Sandbox:Eiman
The following signs may be seen:
- Sunsetting signs
- Associated with tumor
- Associated with disease
- Associated with tumor
- ABC
- DEF
| Stage 1 | Prepubertal external genitalia Prepubertal pubic hair Growth 5-6 cm/year | 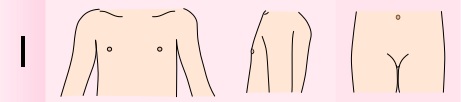 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 2 | Enlargement of scrotum and testes; scrotum skin become hyperpigmented and harder Sparse growth of long, slightly pigmented hair, straight or curled, at base of penis Growth 5-6 cm/year | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boys | Stage 3 | Enlargement of penis (length at first); further testes growth Darker, coarser, and more curled hair, spreading over pubes Growth 7-8 cm/year | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 4 | Increased penis size with growth and development of glans; testes and scrotum larger, scrotum skin darker Adult type hair, but smaller area; no spread to medial surface of thighs Growth 10 cm/year | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 5 | Adult external genitalia Adult type hair with same horizontal distribution ("feminine") No further height increase after 17 years | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tanner staging | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 1 | Prepubertal external genitalia Prepubertal pubic hair Growth 5-6 cm/year | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 2 | Breast bud with elevation of breast and papilla; enlargement of areola Sparse growth of long, slightly pigmented hair, straight or curled, along labia Growth 7-8 cm/year | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Girls | Stage 3 | Further enlargement of breast and areola; no separation of their contour Darker, coarser and more curled hair, spreading sparsely over junction of pubes Growth 8 cm/year | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 4 | Areola and papilla form a secondary mound above level of breast Adult type hair, but smaller area than in adult; no spread to medial surface of thighs Growth 7 cm/year | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stage 5 | Mature breast: projection of papilla only, related to recession of areola Adult type hair with horizontal distribution ("feminine") No further growth after 16 years | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise | Calcium Supplementation | Vitamin D supplementation | Smoking cessation | Reduced alcohol consumption | Hip protectors | Fall protection | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Balance, strength and functional training exercises | Women • 9-18 yrs: 1,300 mg • 19-50 yrs: 1,000 mg • 51-70 yrs: 1,200 mg • 71 and more yrs: 1,200 mg Men • 50-70 yrs: 1,000 mg • 71 and more yrs: 1,200 mg | Women • 9-18 yrs: 600 IU • 19-50 yrs: 600 IU • 51-70 yrs: 600 IU • 71 and more yrs: 800 IU Men • More than 50 yrs: 800-1,000 IU • Serum vitamin D level of 20 ng per mL (50 nmol per L) is recommended for good bone health | • Stop-smoking program and nicotine patch | Limit to: • One drink/day for women • Two drinks/day for men • Moderate alcohol may associated with slightly higher BMD and lower fracture risk in postmenopausal women | • Hard and soft hip protectors, upon preference | Multifactorial interventions: • Individual risk assessment • Tai Chi and other exercise programs • Home safety assessment and modification by an occupational therapist • Gradual withdrawal of psychotropic medication • Visual impairment correction • Improve mobility | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lifestyle modifications | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise | Calcium Supplementation | Vitamin D supplementation | Smoking cessation | Reduced alcohol consumption | Hip protectors | Fall protection | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, strength and functional training exercises | Women • 9-18 yrs: 1,300 mg • 19-50 yrs: 1,000 mg • 51-70 yrs: 1,200 mg • 71 and more yrs: 1,200 mg Men • 50-70 yrs: 1,000 mg • 71 and more yrs: 1,200 mg | Women • 9-18 yrs: 600 IU • 19-50 yrs: 600 IU • 51-70 yrs: 600 IU • 71 and more yrs: 800 IU Men • More than 50 yrs: 800-1,000 IU • Serum vitamin D level of 20 ng per mL (50 nmol per L) is recommended for good bone health | • Stop-smoking program • Nicotine patch | Limit to: • One drink/day for women • Two drinks/day for men • Moderate alcohol may associated with slightly higher BMD and lower fracture risk in postmenopausal women | Hard and soft hip protectors, upon preference | Multifactorial interventions: • Individual risk assessment • Tai Chi and other exercise programs • Home safety assessment and modification by an occupational therapist • Gradual withdrawal of psychotropic medication • Visual impairment correction • Improve mobility | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chronic corticosteroid use | Children and adolescent | Adults | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Men | Women | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Young hypogonadal • More than 70 yrs • Less than 70 yrs with: ••Low body weight ••Prior fracture ••High risk medication use ••Disease or condition associated with bone loss | • More than 65 yrs • Postmenopausal women younger than 65 yrs with: ••History of fragility fracture •• Weigh less than 127 lb (58 kg) ••Medications or diseases that cause bone loss •• Parental history of hip fracture •• smoking •• Alcoholism •• Rheumatoid arthritis. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||