Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
[[Image: CARDIAC TAPVC.jpg|250px|left]] | [[Image: CARDIAC TAPVC.jpg|250px|left]] | ||
<br clear"left"/> | <br clear"left"/> | ||
Revision as of 16:10, 8 April 2013
|
Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection pathophysiology |
|
FDA on Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection pathophysiology |
|
CDC on Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection pathophysiology |
|
Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection pathophysiology in the news |
|
Blogs on Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]; Keri Shafer, M.D. [3] Priyamvada Singh, MBBS [[4]] Assistant Editor-In-Chief: Kristin Feeney, B.S. [[5]]
Overview
In patients of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (TAPVC) there is a mixing of oxygenated pulmonary venous blood with deoxygenated blood from systemic circulation.
Pathophysiology
Mixing of blood could occur at three levels i.e. supracardiac, infracardiac and cardiac. In the former two the mixing occurs outside the heart and in latter inside the heart (right atrium).
This mixed deoxygenated blood is shunted from right-to-left side of heart (patent foramen ovale, atrial septal defect or patent ductus arteriosus). This right to left shunting causes cyanosis in the patient.
Since, the right side of heart is receiving blood both from pulmonary and systemic circulation it leads to development of pulmonary hypertension, right atrial and ventricular hypertrophy.
Obstructive forms: In this pulmonary blood flow is restricted by the compression of pulmonary venous system by sorrounding structure or by the patency of pulmonary vein or vertebral vein. Level of obstructions seen are:
- Supracardiac (43%)
- Infracardiac (27%)
- Cardiac (18%)
- Mixed (12%)
Unobstructed forms: No significant stenosis of the pulmonary veins. {{#ev:youtube|eODH6E_OA_M}}
{{#ev:youtube|iiEI5TQ383w}}
Gross Pathology
Picture below shows cardiac type of TAPVC with opening of cardiac vein into right atrium:

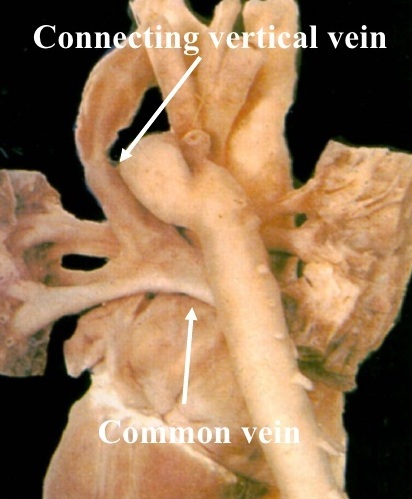
Picture below shows supracardiac type of TAPVC with connecting vertical vein: