Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gloria Picoy [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide is a kinase inhibitor that is FDA approved for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E or V600K mutations as detected by an FDA-approved test in combination with dabrafenib. Common adverse reactions include {{{adverseReactions}}}.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide as a single agent and in combination with dabrafenib is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600E or V600K mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test.
- Dosage:
- 2 mg orally taken once daily as a single agent
- 2 mg orally taken once daily in combination with dabrafenib 150 mg orally taken twice daily
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Safety and effectiveness not established in pediatric patients
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
None
Warnings
New Primary Malignancies
New primary malignancies, cutaneous and non-cutaneous, can occur when MEKINIST is used in combination with dabrafenib and with dabrafenib as a single agent.
Cutaneous Malignancies
In Trial 2, the incidence of basal cell carcinoma was increased in patients receiving MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib, with an incidence of 9% (5/55) in patients receiving MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib compared with 2% (1/53) in patients receiving dabrafenib as a single agent. The range of time to diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma was 28 to 249 days in patients receiving MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib and was 197 days for the patient receiving dabrafenib as a single agent.
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas (SCC), including keratoacanthoma, occurred in 7% of patients receiving MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib and 19% of patients receiving dabrafenib as a single agent. The range of time to diagnosis of cuSCC was 136 to 197 days in the combination arm and was 9 to 197 days in the arm receiving dabrafenib as a single agent.
New primary melanoma occurred in 2% (1/53) of patients receiving dabrafenib and in none of the 55 patients receiving MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib.
Perform dermatologic evaluations prior to initiation of MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib, every 2 months while on therapy, and for up to 6 months following discontinuation of the combination. No dose modifications of MEKINIST or dabrafenib are recommended in patients who develop new primary cutaneous malignancies.
Non-Cutaneous Malignancies
Based on its mechanism of action, dabrafenib may promote growth and development of malignancies with activation of RAS through mutation or other mechanisms. In patients receiving MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib, four cases of non-cutaneous malignancies were identified: KRAS mutation-positive pancreatic adenocarcinoma (n = 1), recurrent NRAS mutation-positive colorectal carcinoma (n = 1), head and neck carcinoma (n = 1), and glioblastoma (n = 1). Monitor patients receiving the combination closely for signs or symptoms of non-cutaneous malignancies. If used in combination with dabrafenib, no dose modification is required for MEKINIST in patients who develop non-cutaneous malignancies. Permanently discontinue dabrafenib in patients who develop RAS mutation-positive non-cutaneous malignancies.
Hemorrhage
Hemorrhages, including major hemorrhages defined as symptomatic bleeding in a critical area or organ, can occur when MEKINIST is used in combination with dabrafenib.
In Trial 2, treatment with MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib resulted in an increased incidence and severity of any hemorrhagic event: 16% (9/55) of patients treated with MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib compared with 2% (1/53) of patients treated with dabrafenib as a single agent. The major hemorrhagic events of intracranial or gastric hemorrhage occurred in 5% (3/55) of patients treated with MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib compared with none of the 53 patients treated with dabrafenib as a single agent. Intracranial hemorrhage was fatal in two (4%) patients receiving the combination of MEKINIST and dabrafenib.
Permanently discontinue MEKINIST, and also permanently discontinue dabrafenib if administered in combination, for all Grade 4 hemorrhagic events and for any Grade 3 hemorrhagic events that do not improve. Withhold MEKINIST for up to 3 weeks for Grade 3 hemorrhagic events; if improved resume at a lower dose level. Withhold dabrafenib for Grade 3 hemorrhagic events; if improved resume at a lower dose level.
Venous Thromboembolism
Venous thromboembolism can occur when MEKINIST is used in combination with dabrafenib.
In Trial 2, treatment with MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib resulted in an increased incidence of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE): 7% (4/55) of patients treated with MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib compared with none of the 53 patients treated with dabrafenib as a single agent. Pulmonary embolism was fatal in one (2%) patient receiving the combination of MEKINIST and dabrafenib.
Advise patients to immediately seek medical care if they develop symptoms of DVT or PE, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or arm or leg swelling. Permanently discontinue MEKINIST and dabrafenib for life threatening PE. Withhold MEKINIST for uncomplicated DVT and PE for up to 3 weeks; if improved, MEKINIST may be resumed at a lower dose level. Do not modify the dose of dabrafenib.
