WBR0495: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
m (refreshing WBR questions) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{WBRQuestion | {{WBRQuestion | ||
|QuestionAuthor=William J Gibson | |QuestionAuthor=William J Gibson (Reviewed by Serge Korjian) | ||
|ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | ||
|MainCategory=Anatomy | |MainCategory=Anatomy | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|MainCategory=Anatomy | |MainCategory=Anatomy | ||
|SubCategory=Musculoskeletal/Rheumatology, Oncology, General Principles | |SubCategory=Musculoskeletal/Rheumatology, Oncology, General Principles | ||
|MainCategory=Anatomy | |||
|MainCategory=Anatomy | |MainCategory=Anatomy | ||
|MainCategory=Anatomy | |MainCategory=Anatomy | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
|MainCategory=Anatomy | |MainCategory=Anatomy | ||
|SubCategory=Musculoskeletal/Rheumatology, Oncology, General Principles | |SubCategory=Musculoskeletal/Rheumatology, Oncology, General Principles | ||
|Prompt=A 52 year old woman presents to her primary care physician after noticing a firm lump in her breast. She undergoes fine needle aspiration of the mass, which reveals a grade 3 invasive ductal carcinoma with overexpression of the HER2/Neu oncogene. | |Prompt=A 52-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician after noticing a firm lump in her right breast. She undergoes fine needle aspiration of the mass, which reveals a grade 3 invasive ductal carcinoma with overexpression of the HER2/Neu oncogene. Following surgical resection of the mass and axillary lymph node dissection, the patient undergoes breast reconstructive surgery. Two weeks after her surgery, she starts noticing a bony protrusion in her back everytime she lifts her right arm. Which of the following is the most likely origin of the injured nerve in this patient? | ||
|Explanation= | |Explanation=[[File:Brachial_plexus_long_thoracic_nerve.jpg|900px]] | ||
The patient in this vignette has suffered damage to the long thoracic nerve as a result of radical mastectomy. The long thoracic nerve arises from the nerve roots of C5-C7 to innervate the serratus anterior muscle. The serratus anterior normally serves to abduct the arm beyond 90 degrees to the body. Lesion of this nerve can lead to “winging” of the scapula. | |||
|AnswerA=C5-C6 | |AnswerA=C5-C6 | ||
|AnswerAExp= | |AnswerAExp=The C5-C6 nerve roots give rise to the axillary nerve and the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. These nerves are damaged in Erb’s palsy. | ||
|AnswerB=C5-C7 | |AnswerB=C5-C7 | ||
|AnswerBExp= | |AnswerBExp=The C5-C7 nerve roots give rise to the long thoracic nerve. The long thoracic nerve innervates the serratus anterior. | ||
|AnswerC=C8-T1 | |AnswerC=C8-T1 | ||
|AnswerCExp= | |AnswerCExp=The C8-T1 nerve roots give rise to the inferior trunk of the brachial plexus. These nerves are injured in Krumpke’s palsy. | ||
|AnswerD=Inferior trunk of the brachial plexus | |AnswerD=Inferior trunk of the brachial plexus | ||
|AnswerDExp=The inferior trunk of the brachial plexus is injured in Krumpke’s palsy. | |||
|AnswerDExp= | |||
|AnswerE=Posterior cord of the brachial plexus | |AnswerE=Posterior cord of the brachial plexus | ||
|AnswerEExp= | |AnswerEExp=The posterior cord of the brachial plexus gives rise to the axillary and radial nerves. | ||
