoglobin increase by greater than 1.5 g/dL, or a reduction in greater than or equal to 4 units of RBC transfusions for 8 consecutive weeks; 3) ANC increase of 100% or an ANC increase greater than 0.5 x 109/L. Eltrombopag olamine was discontinued after 16 weeks if no hematologic response was observed. Patients who responded continued therapy in an extension phase of the trial.
- The treated population had median age of 45 years (range 17 to 77 years) and 56% were male. At baseline, the median platelet count was 20 x 109/L, hemoglobin was 8.4 g/dL, ANC was 0.58 x 109/L and absolute reticulocyte count was 24.3 x109/L. Eighty-six percent of patients were RBC transfusion dependent and 91% were platelet transfusion dependent. The majority of patients (84%) received at least 2 prior immunosuppressive therapies. Three patients had cytogenetic abnormalities at baseline.
- Table 11 presents the primary efficacy results.
- In the 17 responders, the platelet transfusion-free period ranged from 8 to 1,096 days with a median of 200 days, and the RBC transfusion-free period ranged from 15 to 1,082 days with a median of 208 days.
- In the extension phase, 8 patients achieved a multi-lineage response; 4 of these patients subsequently tapered off treatment with Eltrombopag olamine and maintained the response(median follow up: 8.1 months, range: 7.2 to 10.6 months).
How Supplied
- The 12.5-mg tablets are round, biconvex, white, film-coated tablets debossed with GS MZ1 and 12.5 on one side and are available in bottles of 30: NDC 0007-4643-13.
- The 25-mg tablets are round, biconvex, orange, film-coated tablets debossed with GS NX3 and 25 on one side and are available in bottles of 30: NDC 0007-4640-13.
- The 50-mg tablets are round, biconvex, blue, film-coated tablets debossed with GS UFU and 50 on one side and are available in bottles of 30: NDC 0007-4641-13.
- The 75-mg tablets are round, biconvex, pink, film-coated tablets debossed with GS FFS and 75 on one side and are available in bottles of 30: NDC 0007-4642-13.
- The 100-mg tablets are round, biconvex, green, film-coated tablets debossed with GS 1L5 and are available in bottles of 30: NDC 0007-4646-13. This product contains a desiccant.
- Store at room temperature between 20°C and 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not remove desiccant if present. Dispense in original bottle.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Eltrombopag Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Eltrombopag |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Eltrombopag |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- Prior to treatment, patients should fully understand and be informed of the following risks and considerations for Eltrombopag olamine:
- For patients with chronic ITP, therapy with Eltrombopag olamine is administered to achieve and maintain a platelet count greater than or equal to 50 x 10 9/L as necessary to reduce the risk for bleeding.
- For patients with chronic hepatitis C, therapy with Eltrombopag olamine is administered to achieve and maintain a platelet count necessary to initiate and maintain antiviral therapy with pegylated interferon and ribavirin.
- Therapy with Eltrombopag olamine may be associated with hepatobiliary laboratory abnormalities.
- Advise patients with chronic hepatitis C and cirrhosis that they may be at risk for hepatic decompensation when receiving alfa interferon therapy.
- Advise patients that they should report any of the following signs and symptoms of liver problems to their healthcare provider right away.
- Advise patients that thrombocytopenia and risk of bleeding may reoccur upon discontinuing Eltrombopag olamine, particularly if Eltrombopag olamine is discontinued while the patient is on anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents.
- Advise patients that too much Eltrombopag olamine may result in excessive platelet counts and a risk for thrombotic/thromboembolic complications.
- Advise patients that during therapy with Eltrombopag olamine, they should continue to avoid situations or medications that may increase the risk for bleeding.
- Advise patients to have a baseline ocular examination prior to administration of Eltrombopag olamine and be monitored for signs and symptoms of cataracts during therapy.
- Advise patients to keep at least a 4-hour interval between Eltrombopag olamine and foods, mineral supplements, and antacids which contain polyvalent cations such as iron, calcium, aluminum, magnesium, selenium, and zinc.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Eltrombopag interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Eltrombopag olamine
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Eltrombopag Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Eltrombopag |Label Name=Eltrombopag12.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Eltrombopag |Label Name=Eltrombopag13.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Eltrombopag |Label Name=Eltrombopag14.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Eltrombopag |Label Name=Eltrombopag15.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Eltrombopag |Label Name=Eltrombopag16.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Eltrombopag |Label Name=Eltrombopag17.png
}}