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy can occur when MEKINIST is administered as a single agent or when used in combination with dabrafenib.
In Trial 1, cardiomyopathy (defined as cardiac failure, left ventricular dysfunction, or decreased left ventricular ejection fraction [LVEF]) occurred in 7% (14/211) of patients treated with MEKINIST; no chemotherapy-treated patients in Trial 1 developed cardiomyopathy. In Trial 2, cardiomyopathy occurred in 9% (5/55) of patients treated with MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib and in none of patients treated with dabrafenib as a single agent. The median time to onset of cardiomyopathy in patients treated with MEKINIST was 63 days (range: 16 to 156 days) for Trial 1 and 86 days (range: 27 to 253 days) for Trial 2.
Cardiomyopathy was identified within the first month of treatment with MEKINIST in 5 of 14 patients in Trial 1 and in 2 of 5 patients in Trial 2. Development of cardiomyopathy resulted in dose reduction (7/211) and/or discontinuation (4/211) of study drug in Trial 1, and resulted in dose reduction (4/55) and/or dose interruption (1/55) in Trial 2. Cardiomyopathy resolved in 10 of 14 (71%) patients in Trial 1 and in all 5 patients in Trial 2.
Across clinical trials of MEKINIST administered either as a single agent (N = 329), or in combination with dabrafenib (N = 202), 11% and 8% of patients, respectively, developed evidence of cardiomyopathy (decrease in LVEF below institutional lower limits of normal with an absolute decrease in LVEF ≥10% below baseline). Five percent and 2% in single-agent and in combination trials, respectively, demonstrated a decrease in LVEF below institutional lower limits of normal with an absolute decrease in LVEF of ≥20% below baseline.
Assess LVEF by echocardiogram or multigated acquisition (MUGA) scan before initiation of MEKINIST as a single agent and in combination with dabrafenib, one month after initiation, and then at 2- to 3-month intervals while on treatment. Withhold treatment with MEKINIST for up to 4 weeks if absolute LVEF value decreases by 10% from pretreatment values and is less than the lower limit of normal. For symptomatic cardiomyopathy or persistent, asymptomatic LV dysfunction that does not resolve within 4 weeks, permanently discontinue MEKINIST and withhold dabrafenib. Resume dabrafenib at the same dose upon recovery of cardiac function.
Ocular Toxicities
Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO)
Across all clinical trials of MEKINIST, the incidence of RVO was 0.2% (4/1,749). RVO may lead to macular edema, decreased visual function, neovascularization, and glaucoma.
Urgently (within 24 hours) perform ophthalmological evaluation for patient-reported loss of vision or other visual disturbances. Permanently discontinue MEKINIST in patients with documented RVO. If MEKINIST is used in combination with dabrafenib, do not modify dabrafenib dose.
Retinal Pigment Epithelial Detachment (RPED)
Retinal pigment epithelial detachment (RPED) can occur when MEKINIST is administered as a single agent or when used in combination with dabrafenib.
In Trial 1 and Trial 2, ophthalmologic examinations including retinal evaluation were performed pretreatment and at regular intervals during treatment.
In Trial 1, one patient (0.5%) receiving MEKINIST developed RPED and no cases of RPED were identified in chemotherapy-treated patients. Across all clinical trials of MEKINIST, the incidence of RPED was 0.8% (14/1,749). Retinal detachments were often bilateral and multifocal, occurring in the macular region of the retina. RPED led to reduction in visual acuity that resolved after a median of 11.5 days (range: 3 to 71 days) following the interruption of dosing with MEKINIST, although Ocular Coherence Tomography (OCT) abnormalities persisted beyond a month in at least several cases.
In Trial 2, one patient (2%) receiving MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib developed RPED.
Perform ophthalmological evaluation at any time a patient reports visual disturbances and compare with baseline, if available. Withhold MEKINIST if RPED is diagnosed. If resolution of the RPED is documented on repeat ophthalmological evaluation within 3 weeks, resume MEKINIST at a lower dose level. Discontinue MEKINIST if no improvement after 3 weeks. If MEKINIST is used in combination with dabrafenib, do not modify the dose of dabrafenib.
Uveitis and Iritis
Uveitis and iritis can occur when MEKINIST is used in combination with dabrafenib and with dabrafenib as a single agent.
Uveitis occurred in 1% (2/202) of patients treated with MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib.
Symptomatic treatment employed in clinical trials included steroid and mydriatic ophthalmic drops. Monitor patients for visual signs and symptoms of uveitis (e.g., change in vision, photophobia, eye pain). If diagnosed, withhold dabrafenib for up to 6 weeks until uveitis/iritis resolves to Grade 0-1. If not improved, permanently discontinue dabrafenib. If MEKINIST is used in combination with dabrafenib, do not modify the dose of MEKINIST.
Interstitial Lung Disease
In clinical trials of MEKINIST (N = 329) as a single agent, ILD or pneumonitis occurred in 2% of patients. In Trial 1, 2% (5/211) of patients treated with MEKINIST developed ILD or pneumonitis; all five patients required hospitalization. The median time to first presentation of ILD or pneumonitis was 160 days (range: 60 to 172 days).
Withhold MEKINIST in patients presenting with new or progressive pulmonary symptoms and findings including cough, dyspnea, hypoxia, pleural effusion, or infiltrates, pending clinical investigations. Permanently discontinue MEKINIST for patients diagnosed with treatment-related ILD or pneumonitis. If MEKINIST is used in combination with dabrafenib, do not modify the dose of dabrafenib.
Serious Febrile Reactions
Serious febrile reactions and fever of any severity accompanied by hypotension, rigors or chills, dehydration, or renal failure, can occur when MEKINIST is used in combination with dabrafenib and with dabrafenib as a single agent.
The incidence and severity of pyrexia are increased when MEKINIST is used in combination with dabrafenib compared with dabrafenib as a single agent.
In Trial 2, the incidence of fever (serious and non-serious) was 71% (39/55) in patients treated with MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib and 26% (14/53) in patients treated with dabrafenib as a single agent. Serious febrile reactions and fever of any severity accompanied by hypotension, rigors, or chills occurred in 25% (14/55) of patients treated with MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib compared with 2% (1/53) of patients treated with dabrafenib as a single agent. Fever was complicated with chills/rigors in 51% (28/55), dehydration in 9% (5/55), renal failure in 4% (2/55), and syncope in 4% (2/55) of patients in Trial 2. In patients treated with MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib, the median time to initial onset of fever was 30 days compared with 19 days in patients treated with dabrafenib as a single agent; the median duration of fever was 6 days with the combination compared with 4 days with dabrafenib as a single agent.
Across clinical trials of MEKINIST administered in combination with dabrafenib (N = 202), the incidence of pyrexia was 57% (116/202).
Withhold dabrafenib for fever of 101.3ºF or higher. Withhold MEKINIST for fever higher than 104ºF. Withhold dabrafenib and MEKINIST for any serious febrile reaction or fever accompanied by hypotension, rigors or chills, dehydration, or renal failure, and evaluate for signs and symptoms of infection. Refer to Table 2 for recommended dose modifications for adverse reactions. Prophylaxis with antipyretics may be required when resuming MEKINIST or dabrafenib.
Serious Skin Toxicity
Serious skin toxicity can occur when MEKINIST is administered as a single agent or when used in combination with dabrafenib. Serious skin toxicity can also occur with dabrafenib as a single agent.
In Trial 1, the overall incidence of any skin toxicity, the most common of which were rash, dermatitis acneiform rash, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, and erythema, was 87% in patients treated with MEKINIST and 13% in chemotherapy-treated patients. Severe skin toxicity occurred in 12% of patients treated with MEKINIST. Skin toxicity requiring hospitalization occurred in 6% of patients treated with MEKINIST, most commonly for secondary infections of the skin requiring intravenous antibiotics or severe skin toxicity without secondary infection. In comparison, no patients treated with chemotherapy required hospitalization for severe skin toxicity or infections of the skin. The median time to onset of skin toxicity in patients treated with MEKINIST was 15 days (range: 1 to 221 days) and median time to resolution of skin toxicity was 48 days (range: 1 to 282 days). Reductions in the dose of MEKINIST were required in 12% and permanent discontinuation of MEKINIST was required in 1% of patients with skin toxicity.
In Trial 2, the incidence of any skin toxicity was similar for patients receiving MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib (65% [36/55]) compared with patients receiving dabrafenib as a single agent (68% [36/53]). The median time to onset of skin toxicity in patients treated with MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib was 37 days (range: 1 to 225 days) and median time to resolution of skin toxicity was 33 days (range: 3 to 421 days). No patient required dose reduction or permanent discontinuation of MEKINIST or dabrafenib for skin toxicity.
Across clinical trials of MEKINIST administered in combination with dabrafenib (n = 202), severe skin toxicity and secondary infection of the skin requiring hospitalization occurred in 2.5% (5/202) of patients treated with MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib.
Withhold MEKINIST, and dabrafenib if used in combination, for intolerable or severe skin toxicity. MEKINIST and dabrafenib may be resumed at lower dose levels in patients with improvement or recovery from skin toxicity within 3 weeks.
Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia can occur when MEKINIST is used in combination with dabrafenib and with dabrafenib as a single agent. Hyperglycemia requiring an increase in the dose of, or initiation of insulin or oral hypoglycemic agent therapy occurred with dabrafenib as a single agent.
In Trial 2, the incidence of Grade 3 hyperglycemia based on laboratory values was 5% (3/55) in patients treated with MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib compared with 2% (1/53) in patients treated with dabrafenib as a single agent.
Monitor serum glucose levels as clinically appropriate during treatment with MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib in patients with pre-existing diabetes or hyperglycemia. Advise patients to report symptoms of severe hyperglycemia.
Embryofetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action, MEKINIST can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. MEKINIST was embryotoxic and abortifacient in rabbits at doses greater than or equal to those resulting in exposures approximately 0.3 times the human exposure at the recommended clinical dose. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to a fetus.
Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use highly effective contraception during treatment with MEKINIST and for 4 months after treatment. Advise patients to use a highly effective non-hormonal method of contraception when MEKINIST is administered in combination with dabrafenib, since dabrafenib can render hormonal contraceptives ineffective. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they become pregnant, or if pregnancy is suspected, while taking MEKINIST.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide Clinical Trials Experience in the drug label.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
No formal clinical trials have been conducted to evaluate human cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme-mediated drug interactions with trametinib.
Dabrafenib
Coadministration of MEKINIST 2 mg once daily and dabrafenib 150 mg twice daily resulted in no clinically relevant pharmacokinetic drug interactions.
Refer to the Full Prescribing Information for dabrafenib for further details on the drug interaction potential of dabrafenib. Avoid concurrent administration of strong inhibitors or strong inducers of CYP3A4 or CYP2C8 with dabrafenib. If concomitant use of strong inhibitors or strong inducers of CYP3A4 or CYP2C8 is unavoidable, monitor patients closely for adverse reactions when taking strong inhibitors or loss of efficacy when taking strong inducers. Concomitant use of dabrafenib with agents that are sensitive substrates of CYP3A4, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, or CYP2B6 may result in loss of efficacy of these agents. Substitute for these medications or monitor patients for loss of efficacy if use of these medications is unavoidable.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
MEKINIST can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Trametinib was embryotoxic and abortifacient in rabbits at doses greater than or equal to those resulting in exposures approximately 0.3 times the human exposure at the recommended clinical dose. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
Animal Data
In reproductive toxicity studies, administration of trametinib to rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in decreased fetal weights at doses greater than or equal to 0.031 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.3 times the human exposure based on AUC at the recommended dose). In rats, at a dose resulting in exposures 1.8-fold higher than the human exposure at the recommended dose, there was maternal toxicity and an increase in post-implantation loss.
In pregnant rabbits, administration of trametinib during the period of organogenesis resulted in decreased fetal body weight and increased incidence of variations in ossification at doses greater than or equal to 0.039 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.08 times the human exposure at the recommended dose based on AUC). In rabbits administered trametinib at 0.15 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.3 times the human exposure at the recommended dose based on AUC) there was an increase in post-implantation loss, including total loss of pregnancy, compared with control animals.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is present in human milk. Because many drugs are present in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from MEKINIST, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of MEKINIST as a single agent or in combination with dabrafenib have not been established in pediatric patients.
Adequate juvenile animal studies using trametinib have not been completed. In a repeat-dose toxicity study in juvenile rats, an increased incidence of kidney cysts and tubular deposits were noted at doses as low as 0.2 times the human exposure at the recommended adult dose of dabrafenib based on AUC. Additionally, forestomach hyperplasia, decreased bone length, and early vaginal opening were noted at doses as low as 0.8 times the human exposure at the recommended adult dose based on AUC.
Geriatic Use
Clinical trials of MEKINIST as a single agent did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. In Trial 1, 49 patients (23%) were 65 years of age and older, and 9 patients (4%) were 75 years of age and older.
Across all clinical trials of MEKINIST administered in combination with dabrafenib, there was an insufficient number of patients aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. In Trial 2, 11 patients (20%) were 65 years of age and older, and 2 patients (4%) were 75 years of age and older.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
No formal clinical trial has been conducted to evaluate the effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of trametinib. No dose adjustment is recommended in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis. The appropriate dose of MEKINIST has not been established in patients with severe renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
No formal clinical trial has been conducted to evaluate the effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of trametinib. No dose adjustment is recommended in patients with mild hepatic impairment based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis.
The appropriate dose of MEKINIST has not been established in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
Contraception
Females: MEKINIST can cause fetal harm when administered during pregnancy. Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use highly effective contraception during treatment and for 4 months after the last dose of MEKINIST. When MEKINIST is used in combination with dabrafenib, counsel patients to use a non-hormonal method of contraception since dabrafenib can render hormonal contraceptives ineffective. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they become pregnant, or if pregnancy is suspected, while taking MEKINIST.
Infertility
- Females: MEKINIST may impair fertility in female patients.
- Males: Effects on spermatogenesis have been observed in animals treated with dabrafenib. Advise male patients of the potential risk for impaired spermatogenesis, and to seek counseling on fertility and family planning options prior to starting treatment with MEKINIST in combination with dabrafenib.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There were no reported cases of overdosage with MEKINIST. The highest doses of MEKINIST evaluated in clinical trials were 4 mg orally once daily and 10 mg administered orally once daily on 2 consecutive days followed by 3 mg once daily. In seven patients treated on one of these two schedules, there were two cases of retinal pigment epithelial detachments for an incidence of 28%. Since trametinib is highly bound to plasma proteins, hemodialysis is likely to be ineffective in the treatment of overdose with MEKINIST.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
Trametinib is a reversible inhibitor of mitogen-activated extracellular signal regulated kinase 1 (MEK1) and MEK2 activation and of MEK1 and MEK2 kinase activity. MEK proteins are upstream regulators of the extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) pathway, which promotes cellular proliferation. BRAF V600E mutations result in constitutive activation of the BRAF pathway which includes MEK1 and MEK2. Trametinib inhibits BRAF V600 mutation-positive melanoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo.
Trametinib and dabrafenib target two different tyrosine kinases in the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. Use of trametinib and dabrafenib in combination resulted in greater growth inhibition of BRAF V600 mutation-positive melanoma cell lines in vitro and prolonged inhibition of tumor growth in BRAF V600 mutation positive melanoma xenografts compared with either drug alone.
Structure
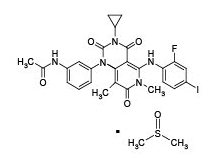
Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide has the following chemical structure:
Pharmacodynamics
Administration of 1 mg and 2 mg trametinib to patients with BRAF V600 mutation-positive melanoma resulted in dose-dependent changes in tumor biomarkers including inhibition of phosphorylated ERK, inhibition of Ki67 (a marker of cell proliferation), and increases in p27 (a marker of apoptosis).
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics (PK) of trametinib were characterized following single- and repeat-oral administration in patients with solid tumors and BRAF V600 mutation-positive metastatic melanoma.
Absorption
After oral administration, the median time to achieve peak plasma concentrations (Tmax) is 1.5 hours post-dose. The mean absolute bioavailability of a single 2-mg oral dose of trametinib tablet is 72%. The increase in Cmax was dose proportional after a single dose of 0.125 to 10 mg while the increase in AUC was greater than dose proportional. After repeat doses of 0.125 to 4 mg daily, both Cmax and AUC increase proportionally with dose. Inter-subject variability in AUC and Cmax at steady state is 22% and 28%, respectively.
Administration of a single dose of trametinib with a high-fat, high-calorie meal decreased AUC by 24%, Cmax by 70%, and delayed Tmax by approximately 4 hours as compared with fasted conditions.
Distribution
Trametinib is 97.4% bound to human plasma proteins. The apparent volume of distribution (Vc/F) is 214 L.
Metabolism
Trametinib is metabolized predominantly via deacetylation alone or with mono-oxygenation or in combination with glucuronidation biotransformation pathways in vitro. Deacetylation is likely mediated by hydrolytic enzymes, such as carboxyl-esterases or amidases.
Following a single dose of [14C]-trametinib, approximately 50% of circulating radioactivity is represented as the parent compound. However, based on metabolite profiling after repeat dosing of trametinib, ≥75% of drug-related material in plasma is the parent compound.
Elimination
The estimated elimination half-life based on the population PK model is 3.9 to 4.8 days. The apparent clearance is 4.9 L/h.
Following oral administration of [14C]-trametinib, >80% of excreted radioactivity was recovered in the feces while <20% of excreted radioactivity was recovered in the urine with <0.1% of the excreted dose as parent.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with trametinib have not been conducted. Trametinib was not genotoxic in studies evaluating reverse mutations in bacteria, chromosomal aberrations in mammalian cells, and micronuclei in the bone marrow of rats.
Trametinib may impair fertility in humans. In female rats given trametinib for up to 13 weeks, increased follicular cysts and decreased corpora lutea were observed at doses ≥0.016 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.3 times the human exposure at the recommended dose based on AUC). In rat and dog toxicity studies up to 13 weeks in duration, there were no treatment effects observed on male reproductive tissues.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Inform patients of the following:
- Evidence of BRAF V600E or V600K mutation within the tumor specimen is necessary to identify patients for whom treatment with MEKINIST is indicated.
- MEKINIST administered in combination with dabrafenib can result in the development of new primary cutaneous and non-cutaneous malignancies. Advise patients to contact their doctor immediately for any new lesions, changes to existing lesions on their skin, or other signs and symptoms of malignancies.
- MEKINIST administered in combination with dabrafenib increases the risk of intracranial and gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider to seek immediate medical attention for signs or symptoms of unusual bleeding or hemorrhage.
- MEKINIST administered in combination with dabrafenib increases the risks of pulmonary embolism and deep venous thrombosis. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention for sudden onset of difficulty breathing, leg pain, or swelling.
- MEKINIST can cause cardiomyopathy. Advise patients to immediately report any signs or symptoms of heart failure to their healthcare provider.
- MEKINIST can cause severe visual disturbances that can lead to blindness. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they experience any changes in their vision.
- MEKINIST can cause interstitial lung disease (or pneumonitis). Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider as soon as possible if they experience signs such as cough or dyspnea.
- MEKINIST used in combination with dabrafenib can cause serious febrile reactions. Instruct patients to contact their healthcare provider if they develop fever while taking MEKINIST with dabrafenib.
- MEKINIST can cause skin toxicities which may require hospitalization. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider for progressive or intolerable rash.
- MEKINIST causes hypertension. Advise patients that they need to undergo blood pressure monitoring and to contact their healthcare provider if they develop symptoms of hypertension such as severe headache, blurry vision, or dizziness.
- MEKINIST often causes diarrhea which may be severe in some cases. Inform patients of the need to contact their healthcare provider if severe diarrhea occurs during treatment.
- MEKINIST should be taken at least 1 hour before or at least 2 hours after a meal.
- MEKINIST can cause fetal harm if taken during pregnancy. Instruct female patients to use highly effective contraception during treatment and for 4 months after treatment. Advise patients to use a highly effective non-hormonal method of contraception when MEKINIST is administered in combination with dabrafenib. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they become pregnant, or if pregnancy is suspected, while taking MEKINIST.
- Nursing infants may experience serious adverse reactions if the mother is taking MEKINIST. Advise lactating mothers to discontinue nursing while taking MEKINIST.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Trametinib dimethyl sulfoxide Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.