|
|
| (33 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| == Patient information== | | ==Physical examination== |
| '''For the WikiDoc page for this topic, click [[Diarrhea|here]]'''
| |
| | |
| {{Diarrhea (patient information)}}
| |
| | |
| {{CMG}}; '''Assistant Editor-in-Chief:''' Meagan E. Doherty
| |
| | |
| ==Overview==
| |
| Diarrhea is loose, watery stools. A person with diarrhea typically passes stool more than three times a day. People with diarrhea may pass more than a quart of stool a day. Acute diarrhea is a common problem that usually lasts 1 or 2 days and goes away on its own without special treatment. Prolonged diarrhea persisting for more than 2 days may be a sign of a more serious problem and poses the risk of [[dehydration]]. Chronic diarrhea may be a feature of a chronic disease. Diarrhea can cause dehydration, which means the body lacks enough fluid to function properly. Dehydration is particularly dangerous in children and older people, and it must be treated promptly to avoid serious health problems. People of all ages can get diarrhea and the average adult has a bout of acute diarrhea about four times a year. In the United States, each child will have had seven to 15 episodes of diarrhea by age 5.
| |
| | |
| ==What are the symptoms of Diarrhea?==
| |
| Diarrhea may be accompanied by [[cramping]], [[abdominal pain]], [[bloating]], [[nausea]], or an urgent need to use the bathroom. Depending on the cause, a person may have a [[fever]] or bloody stools.
| |
| | |
| ==What are the causes of Diarrhea?==
| |
| Acute diarrhea is usually related to a bacterial, viral, or parasitic infection. Chronic diarrhea is usually related to functional disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome or inflammatory bowel disease.
| |
| | |
| A few of the more common causes of diarrhea include the following:
| |
| *'''Bacterial infections'''. Several types of bacteria consumed through contaminated food or water can cause diarrhea. Common culprits include [[Campylobacter]], [[Salmonella]], [[Shigella]], and [[Escherichia coli]] (E. coli).
| |
| *'''Viral infections'''. Many viruses cause diarrhea, including [[rotavirus]], [[Norwalk virus]], [[cytomegalovirus]], [[herpes simplex virus]], and [[viral hepatitis]].
| |
| *'''Food intolerances'''. Some people are unable to digest food components such as artificial sweeteners and lactose—the sugar found in milk.
| |
| *'''Parasites'''. Parasites can enter the body through food or water and settle in the digestive system. Parasites that cause diarrhea include [[Giardia lamblia]], [[Entamoeba histolytica]], and [[Cryptosporidium]].
| |
| *'''Reaction to medicines'''. [[Antibiotics]], [[blood pressure medications]], [[cancer drugs]], and [[antacids]] containing [[magnesium]] can all cause diarrhea.
| |
| *'''Intestinal diseases'''. [[Inflammatory bowel disease]], [[colitis]], [[Crohn’s disease]], and [[celiac disease]] often lead to diarrhea.
| |
| *'''Functional bowel disorders'''. Diarrhea can be a symptom of [[irritable bowel syndrome]].
| |
| | |
| Some people develop diarrhea after stomach surgery or removal of the [[gallbladder]]. The reason may be a change in how quickly food moves through the [[digestive system]] after stomach surgery or an increase in [[bile]] in the [[colon]] after gallbladder surgery.
| |
| | |
| People who visit foreign countries are at risk for traveler’s diarrhea, which is caused by eating food or drinking water contaminated with bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Traveler’s diarrhea can be a problem for people visiting developing countries. Visitors to the United States, Canada, most European countries, Japan, Australia, and New Zealand do not face much risk for traveler’s diarrhea.
| |
| | |
| In many cases, the cause of diarrhea cannot be found. As long as diarrhea goes away on its own, an extensive search for the cause is not usually necessary.
| |
| | |
| ==Who is at risk for Diarrhea?==
| |
| Anyone can get diarrhea. This common problem can last a day or two or for months or years, depending on the cause. Most people get better on their own, but diarrhea can be serious for babies and older people if lost fluids are not replaced. Many people throughout the world die from diarrhea because of the large volume of water lost and the accompanying loss of salts.
| |
| | |
| ==Diagnosis==
| |
| Diagnostic tests to find the cause of diarrhea may include the following:
| |
| *'''Medical history and physical examination.''' The doctor will ask you about your eating habits and medication use and will examine you for signs of illness.
| |
| *'''Stool culture.''' A sample of stool is analyzed in a laboratory to check for [[bacteria]], [[parasites]], or other signs of disease and infection.
