Temporal arteritis: Difference between revisions
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
The disorder may coexist (in one quarter of cases) with [[polymyalgia rheumatica]] (PMR), which is characterized by sudden onset of pain and stiffness in muscles ([[pelvis]], [[shoulder]]) of the body and seen in the elderly. Other diseases related with temporal arteritis are systemic [[lupus erythematosus]], [[rheumatoid arthritis]] and severe [[infection]]s. | The disorder may coexist (in one quarter of cases) with [[polymyalgia rheumatica]] (PMR), which is characterized by sudden onset of pain and stiffness in muscles ([[pelvis]], [[shoulder]]) of the body and seen in the elderly. Other diseases related with temporal arteritis are systemic [[lupus erythematosus]], [[rheumatoid arthritis]] and severe [[infection]]s. | ||
Revision as of 20:49, 29 August 2012
| Temporal arteritis | |
 | |
|---|---|
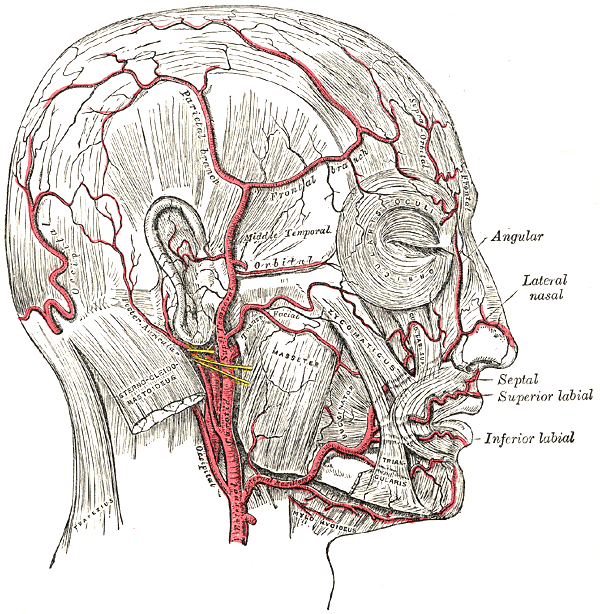
| The arteries of the face and scalp. | |
| ICD-10 | M31.5 |
| ICD-9 | 446.5 |
| OMIM | 187360 |
| DiseasesDB | 12938 |
| MeSH | D013700 |
|
Temporal Arteritis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Temporal arteritis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Temporal arteritis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Synonyms and keywords: GCA; giant cell arteritis; cranial arteritis; Horton's disease; Horton disease; Horton's arteritis; Horton syndrome; Horton's syndrome; granulomatous arteritis; polymyalgia arteritica
Overview
The disorder may coexist (in one quarter of cases) with polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR), which is characterized by sudden onset of pain and stiffness in muscles (pelvis, shoulder) of the body and seen in the elderly. Other diseases related with temporal arteritis are systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and severe infections.
This diagnosis should be considered in any patient over the age of 50 with the new onset of headache, particularly is the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is elevated.
Prompt treatment with steroids is a medical emergency to reduce the risk of blindness.
Diganosis
Diagnosis
Treatment
References
Additional Resources
Template:Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue