Renal corpuscle: Difference between revisions
Brian Blank (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
m Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{SIB}} +, -{{EH}} +, -{{EJ}} +, -{{Editor Help}} +, -{{Editor Join}} +) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{SI}} | {{SI}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
{{kidney}} | {{kidney}} | ||
[[Category:Urinary system]] | [[Category:Urinary system]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:38, 20 August 2012
|
WikiDoc Resources for Renal corpuscle |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Renal corpuscle Most cited articles on Renal corpuscle |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Renal corpuscle |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Renal corpuscle at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Renal corpuscle Clinical Trials on Renal corpuscle at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Renal corpuscle NICE Guidance on Renal corpuscle
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Renal corpuscle Discussion groups on Renal corpuscle Patient Handouts on Renal corpuscle Directions to Hospitals Treating Renal corpuscle Risk calculators and risk factors for Renal corpuscle
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Renal corpuscle |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Overview
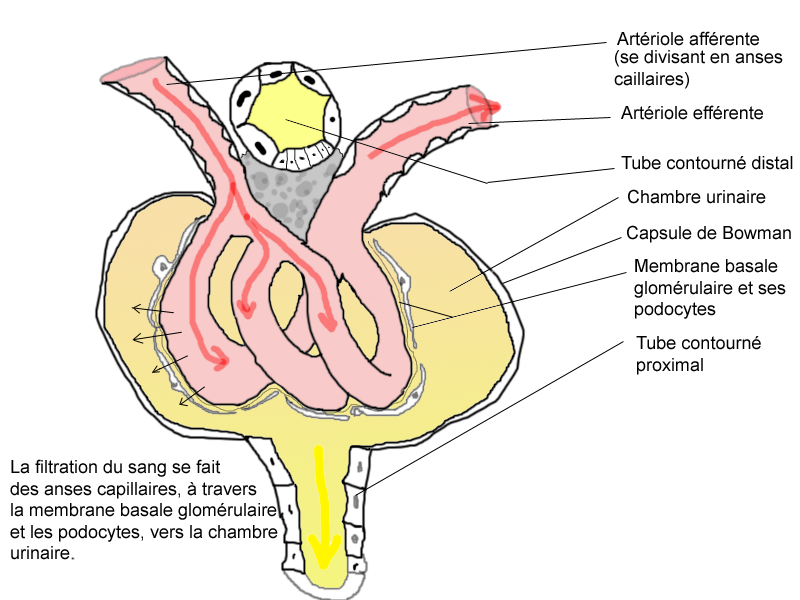
In the kidney, a renal corpuscle is the initial blood-filtering component of a nephron. It consists of two structures: a glomerulus and a Bowman's capsule. The glomerulus is a small tuft of capillaries containing two cell types. Endothelial cells, which have large fenestrae, are not covered by diaphragms. Mesangial cells are modified smooth muscle cells that lie between the capillaries and the glomerulus. They regulate blood flow by their contractile activity and secrete extracellular matrix, prostaglandins, and cytokines. Mesangial cells also have phagocytic activity, removing proteins and other molecules trapped in the glomerular basement membrane or filtration barrier. The Bowman's capsule has an outer parietal layer composed of simple squamous epithelium. The visceral layer, composed of modified simple squamous epithelium, is lined by podocytes. Podocytes have foot processes, pedicels, that wrap around glomerular capillaries. These pedicels interdigitate with pedicels of adjacent podocytes forming filtration slits.
The renal corpuscle filtration barrier is composed of: the fenestrated endothelium of glomerular capillaries, the fused basal lamina of endothelial cells and podocytes, and the filtration slits of the podocytes. This barrier permits passage of water, ions, and small molecules from the bloodstream into Bowman's space (the space between the visceral and parietal layers). Large and/or negatively charged proteins are prevented from passing into Bowman's space, thus retaining these proteins in the circulation. The basal lamina is composed of 3 layers: lamina rara externa, lamina densa, and lamina rara interna. The lamina rara externa is adjacent to the podocyte processes. The lamina densa is the central layer consisting of type IV collagen and laminin. This layer acts as a selective macromolecular filter, preventing the passage of large protein molecules into Bowman's space. The lamina rara intena is adjacent to endothelial cells. This layer contains heparan sulfate, a negatively charged glycosaminoglycan that contributes to the electrostatic barrier of the glomerular filter.
There are two poles in the renal corpuscle, a vascular pole, and a urinary pole. The vascular pole is where the afferent and efferent arterioles communicate with the glomerulus. The urinary pore is where the corpuscle opens into the lumen of the proximal convoluted tubule.
Fluid from blood in the glomerulus is collected in the Bowman's capsule to form "glomerular filtrate", which is then further processed along the nephron to form urine.
Eponym
A renal corpuscle is also known as a Malpighian corpuscle, named after Marcello Malpighi (1628-1694), an Italian physician and biologist. This name is not used widely anymore, probably to avoid confusion with a Malpighian corpuscle in the spleen.
Additional images
-
Glomerulus.
External links
- Template:EMedicineDictionary
- Histology image: 16003loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University