| |
| *'''Blood tests.''' Blood tests can be helpful in ruling out certain diseases.
| |
| *'''Fasting tests.''' To find out if a food intolerance or allergy is causing the diarrhea, the doctor may ask you to avoid [[lactose]], [[carbohydrates]], wheat, or other foods to see whether the diarrhea responds to a change in diet.
| |
| *'''Sigmoidoscopy'''. For this test, the doctor uses a special instrument to look at the inside of the [[rectum]] and lower part of the [[colon]].
| |
| *'''Colonoscopy'''. This test is similar to a [[sigmoidoscopy]], but it allows the doctor to view the entire [[colon]].
| |
| *'''Imaging tests'''. These tests can rule out structural abnormalities as the cause of diarrhea.
| |
| | |
| ==When to seek urgent medical care==
| |
| Diarrhea is not usually harmful, but it can become dangerous or signal a more serious problem. You should see the doctor if you experience any of the following:
| |
| * Diarrhea for more than 3 days
| |
| * Severe pain in the [[abdomen]] or [[rectum]]
| |
| * A [[fever]] of 102 degrees or higher
| |
| * Blood in your stool or black, tarry stools
| |
| * Signs of [[dehydration]]
| |
| | |
| ==Treatment options==
| |
| In most cases of diarrhea, replacing lost fluid to prevent [[dehydration]] is the only treatment necessary. Medicines that stop diarrhea may be helpful, but they are not recommended for people whose diarrhea is caused by a bacterial infection or parasite. If you stop the diarrhea before having purged the bacteria or parasite, you will trap the organism in the intestines and prolong the problem. Rather, doctors usually prescribe [[antibiotics]] as a first-line treatment. [[Viral infections]] are either treated with medication or left to run their course, depending on the severity and type of virus.
| |
| | |
| ===Tips About Food===
| |
| Until diarrhea subsides, try to avoid caffeine, milk products, and foods that are greasy, high in fiber, or very sweet. These foods tend to aggravate diarrhea.
| |
| | |
| As you improve, you can add soft, bland foods to your diet, including bananas, plain rice, boiled potatoes, toast, crackers, cooked carrots, and baked chicken without the skin or fat. For children, the pediatrician may also recommend a bland diet. Once the diarrhea has stopped, the pediatrician will likely encourage children to return to a normal and healthy diet if it can be tolerated.
| |
| | |
| ===Contraindicated medications===
| |
| {{MedCondContrPI
| |
| | |
| |MedCond =Diarrhea|Ethacrynic acid}}
| |
| | |
| ==Where to find medical care for Diarrhea==
| |
| [http://maps.google.com/maps?f=q&hl=en&geocode=&q={{urlencode:{{#if:{{{1|}}}|{{{1}}}|yourdisease}}}}&sll=37.0625,-95.677068&sspn=65.008093,112.148438&ie=UTF8&ll=37.0625,-95.677068&spn=91.690419,149.414063&z=2&source=embed Directions to Hospitals Treating Diarrhea]
| |
| | |
| ==Prevention of Diarrhea==
| |
| * Wash your hands often, especially after going to the bathroom and before eating.
| |
| * Teach children to not put objects in their mouth.
| |
| * When taking antibiotics, try eating food with Lactobacillus acidophilus, a healthy bacteria. This helps replenish the good bacteria that antibiotics can kill. Yogurt with active or live cultures is a good source of this healthy bacteria.
| |
| * Use alcohol-based hand gel frequently.
| |
| | |
| Traveler’s diarrhea happens when you consume food or water contaminated with bacteria, viruses, or parasites. You can take the following precautions to prevent traveler’s diarrhea when you travel outside of the United States:
| |
| * Do not drink tap water or use it to brush your teeth.
| |
| * Do not drink unpasteurized milk or dairy products.
| |
| * Do not use ice made from tap water.
| |
| * Avoid all raw fruits and vegetables, including lettuce and fruit salads, unless they can be peeled and you peel them yourself.
| |
| * Do not eat raw or rare meat and fish.
| |
| * Do not eat meat or shellfish that is not hot when served.
| |
| * Do not eat food from street vendors.
| |
| | |
| You can safely drink bottled water—if you are the one to break the seal—along with carbonated soft drinks, and hot drinks such as coffee or tea.
| |
| | |
| Depending on where you are going and how long you will stay, your doctor may recommend that you take antibiotics before leaving to protect you from possible infection.