|EducationalObjectives=Lesions of the long thoracic nerve, derived from the C5-C7 nerve roots, leads to winging of the scapula. | |||
|References=First Aid 2014 page 413 | |||
|RightAnswer=B | |RightAnswer=B | ||
|WBRKeyword=Breast, Nerve, Long thoracic nerve, Brachial, Brachial plexus, Arm, Paralysis, Serratus, Muscle, | |WBRKeyword=Breast, Nerve, Long thoracic nerve, Brachial, Brachial plexus, Arm, Paralysis, Serratus anterior, Muscle, | ||
|Approved=Yes | |Approved=Yes | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 00:45, 28 October 2020
| Author | PageAuthor::William J Gibson (Reviewed by Serge Korjian) |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Anatomy |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Musculoskeletal/Rheumatology, SubCategory::Oncology, SubCategory::General Principles |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 52-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician after noticing a firm lump in her right breast. She undergoes fine needle aspiration of the mass, which reveals a grade 3 invasive ductal carcinoma with overexpression of the HER2/Neu oncogene. Following surgical resection of the mass and axillary lymph node dissection, the patient undergoes breast reconstructive surgery. Two weeks after her surgery, she starts noticing a bony protrusion in her back everytime she lifts her right arm. Which of the following is the most likely origin of the injured nerve in this patient?]] |
| Answer A | AnswerA::C5-C6 |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp::The C5-C6 nerve roots give rise to the axillary nerve and the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. These nerves are damaged in Erb’s palsy. |
| Answer B | AnswerB::C5-C7 |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp::The C5-C7 nerve roots give rise to the long thoracic nerve. The long thoracic nerve innervates the serratus anterior. |
| Answer C | AnswerC::C8-T1 |
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp::The C8-T1 nerve roots give rise to the inferior trunk of the brachial plexus. These nerves are injured in Krumpke’s palsy. |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Inferior trunk of the brachial plexus |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp::The inferior trunk of the brachial plexus is injured in Krumpke’s palsy. |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Posterior cord of the brachial plexus |
| Answer E Explanation | AnswerEExp::The posterior cord of the brachial plexus gives rise to the axillary and radial nerves. |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::B |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::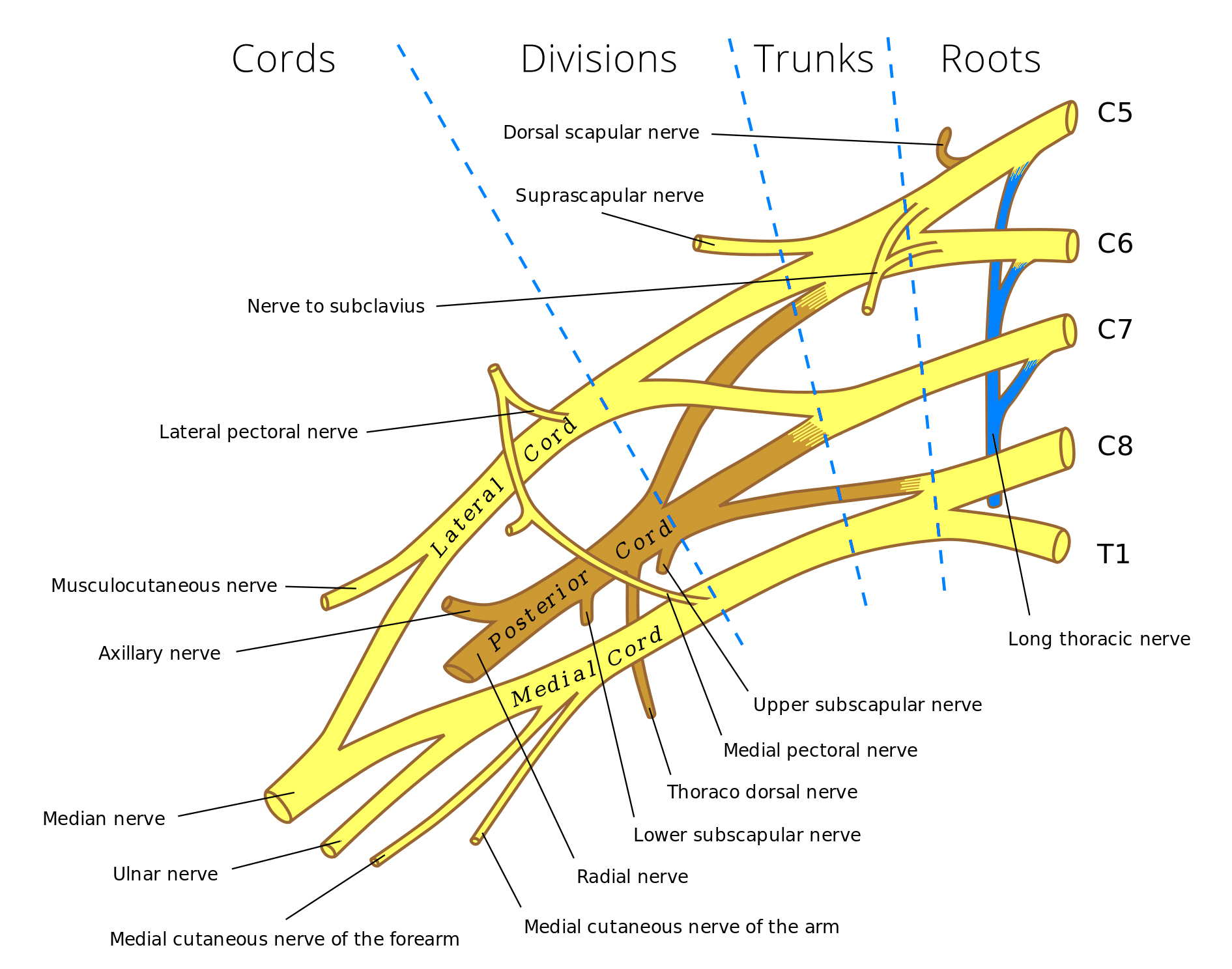
The patient in this vignette has suffered damage to the long thoracic nerve as a result of radical mastectomy. The long thoracic nerve arises from the nerve roots of C5-C7 to innervate the serratus anterior muscle. The serratus anterior normally serves to abduct the arm beyond 90 degrees to the body. Lesion of this nerve can lead to “winging” of the scapula. |
| Approved | Approved::Yes |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Breast, WBRKeyword::Nerve, WBRKeyword::Long thoracic nerve, WBRKeyword::Brachial, WBRKeyword::Brachial plexus, WBRKeyword::Arm, WBRKeyword::Paralysis, WBRKeyword::Serratus anterior, WBRKeyword::Muscle |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |