Hypopharyngeal cancer CT: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Hypopharyngeal cancer}} | {{Hypopharyngeal cancer}} | ||
{{CMG}} {{AE}}{{Faizan}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{G.D.}}, {{Faizan}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Head and neck [[CT scan]] may be helpful in the diagnosis of hypopharyngeal cancer. Findings on CT scan suggestive of hypopharyngeal cancer include | [[Head]] and [[ neck]] [[CT scan]] may be helpful in the [[diagnosis]] of hypopharyngeal cancer. Findings on [[CT scan]] suggestive of hypopharyngeal cancer include [[soft]] [[tissue]] [[mass]], irregular [[thickening]] of [[mucosa]], and [[necrotic]] region which is a sign of [[ metastasis]]. | ||
==CT Scan== | ==CT Scan== | ||
Head and neck [[CT scan]] may be helpful in the diagnosis of hypopharyngeal cancer. Findings on CT scan suggestive of hypopharyngeal cancer include: | [[Head]] and [[neck]] [[CT scan]] may be helpful in the [[diagnosis]] of hypopharyngeal cancer. Findings on [[CT scan]] suggestive of hypopharyngeal cancer include:<ref name="pmid27487932">{{cite journal |vauthors=Tshering Vogel DW, Thoeny HC |title=Cross-sectional imaging in cancers of the head and neck: how we review and report |journal=Cancer Imaging |volume=16 |issue=1 |pages=20 |date=August 2016 |pmid=27487932 |pmc=4971750 |doi=10.1186/s40644-016-0075-3 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid27841124">{{cite journal |vauthors=Pracy P, Loughran S, Good J, Parmar S, Goranova R |title=Hypopharyngeal cancer: United Kingdom National Multidisciplinary Guidelines |journal=J Laryngol Otol |volume=130 |issue=S2 |pages=S104–S110 |date=May 2016 |pmid=27841124 |pmc=4873926 |doi=10.1017/S0022215116000529 |url=}}</ref> | ||
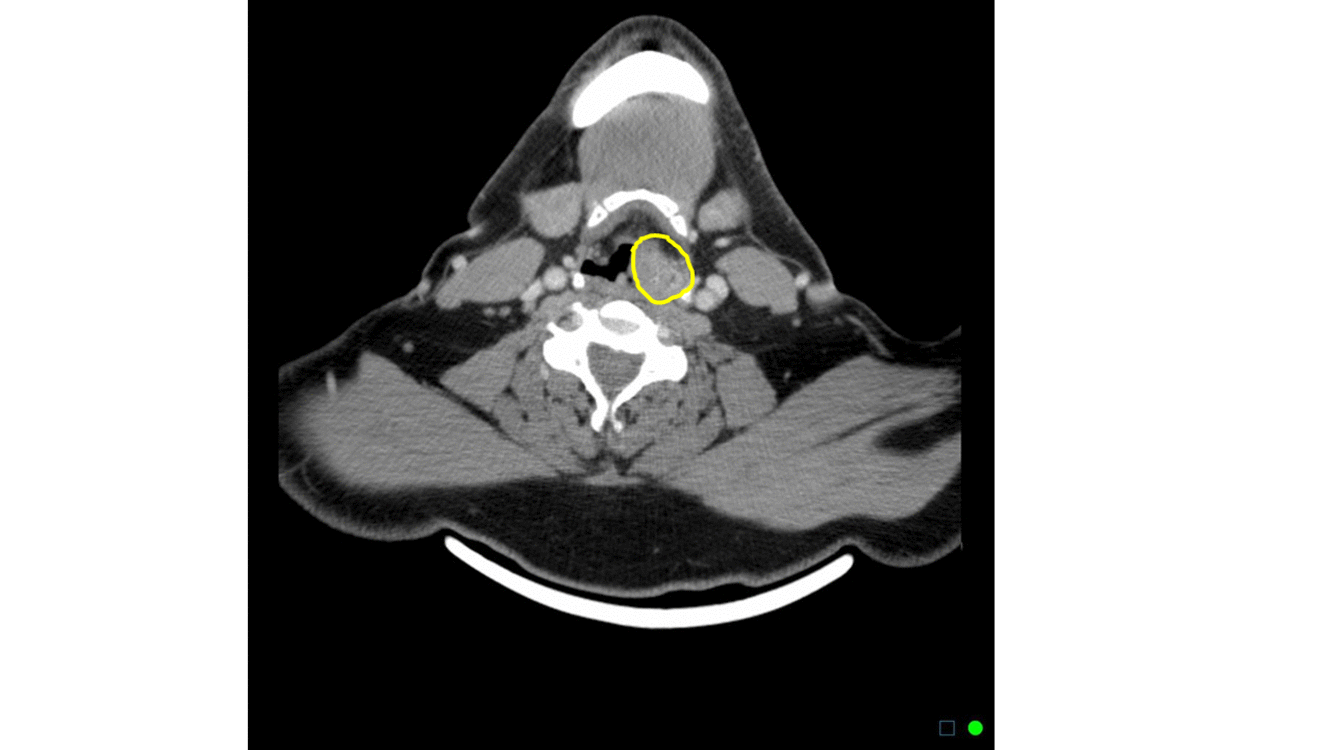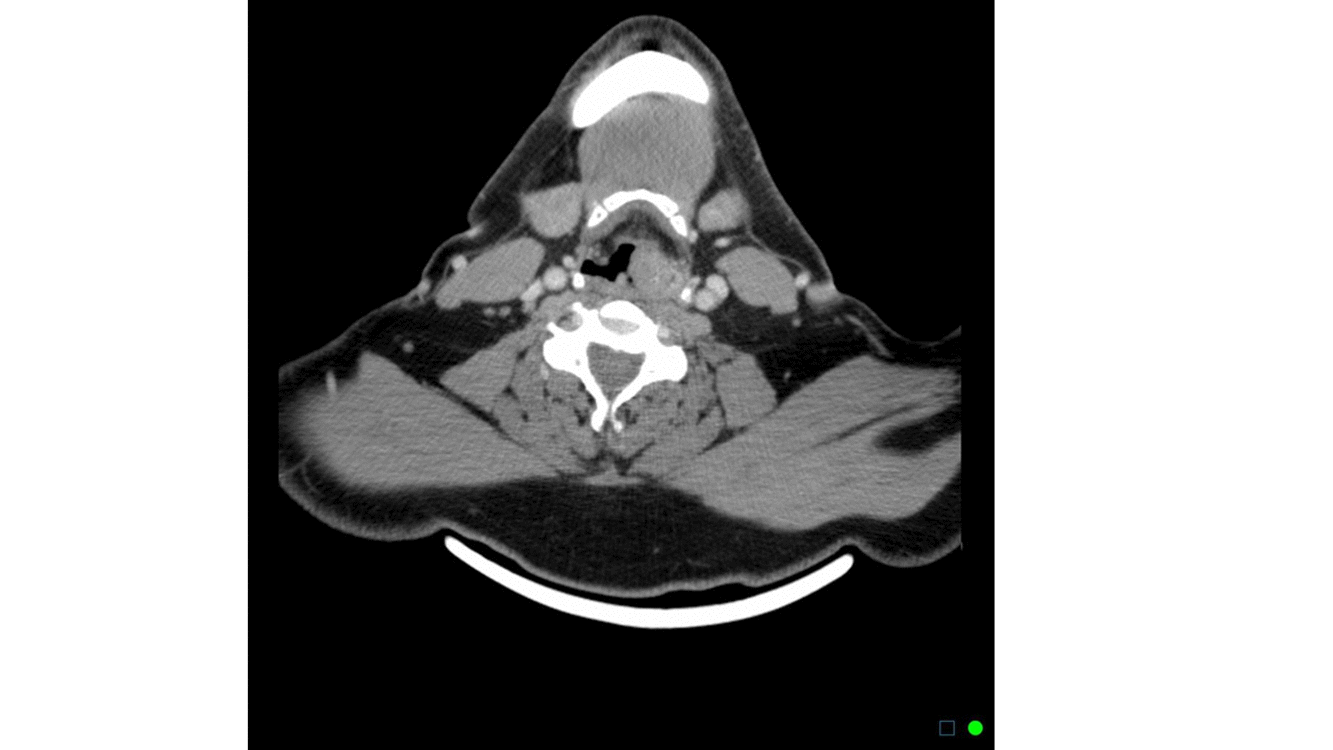
* | *[[Soft]] [[tissue]] [[mass]] | ||
* | *Irregular thickening of [[mucosa]] | ||
* | *[[Necrotic]] region which is a sign of [[metastasis]] | ||
