WBR0570: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Educational objective: Poliomyelitis causes lesions in the anterior horn of the spinal cord. | Educational objective: Poliomyelitis causes lesions in the anterior horn of the spinal cord. | ||
Reference: WHO (http://www.who.int/topics/poliomyelitis/en/) | |||
|AnswerA=[[Image:Syringomyelia spinal cord.gif|300px]] | |AnswerA=[[Image:Syringomyelia spinal cord.gif|300px]] | ||
|AnswerAExp=This image illustrates a lesion in the central cord depicting [[syringomyelia]]. Poliomyelitis is not associated with lesions in the central cord. | |AnswerAExp=This image illustrates a lesion in the central cord depicting [[syringomyelia]]. Poliomyelitis is not associated with lesions in the central cord. | ||
Revision as of 03:21, 2 October 2013
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Rim Halaby, M.D. [1]]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Pathophysiology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Neurology |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A previously healthy 7-year-old boy is brought by his mother because he has been having worsening limping since two days. The mother reports that her child has been having fever, headache and vomiting for the last week. The child reports muscle pain in his legs and arms and he says, “ I feel my legs are heavy and I can not move them easily”. The mother informs you that the family has recently emigrated from Nigeria less than a month ago. Neurological physical exam reveals muscle weakness more pronounced in the legs than in the arms, absent reflexes in the legs bilaterally, in addition to fasciculation noted in the left thigh. The sensation and sense of vibration are intact in the upper and lower extremities. A neurological lesion in the spinal cord is suspected. Which of the below listed spinal cord images with lesions depicted in red represent the site of the neurological lesion of the child?]] |
| Answer A | [[AnswerA:: ]] ]]
|
| Answer A Explanation | [[AnswerAExp::This image illustrates a lesion in the central cord depicting syringomyelia. Poliomyelitis is not associated with lesions in the central cord.]] |
| Answer B | [[AnswerB:: ]] ]]
|
