Transposition of the great vessels corrective surgery: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
==Surgery== | |||
=== ACC / AHA Guidelines- Recommendations for Surgical Intervention=== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" style="text-align:center; background:LightGreen"|[[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Classification of Recommendations|Class I]] | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="LightGreen"|<nowiki>"</nowiki>'''1.''' Surgeons with training and expertise in CHD should | |||
perform operations for patients with CCTGA for the following indications: | |||
a. Unrepaired CCTGA and severe AV valve regurgitation. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B]])'' | |||
b. Anatomic repair with atrial and arterial level switch/Rastelli repair in cases in which the left ventricle is functioning at systemic pressures. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B]])'' | |||
c. Simple VSD closure when the VSD is not favorable for left ventricle–to–aorta baffling or is restrictive. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B]])'' | |||
d. LV–to–pulmonary artery conduit in rare cases with LV dysfunction and severe LV outflow obstruction. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B]])'' | |||
e. Evidence of moderate or progressive systemic AV valve regurgitation. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B]])'' | |||
f. Conduit obstruction with systemic or nearly systemic RV pressures and/or RV dysfunction after anatomic repair. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B]])'' | |||
g. Conduit obstruction and systemic or suprasystemic LV pressures in a patient with nonanatomic correction. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B]])'' | |||
h. Moderate or severe AR/neo-AR and onset of ventricular dysfunction or progressive ventricular dilatation. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B]])''<nowiki>"</nowiki> | |||
|} | |||
==[[Dextro-transposition of the great arteries general features surgery|General features]]== | ===[[Dextro-transposition of the great arteries general features surgery|General features]]=== | ||
==[[Dextro-transposition of the great arteries arterial switch or jatene operation|Arterial switch or Jatene Operation]]== | ====[[Dextro-transposition of the great arteries arterial switch or jatene operation|Arterial switch or Jatene Operation]]==== | ||
{| | {| | ||
| Line 22: | Line 47: | ||
| [[Image:Postop Jatene neonate.jpg|thumb|left|Immediate post-operative (Jatene procedure) d-TGA + VSD neonate.]] | | [[Image:Postop Jatene neonate.jpg|thumb|left|Immediate post-operative (Jatene procedure) d-TGA + VSD neonate.]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
==[[Dextro-transposition of the great arteries atrial switch repair|Atrial switch repair]]== | ====[[Dextro-transposition of the great arteries atrial switch repair|Atrial switch repair]]==== | ||
'''Below are the images depicting different arterial switch procedures for TGA''' | '''Below are the images depicting different arterial switch procedures for TGA''' | ||
| Line 30: | Line 55: | ||
|} | |} | ||
==[[Dextro-transposition of the great arteries rastelli operation|Rastelli operation]]== | ====[[Dextro-transposition of the great arteries rastelli operation|Rastelli operation]]==== | ||
'''Below is an image depicting the procedure of Rasteli operation for TGA:''' | '''Below is an image depicting the procedure of Rasteli operation for TGA:''' | ||
[[Image:Rastelli procedure.jpg|350px|left]] | [[Image:Rastelli procedure.jpg|350px|left]] | ||
Revision as of 20:40, 3 October 2012
|
Dextro-transposition of the great arteries Microchapters |
|
Differentiating dextro-transposition of the great arteries from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Transposition of the great vessels corrective surgery On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Transposition of the great vessels corrective surgery |
|
FDA on Transposition of the great vessels corrective surgery |
|
CDC on Transposition of the great vessels corrective surgery |
|
Transposition of the great vessels corrective surgery in the news |
|
Blogs on Transposition of the great vessels corrective surgery |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Transposition of the great vessels corrective surgery |
|
Transposition of the great vessels Microchapters |
|
Classification |
|---|
|
Differentiating Transposition of the great vessels from other Diseases |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Surgery |
|
Case Studies |
|
Transposition of the great vessels corrective surgery On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Transposition of the great vessels corrective surgery |
|
FDA on Transposition of the great vessels corrective surgery |
|
CDC on Transposition of the great vessels corrective surgery |
|
Transposition of the great vessels corrective surgery in the news |
|
Blogs on Transposition of the great vessels corrective surgery |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Transposition of the great vessels corrective surgery |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-In-Chief: Priyamvada Singh, M.B.B.S. [2]; Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [3]; Keri Shafer, M.D. [4]; Assistant Editor(s)-In-Chief: Kristin Feeney, B.S. [5]
Overview
Recent advances in surgical correction of transposition of the great arteries have reduced the mortality drastically from 95% in uncorrected patients to 5% in corrected patients[1].
{{#ev:youtube|sqfMNwEagWw}}
Surgery
ACC / AHA Guidelines- Recommendations for Surgical Intervention
| Class I |
| "1. Surgeons with training and expertise in CHD should
perform operations for patients with CCTGA for the following indications: a. Unrepaired CCTGA and severe AV valve regurgitation. (Level of Evidence: B) b. Anatomic repair with atrial and arterial level switch/Rastelli repair in cases in which the left ventricle is functioning at systemic pressures. (Level of Evidence: B) c. Simple VSD closure when the VSD is not favorable for left ventricle–to–aorta baffling or is restrictive. (Level of Evidence: B) d. LV–to–pulmonary artery conduit in rare cases with LV dysfunction and severe LV outflow obstruction. (Level of Evidence: B) e. Evidence of moderate or progressive systemic AV valve regurgitation. (Level of Evidence: B) f. Conduit obstruction with systemic or nearly systemic RV pressures and/or RV dysfunction after anatomic repair. (Level of Evidence: B) g. Conduit obstruction and systemic or suprasystemic LV pressures in a patient with nonanatomic correction. (Level of Evidence: B) h. Moderate or severe AR/neo-AR and onset of ventricular dysfunction or progressive ventricular dilatation. (Level of Evidence: B)" |
General features
Arterial switch or Jatene Operation
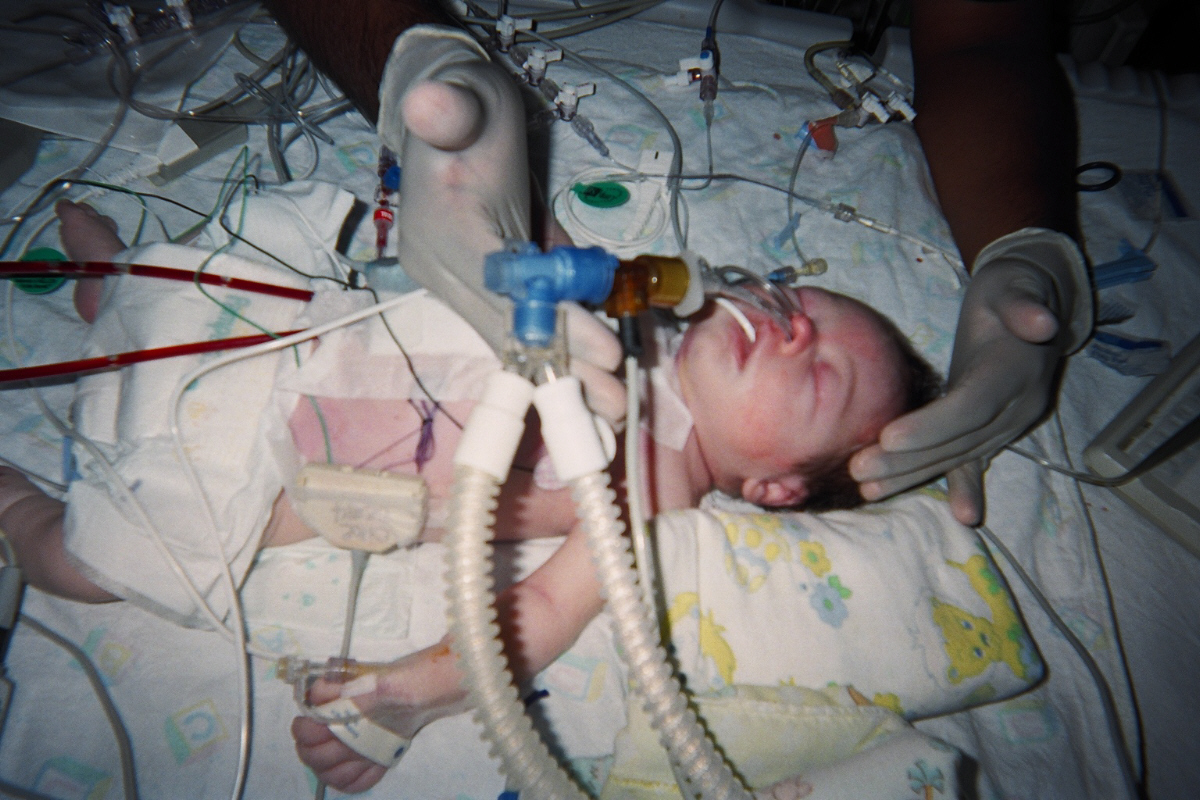 |
Atrial switch repair
Below are the images depicting different arterial switch procedures for TGA
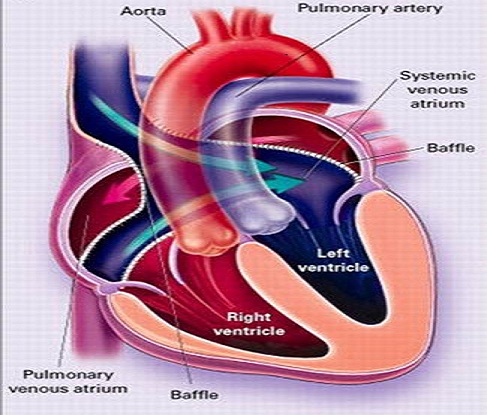 |
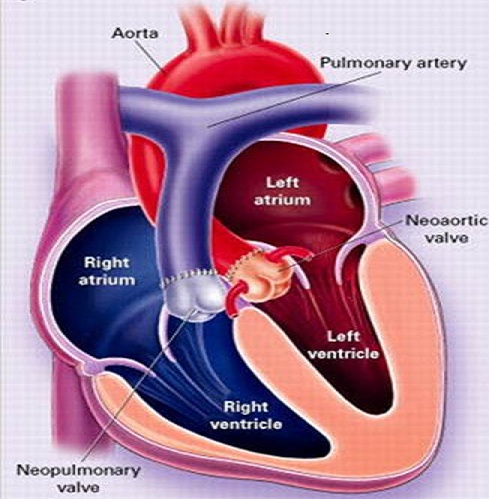 |
Rastelli operation
Below is an image depicting the procedure of Rasteli operation for TGA:
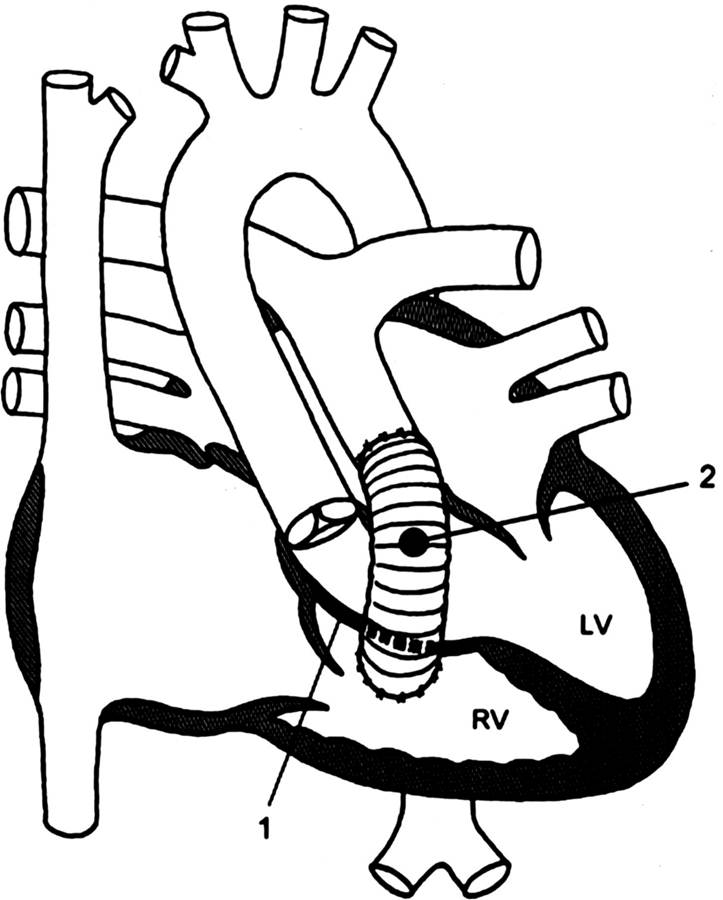
References
- ↑ Hutter PA, Kreb DL, Mantel SF, Hitchcock JF, Meijboom EJ, Bennink GB (2002). "Twenty-five years' experience with the arterial switch operation". J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 124 (4): 790–7. PMID 12324738.
Acknowledgements and Initial Contributors to Page
Leida Perez, M.D.