[[File:CT scan of hypopharyngeal cancer.gif |thumb|300px|none|Hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma<ref>Case courtesy of Dr Frank Gaillard, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 8891. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/hypopharyngeal-squamous-cell-carcinoma</ref>]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
[[Category:Oncology]] | |||
[[Category:Medicine]] | |||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | |||
[[Category:Otolaryngology]] | |||
[[Category:Surgery]] | |||
[[Category:Radiology]] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:18, 12 February 2019
|
Hypopharyngeal cancer Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Hypopharyngeal cancer CT On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Hypopharyngeal cancer CT |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Hypopharyngeal cancer CT |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gertrude Djouka, M.D.[2], Faizan Sheraz, M.D. [3]
Overview
Head and neck CT scan may be helpful in the diagnosis of hypopharyngeal cancer. Findings on CT scan suggestive of hypopharyngeal cancer include soft tissue mass, irregular thickening of mucosa, and necrotic region which is a sign of metastasis.
CT Scan
Head and neck CT scan may be helpful in the diagnosis of hypopharyngeal cancer. Findings on CT scan suggestive of hypopharyngeal cancer include:[1][2]
References
- ↑ Tshering Vogel DW, Thoeny HC (August 2016). "Cross-sectional imaging in cancers of the head and neck: how we review and report". Cancer Imaging. 16 (1): 20. doi:10.1186/s40644-016-0075-3. PMC 4971750. PMID 27487932.
- ↑ Pracy P, Loughran S, Good J, Parmar S, Goranova R (May 2016). "Hypopharyngeal cancer: United Kingdom National Multidisciplinary Guidelines". J Laryngol Otol. 130 (S2): S104–S110. doi:10.1017/S0022215116000529. PMC 4873926. PMID 27841124.
- ↑ Case courtesy of Dr Frank Gaillard, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 8891. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/hypopharyngeal-squamous-cell-carcinoma