| Answer B Explanation | [[AnswerBExp::This image depicts asymmetric lesions in the white matter, which is characteristic of multiple sclerosis. Poliomyelitis is not associated with asymmetric lesions in the white matter.]] |
| Answer C | [[AnswerC::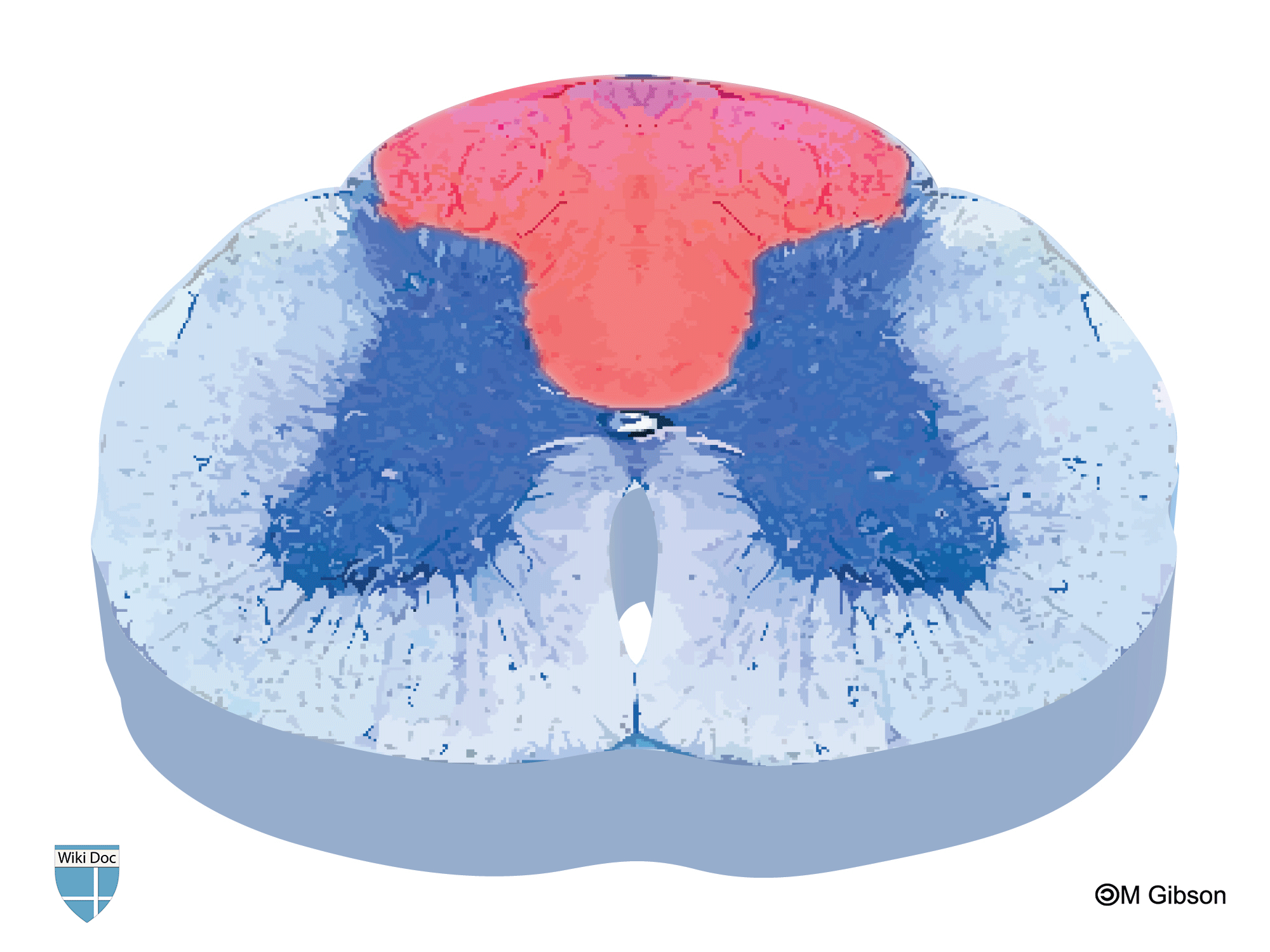 ]] ]]
|
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp::This image depicts lesions in the dorsal columns which may be found in vitamin B12 deficiency. Poliomyelitis is characterized by lesions in the anterior horn. |
| Answer D | [[AnswerD::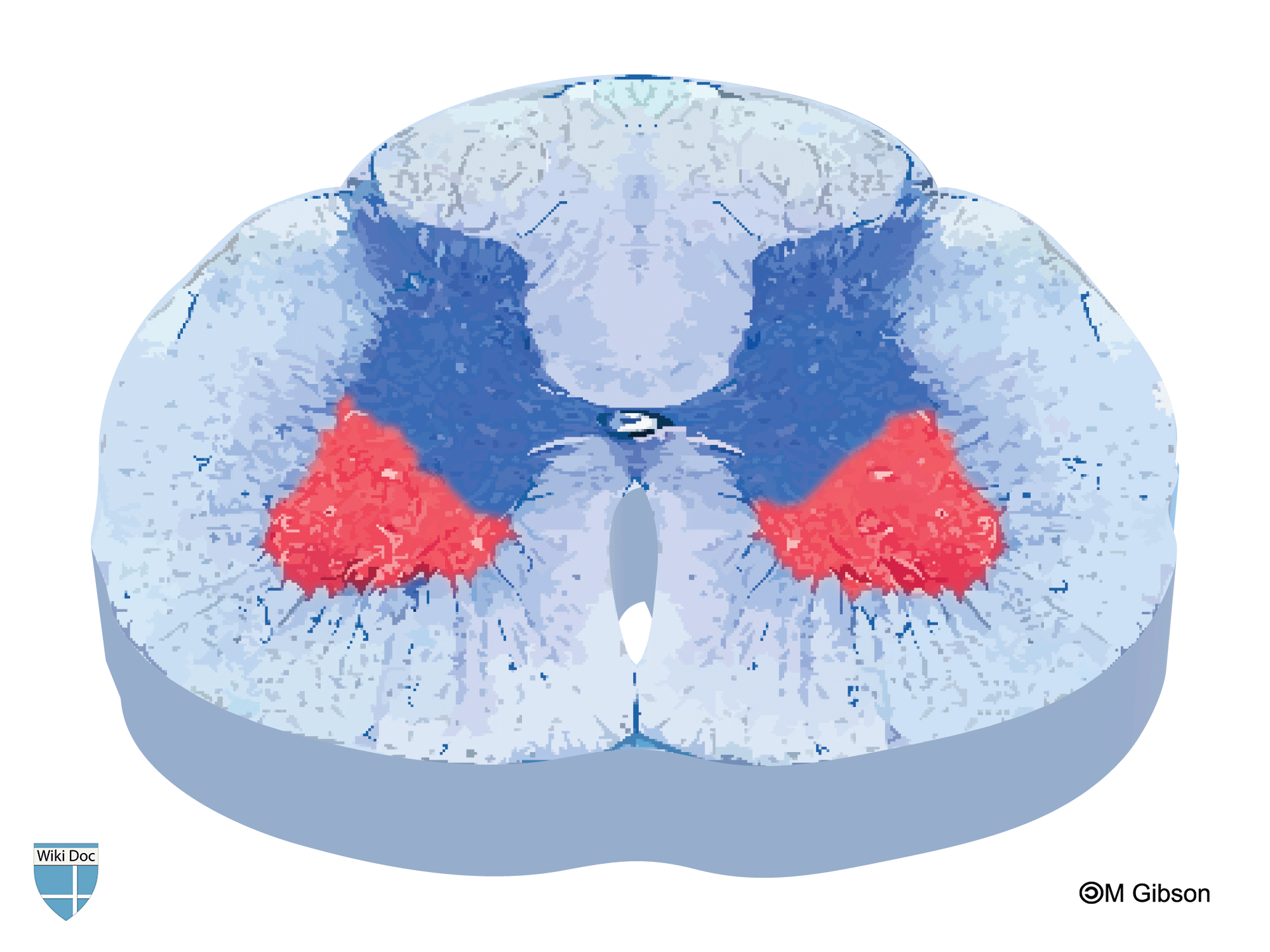 ]] ]]
|
| Answer D Explanation | [[AnswerDExp::This image depicts lesions in the anterior horn of the spinal cord which is characteristics of poliomyelitis.]] |
| Answer E | [[AnswerE::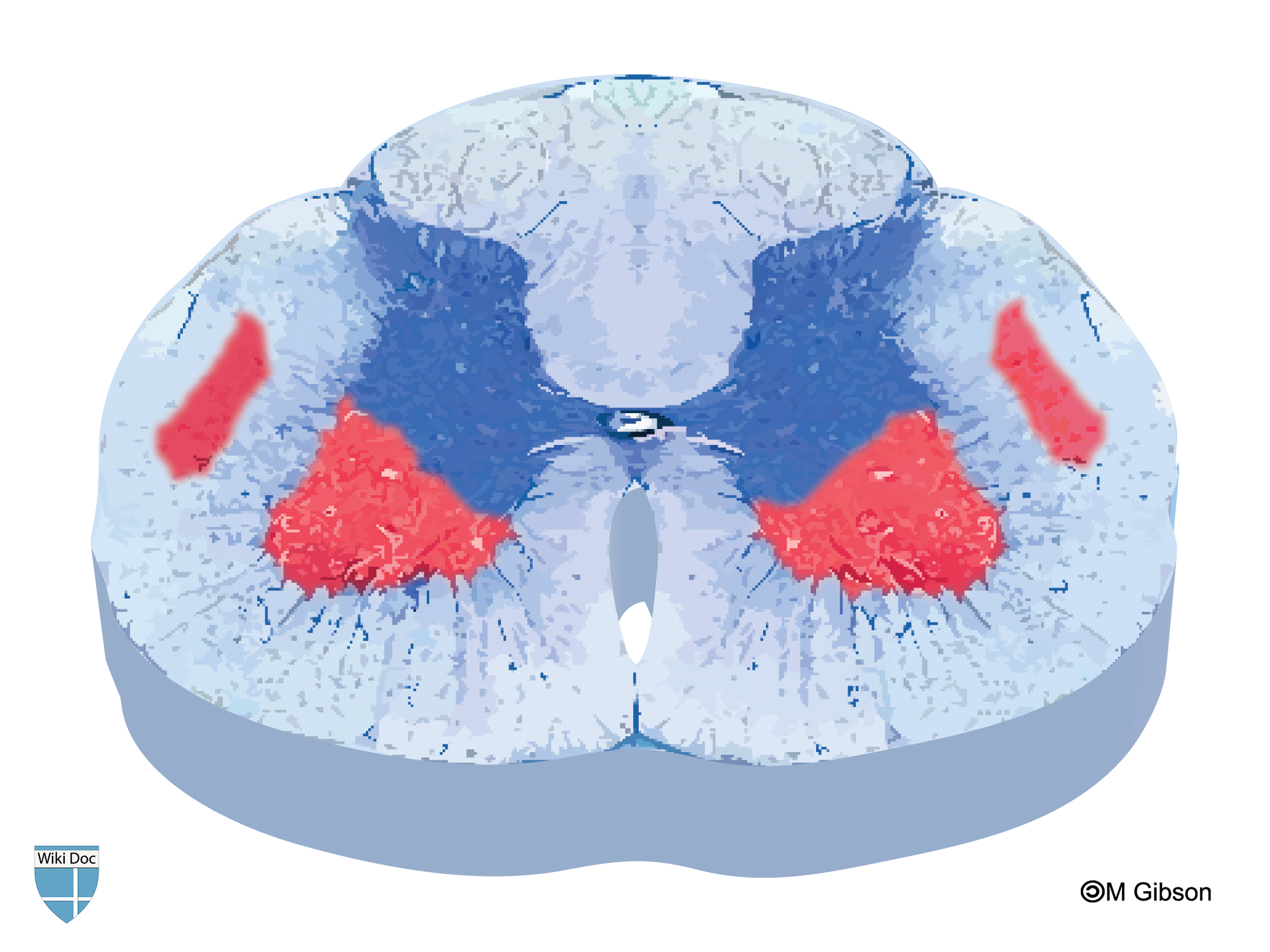 ]] ]]
|
| Answer E Explanation | [[AnswerEExp::This image depicts lesions in the white matter and grey matter. This pattern of lesions is found in ALS which presents with upper motor neurons and lower motor neurons symptoms. Lesions involving both the white matter and grey matter is not characteristic of poliomyelitis.]] |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::D |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::The child is presenting for an acute limping following a prodromal week of fever, headache and vomiting. The findings of muscle weakness, fasciculation and absent reflexes are consistent with lower motor neuron symptoms. Given the clinical history, physical exam findings and history of emigration from Nigeria, the most likely diagnosis is poliomyelitis. Poliomyelitis is a condition caused by a water and foodborne infection with poliovirus. Polio has been almost 99% irradiated in the world except in Nigeria, Pakistan and Afghanistan. Polio can be asymptomatic or can have a subclinical presentation that may or not involve the central nervous system. The involvement of the spinal cord is usually at the level of the anterior horns leading to lower motor neuron symptoms.
Educational objective: Poliomyelitis causes lesions in the anterior horn of the spinal cord. Reference: WHO (http://www.who.int/topics/poliomyelitis/en/) |
| Approved | Approved::No |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Spinal cord, WBRKeyword::polio, WBRKeyword::poliomyelitis |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |