Supraventricular arrhythmias
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Overview
| example (lead II) | regularity | atrial frequency | ventricular frequency | origin (SVT/VT) | p-wave | effect of adenosine | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Narrow complex (QRS<0.12) | |||||||
| Sinus tachycardia | regular | 100-180 bpm | 100-180 bpm | sinus node (SVT) | precedes every QRS complex | gradual slowing | |
| Atrial Fibrillation | grossly irregular | 400-600 bpm | 75-175 bpm | atria (SVT) | absent | slows down rate; irregularity remains | |
| Atrial Flutter | regular (sometimes alternating block) | 250-350 bpm | 75-150 bpm (3:1 or 2:1 block is most common) | atria (SVT) | negative sawtooth in lead II | temporary reduced conduction (e.g. 4:1) | |
| AVNRT | regular | 180-250 bpm | 180-250 bpm | AV-node (SVT) | in QRS complex (R') | stops | |
| Atrial tachycardia | regular | 120-250 bpm | 75-200 bpm | atria | precedes QRS, p wave differs from sinus-p | temporary AV-block | |
| Atrio-Ventricular Reentry Tachycardia (AVRT)- orthodromic | regular | 150-250 bpm | 150-250 bpm | circle: av-node - ventricles - bypass - atria | RP < PR | stops | |
| AV junctional tachycardia | regular | 60-100 bpm | 70-130 bpm | AV node | RP < PR | reduces rate | |
| Wide complex (QRS>0.12) | |||||||
| Supraventricular tachycardia with block | (ir)regular depending on SVT | 100-250 bpm | 75-200 bpm | atria (SVT) | absent | temporary increased AV-block (eg 4:1) | |
| Atrio-ventricular Reentry Tachycardia (AVRT) - antidrome | regular | 150-250 bpm | 150-250 bpm | circular: bypass - atria - av-node - ventricles | RP < PR | stops | |
Supraventricular ectopic beats
Also read
- Flowchart: Approach to the Narrow Complex Tachycardia Adapted from ESCnarrowQRS.
- Introduction to Arrhythmias
- Mechanisms of Arrhythmias
- Sinus node rhythms and arrhythmias
- Junctional Tachycardias
- Ventricular Arrhythmias
EKG Examples
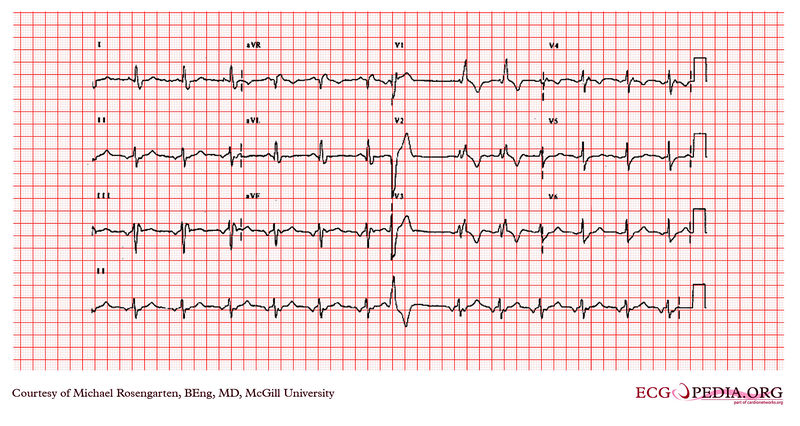
This is an electrocardiogram from a woman in her forties who had several operations for congenital heart disease. At the time of the electrocardiogram the patient was taking flecainide and metoprolol .
This patient was being treated for ventricular tachycardia. She was initially treated with amiodarone and then was switched to a combination of flecainide and metoprolol. She was doing well. The underlying congenital heart disease was Tetralogy of Fallot. The electrocardiogram shows a supraventricular rhythm which is probably not sinus as indicated by the negative P waves in the inferior leads. The cardiogram also shows 1 PVC and a right Branch block with a left anterior hemi-block.
Causes
Drug Side Effect
References
<biblio>
- ESCnarrowQRS pmid=14563598
</biblio>