Hepatitis B vertical transmission: Difference between revisions
Category |
m Bot: Removing from Primary care |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
{{WH}} | |||
{{WS}} | |||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | [[Category:Gastroenterology]] | ||
[[Category:FinalQCRequired]] | [[Category:FinalQCRequired]] | ||
[[Category:Emergency mdicine]] | |||
[[Category:Disease]] | [[Category:Disease]] | ||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | [[Category:Up-To-Date]] | ||
[[Category:Infectious disease]] | [[Category:Infectious disease]] | ||
[[Category:Hepatology]] | [[Category:Hepatology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:05, 29 July 2020
|
Hepatitis B |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Hepatitis B vertical transmission On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Hepatitis B vertical transmission |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Hepatitis B vertical transmission |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sara Mehrsefat, M.D. [2]
Overview
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in a pregnant woman poses a serious risk to her infant at birth. Without postexposure immunoprophylaxis, approximately 40% of infants born to HBV-infected mothers in the United States will develop chronic HBV infection, approximately one-fourth of whom will eventually die from chronic liver disease.[1]
Hepatitis B vertical transmission
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in a pregnant woman poses a serious risk to her infant at birth. Without postexposure immunoprophylaxis, approximately 40% of infants born to HBV-infected mothers in the United States will develop chronic HBV infection, approximately one-fourth of whom will eventually die from chronic liver disease.[1]
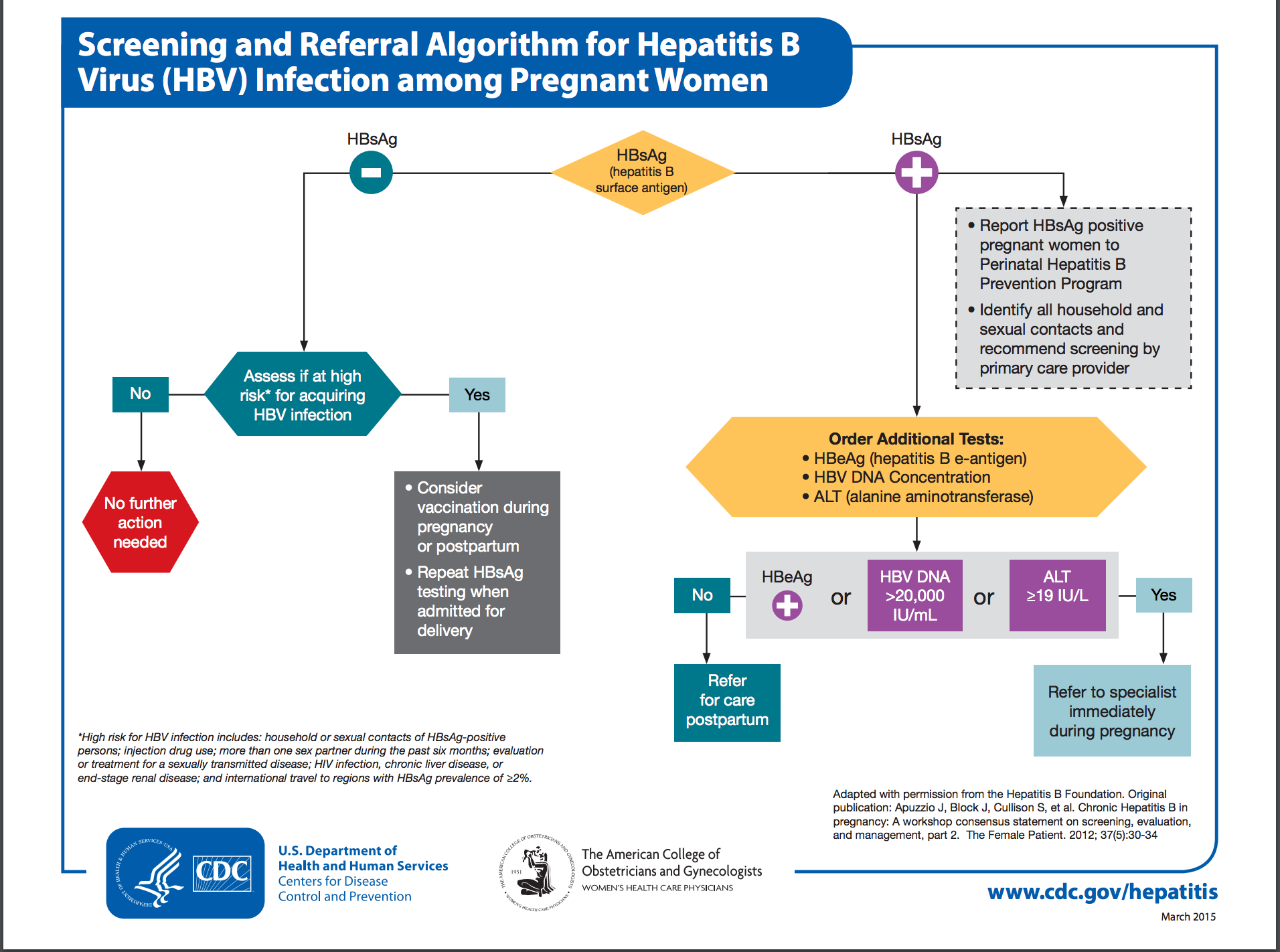
Perinatal HBV transmission can be prevented by identifying HBV-infected (i.e., hepatitis B surface antigen [HBsAg]-positive) pregnant women and providing hepatitis B immune globulin and hepatitis B vaccine to infants born to them within 12 hours of birth.
- Preventing perinatal HBV transmission is an integral part of the national strategy to eliminate hepatitis B in the United States. National guidelines call for the following:[1]
- Universal screening of pregnant women for HBsAg during each pregnancy
- Case management of HBsAg-positive mothers and their infants
- Provision of immunoprophylaxis for infants born to infected mothers, including hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin
- Routine vaccination of all infants with the hepatitis B vaccine series, with the first dose administered at birth
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Viral Hepatitis - Hepatitis B Information. Perinatal Transmission (2016) http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hbv/perinatalxmtn.htm Accessed on October 5th, 2016