WBR0559: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
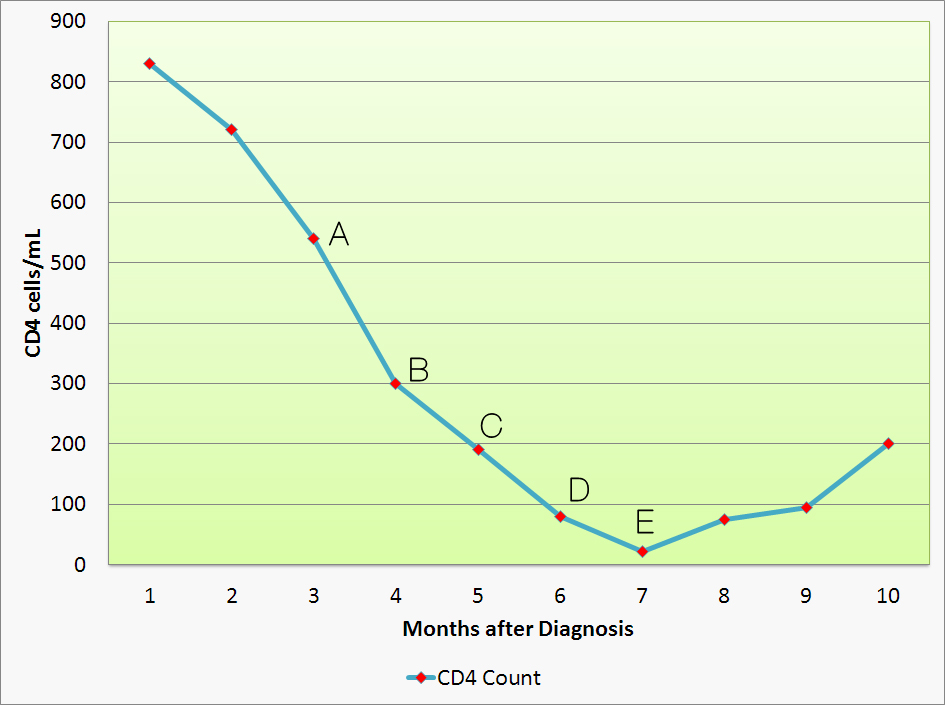
|Explanation=Azithromycin is used in patients with HIV who progressed to AIDS with a CD4 count lower than 50 cells/mL for the prophylaxis for disseminated mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infections. The added benefit of using azithromycin prophylaxis is the coverage for Toxoplasma gondii reactivation even though systematic prophylaxis for Toxoplasma below a CD4 of 100 is not recommended. The table below summarizes the AIDS associated illnesses and the corresponding CD4 counts at which they are observed. | |Explanation=Azithromycin is used in patients with HIV who progressed to AIDS with a CD4 count lower than 50 cells/mL for the prophylaxis for disseminated mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infections. The added benefit of using azithromycin prophylaxis is the coverage for Toxoplasma gondii reactivation even though systematic prophylaxis for Toxoplasma below a CD4 of 100 is not recommended. The table below summarizes the AIDS associated illnesses and the corresponding CD4 counts at which they are observed. | ||
{| | {| {{table}} | ||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''CD4 Count''' | |||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Associated diseases''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
| CD4<500 cells/mL||"Oral candidiasis (Thrush) | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Kaposi's Sarcoma | ||
Kaposi's Sarcoma | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| CD4<100 cells/mL || Cerebral | | " | ||
Disseminated histoplasmosis | |- | ||
| CD4<200 cells/mL||"Pneumocystic jirovecii pneumonia | |||
|- | |||
| Progressive Multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) JC virus | |||
|- | |||
| Cryptosporidium diarrhea" | |||
|- | |||
| CD4<100 cells/mL||"Cerebral Toxoplasmosis | |||
|- | |||
| Disseminated histoplasmosis | |||
|- | |||
| Candida Esophagitis" | |||
|- | |||
| CD4<50 cells/mL||"Cryptococcal meningitis | |||
|- | |||
| CMV retinitis | |||
|- | |||
| Disseminated Mycobacterium Avium Complex (MAC)" | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
|AnswerA=A | |AnswerA=A | ||
Revision as of 03:10, 8 October 2013
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Rim Halaby, M.D. [1]]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Microbiology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Infectious Disease |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 44 year old man with history of multiple unprotected sexual encounters was found to have a positive HIV ELISA during a local screening campaign. He was referred to an HIV clinic where he was advised to monitor his CD4 counts once every month. A trend of his CD4 counts for past 10 months are shown below. At which of the following CD4 values would you advise the patient to receive azithromycin prophylaxis? |
| Answer A | AnswerA::A |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp:: |
| Answer B | AnswerB::B |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp:: |
| Answer C | AnswerC::C |
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp:: |
| Answer D | AnswerD::D |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp:: |
| Answer E | AnswerE::E |
| Answer E Explanation | AnswerEExp:: |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer:: |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::Azithromycin is used in patients with HIV who progressed to AIDS with a CD4 count lower than 50 cells/mL for the prophylaxis for disseminated mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infections. The added benefit of using azithromycin prophylaxis is the coverage for Toxoplasma gondii reactivation even though systematic prophylaxis for Toxoplasma below a CD4 of 100 is not recommended. The table below summarizes the AIDS associated illnesses and the corresponding CD4 counts at which they are observed.
{ |
| Approved | Approved::No |
| Keyword | |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |