Substituted amphetamine
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
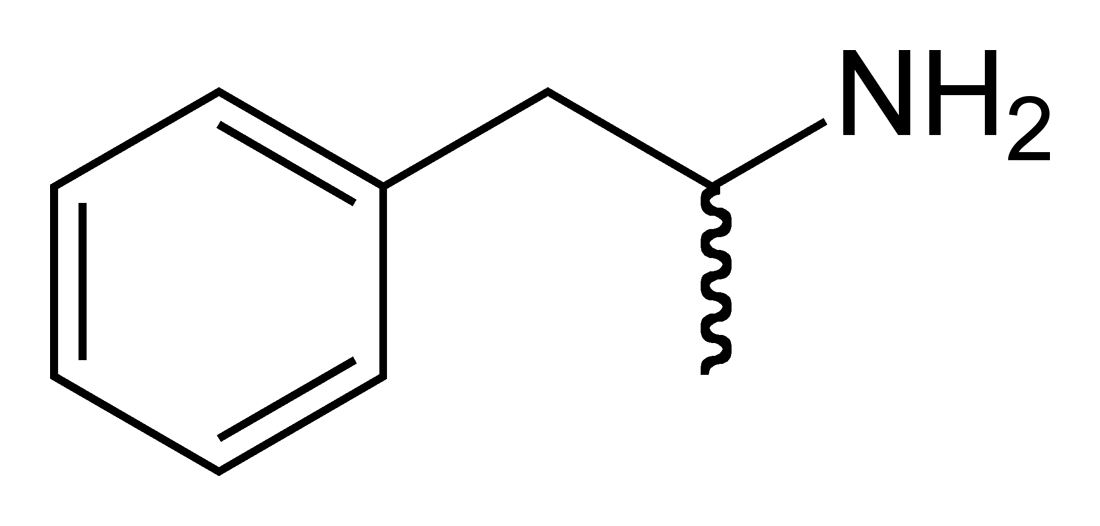
The substituted amphetamines are a family of amphetamine-based stimulants, hallucinogens, and other recreational drugs. They each have a methyl group on the alpha carbon, often have methoxy groups on the 2 and 5 carbons, and have variant groups on the 3, 4, and 5 carbons. Examples include DOB and DOI. Many substituted amphetamines are amphetamine analogues of the 2C's.
| Nomenclature | R3 | R4 | R5 | 2C analog | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3C-BZ | OCH3 | OC(CH)5 | OCH3 | NA | File:3C-BZ.png |
| Aleph | H | SCH3 | H | 2C-T | File:Aleph.png |
| Aleph-2 | H | SCH2CH3 | H | 2C-T-2 | File:Aleph-2.png |
| Aleph-4 | H | SCH(CH3)2 | H | 2C-T-4 | File:Aleph-4.png |
| Aleph-6 | H | SC(CH)5 | H | NA | File:Aleph-6.png |
| Aleph-7 | H | S(CH2)2CH3 | H | 2C-T-7 | File:Aleph-7.png |
| DOB | H | B | H | 2C-B | File:R-DOB chemical structure.png |
| DOI | H | I | H | 2C-I | 
|
| DOM | H | CH3 | H | 2C-D | File:R-DOM chemical structure.png |
| DOBU | H | (CH2)3CH3 | H | NA | File:DOBU.png |
| Ganesha | CH3 | CH3 | H | 2C-G | File:Ganesha chem.png |