| |
| | |
| ==What to expect (Outlook/Prognosis)==
| |
| The Prognosis for diarrhea is usually good. Diarrhea is common and usually goes away on its own unless it is an underlying symptom of a chronic disease. It is important to replace lost fluid due to diarrhea because if you become severely dehydrated it can be fatal.
| |
| | |
| ==Sources==
| |
| http://digestive.niddk.nih.gov/ddiseases/pubs/diarrhea/
| |
| | |
| [[Category:Patient information]]
| |
| [[Category:primary care]]
| |
| [[Category:Gastroenterology]]
| |
| [[Category:Water-borne diseases]]
| |
| [[Category:Digestive disease symptoms]]
| |
| [[Category:Conditions diagnosed by stool test]]
| |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| {{WH}}
| |
| {{WS}}
| |
| | |
| ==Pathophysiology Diarrhea==
| |
| Normal fluid intake for an adult is about 2 L/d. The average amount of gastrointestinal secretions (composed of salivary glands, gastric, biliary, and pancreatic secretions) is 7-8 L/d, depending on the weight and age. The absorptive surface of the small intestine is formed by villis that reabsorb the majority of secreted water and electrolytes. The small intestine absorbs 75% of upper GI tract secretions. The rest of the secretions absorb in the large intestine. Colon absorbs 90% of its exposed volume, means that colon is the most effective absorbing organ in the GI system.<br>
| |
| Decrease in the small intestine absorption, regardless of causes, may not cause diarrhea unless, there is a dysfunction in colon or the volume of the secretions exceeds the absorptive ability of the colon.
| |
| | |
| | |
| {{Family tree | | | | | | B01 | | | |B01='''[[CNS]] dysregulation and [[psychosocial factors]]''' }}
| |
| {{Family tree | | | | | | |!| | | | | }}
| |
| {{Family tree | | | | | | |!| | | | | }}
| |
| {{familytree |boxstyle=text-align: left; | A01 |-|-| A02 |-|-|-| A03 | |A01= '''Intrinsic [[gastrointestinal]] factors''': <br> • [[Motor]] abnormalities <br>• [[Visceral]] [[hypersensitivity]] <br>• [[Immune]] activation and [[mucosal]] inflammation <br>• Altered [[gut]] [[microbiota]] <br>• Abnormal [[serotonin]] pathways | A02= '''IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME'''| A03='''Genetic factors''': <br>• Twin concordance <br>• Familial aggregation <br>• [[SNPs|Single nucleotide polymorphisms(SNPs)]] <br>• TNF polymorphism}}
| |
| | |
| | |
| {{Family tree | | | | | | |!| | | | | }}
| |
| {{Family tree | | | | | | |!| | | | | }}
| |
| {{familytree |boxstyle=text-align: left; | | | | | | B01 | | | |B01= '''Environmental factors''': <br>•Diet <br>•[[Infections]]}}
| |
| {{Family tree/end}}
| |
| | |
| ==References== | | ==References== |
| {{reflist|2}} | | {{reflist|2}} |
| Line 125: |
Line 5: |
| {{WH}} | | {{WH}} |
| {{WS}} | | {{WS}} |
|
| |
| [[Category:Primary care]]
| |
| [[Category:Gastroenterology]]
| |
|
| |
| [[Category:Needs overview]]
| |
| ==D/Ds==
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| ==Differential Diagnosis of Diarrhea of other diseases==
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of diarrhea, click [[#Diarrhea|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of acute diarrhea, click [[Acute diarrhea differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of chronic diarrhea, click [[Chronic diarrhea differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of traveler's diarrhea, click [[Traveler's diarrhea differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of acute watery diarrhea, click [[Acute watery diarrhea differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of acute bloody diarrhea, click [[Acute bloody diarrhea differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of acute fatty diarrhea, click [[Acute fatty diarrhea differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of chronic watery diarrhea, click [[Chronic watery diarrhea differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of chronic bloody diarrhea, click [[Chronic bloody diarrhea differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of chronic fatty diarrhea, click [[Chronic fatty diarrhea differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of acute diarrhea and fever, click [[Acute diarrhea and fever differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of chronic diarrhea and fever, click [[Chronic diarrhea and fever differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of acute diarrhea and abdominal pain, click [[Acute diarrhea and abdominal pain differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of chronic diarrhea and abdominal pain, click [[Chronic diarrhea and abdominal pain differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of acute diarrhea and weight loss, click [[Acute diarrhea and weight loss differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of chronic diarrhea and weight loss, click [[Chronic diarrhea and weight loss differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of acute diarrhea, fever, and abdominal pain, click [[Acute diarrhea, fever, and abdominal pain differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of chronic diarrhea, fever, and abdominal pain, click [[Chronic diarrhea, fever, and abdominal pain differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of acute diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss, click [[Acute diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| '''''To review the differential diagnosis of chronic diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss, click [[Chronic diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss differential diagnosis|here]].'''''
| |
|
| |
| ===Diarrhea===
| |
| '''The following table outlines the major differential diagnoses of diarrhea.'''<ref name="Casburn-JonesFarthing2004">{{cite journal|last1=Casburn-Jones|first1=Anna C|last2=Farthing|first2=Michael Jg|title=Traveler's diarrhea|journal=Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology|volume=19|issue=6|year=2004|pages=610–618|issn=0815-9319|doi=10.1111/j.1440-1746.2003.03287.x}}</ref><ref name="KamatMathur2006">{{cite journal|last1=Kamat|first1=Deepak|last2=Mathur|first2=Ambika|title=Prevention and Management of Travelers’ Diarrhea|journal=Disease-a-Month|volume=52|issue=7|year=2006|pages=289–302|issn=00115029|doi=10.1016/j.disamonth.2006.08.003}}</ref><ref name="PfeifferDuPont2012">{{cite journal|last1=Pfeiffer|first1=Margaret L.|last2=DuPont|first2=Herbert L.|last3=Ochoa|first3=Theresa J.|title=The patient presenting with acute dysentery – A systematic review|journal=Journal of Infection|volume=64|issue=4|year=2012|pages=374–386|issn=01634453|doi=10.1016/j.jinf.2012.01.006}}</ref><ref name="pmid24506120">{{cite journal |vauthors=Barr W, Smith A |title=Acute diarrhea |journal=Am Fam Physician |volume=89 |issue=3 |pages=180–9 |year=2014 |pmid=24506120 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid29255768">{{cite journal |vauthors=Amil Dias J |title=Celiac Disease: What Do We Know in 2017? |journal=GE Port J Gastroenterol |volume=24 |issue=6 |pages=275–278 |year=2017 |pmid=29255768 |doi=10.1159/000479881 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid29254859">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kotloff KL, Riddle MS, Platts-Mills JA, Pavlinac P, Zaidi AKM |title=Shigellosis |journal=Lancet |volume= |issue= |pages= |year=2017 |pmid=29254859 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33296-8 |url=}}</ref><ref name="Yamamoto-FurushoBosques-Padilla2017">{{cite journal|last1=Yamamoto-Furusho|first1=J.K.|last2=Bosques-Padilla|first2=F.|last3=de-Paula|first3=J.|last4=Galiano|first4=M.T.|last5=Ibañez|first5=P.|last6=Juliao|first6=F.|last7=Kotze|first7=P.G.|last8=Rocha|first8=J.L.|last9=Steinwurz|first9=F.|last10=Veitia|first10=G.|last11=Zaltman|first11=C.|title=Diagnóstico y tratamiento de la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal: Primer Consenso Latinoamericano de la Pan American Crohn's and Colitis Organisation|journal=Revista de Gastroenterología de México|volume=82|issue=1|year=2017|pages=46–84|issn=03750906|doi=10.1016/j.rgmx.2016.07.003}}</ref><ref name="BorbélyOsterwalder2017">{{cite journal|last1=Borbély|first1=Yves M|last2=Osterwalder|first2=Alice|last3=Kröll|first3=Dino|last4=Nett|first4=Philipp C|last5=Inglin|first5=Roman A|title=Diarrhea after bariatric procedures: Diagnosis and therapy|journal=World Journal of Gastroenterology|volume=23|issue=26|year=2017|pages=4689|issn=1007-9327|doi=10.3748/wjg.v23.i26.4689}}</ref><ref name="CrawfordRamani2017">{{cite journal|last1=Crawford|first1=Sue E.|last2=Ramani|first2=Sasirekha|last3=Tate|first3=Jacqueline E.|last4=Parashar|first4=Umesh D.|last5=Svensson|first5=Lennart|last6=Hagbom|first6=Marie|last7=Franco|first7=Manuel A.|last8=Greenberg|first8=Harry B.|last9=O'Ryan|first9=Miguel|last10=Kang|first10=Gagandeep|last11=Desselberger|first11=Ulrich|last12=Estes|first12=Mary K.|title=Rotavirus infection|journal=Nature Reviews Disease Primers|volume=3|year=2017|pages=17083|issn=2056-676X|doi=10.1038/nrdp.2017.83}}</ref><ref name="pmid11068510">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kist M |title=[Chronic diarrhea: value of microbiology in diagnosis] |language=German |journal=Praxis (Bern 1994) |volume=89 |issue=39 |pages=1559–65 |year=2000 |pmid=11068510 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid4014291">{{cite journal |vauthors=Guerrant RL, Shields DS, Thorson SM, Schorling JB, Gröschel DH |title=Evaluation and diagnosis of acute infectious diarrhea |journal=Am. J. Med. |volume=78 |issue=6B |pages=91–8 |year=1985 |pmid=4014291 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid10575169">{{cite journal |vauthors=López-Vélez R, Turrientes MC, Garrón C, Montilla P, Navajas R, Fenoy S, del Aguila C |title=Microsporidiosis in travelers with diarrhea from the tropics |journal=J Travel Med |volume=6 |issue=4 |pages=223–7 |year=1999 |pmid=10575169 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="WahnschaffeIgnatius2009">{{cite journal|last1=Wahnschaffe|first1=Ulrich|last2=Ignatius|first2=Ralf|last3=Loddenkemper|first3=Christoph|last4=Liesenfeld|first4=Oliver|last5=Muehlen|first5=Marion|last6=Jelinek|first6=Thomas|last7=Burchard|first7=Gerd Dieter|last8=Weinke|first8=Thomas|last9=Harms|first9=Gundel|last10=Stein|first10=Harald|last11=Zeitz|first11=Martin|last12=Ullrich|first12=Reiner|last13=Schneider|first13=Thomas|title=Diagnostic value of endoscopy for the diagnosis of giardiasis and other intestinal diseases in patients with persistent diarrhea from tropical or subtropical areas|journal=Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology|volume=42|issue=3|year=2009|pages=391–396|issn=0036-5521|doi=10.1080/00365520600881193}}</ref><ref name="pmid27765536">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mena Bares LM, Carmona Asenjo E, García Sánchez MV, Moreno Ortega E, Maza Muret FR, Guiote Moreno MV, Santos Bueno AM, Iglesias Flores E, Benítez Cantero JM, Vallejo Casas JA |title=75SeHCAT scan in bile acid malabsorption in chronic diarrhoea |journal=Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol |volume=36 |issue=1 |pages=37–47 |year=2017 |pmid=27765536 |doi=10.1016/j.remn.2016.08.005 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid19365159">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gibson RJ, Stringer AM |title=Chemotherapy-induced diarrhoea |journal=Curr Opin Support Palliat Care |volume=3 |issue=1 |pages=31–5 |year=2009 |pmid=19365159 |doi=10.1097/SPC.0b013e32832531bb |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23384808">{{cite journal |vauthors=Abraham BP, Sellin JH |title=Drug-induced, factitious, & idiopathic diarrhoea |journal=Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol |volume=26 |issue=5 |pages=633–48 |year=2012 |pmid=23384808 |doi=10.1016/j.bpg.2012.11.007 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid25692805">{{cite journal |vauthors=Reintam Blaser A, Deane AM, Fruhwald S |title=Diarrhoea in the critically ill |journal=Curr Opin Crit Care |volume=21 |issue=2 |pages=142–53 |year=2015 |pmid=25692805 |doi=10.1097/MCC.0000000000000188 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid17373914">{{cite journal |vauthors=McMahan ZH, DuPont HL |title=Review article: the history of acute infectious diarrhoea management--from poorly focused empiricism to fluid therapy and modern pharmacotherapy |journal=Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. |volume=25 |issue=7 |pages=759–69 |year=2007 |pmid=17373914 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2036.2007.03261.x |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23384801">{{cite journal |vauthors=Schiller LR |title=Definitions, pathophysiology, and evaluation of chronic diarrhoea |journal=Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol |volume=26 |issue=5 |pages=551–62 |year=2012 |pmid=23384801 |doi=10.1016/j.bpg.2012.11.011 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid3523719">{{cite journal |vauthors=Giannella RA |title=Chronic diarrhea in travelers: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations |journal=Rev. Infect. Dis. |volume=8 Suppl 2 |issue= |pages=S223–6 |year=1986 |pmid=3523719 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid16151544">{{cite journal| author=Silverberg MS, Satsangi J, Ahmad T, Arnott ID, Bernstein CN, Brant SR et al.| title=Toward an integrated clinical, molecular and serological classification of inflammatory bowel disease: report of a Working Party of the 2005 Montreal World Congress of Gastroenterology. | journal=Can J Gastroenterol | year= 2005 | volume= 19 Suppl A | issue= | pages= 5A-36A | pmid=16151544 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16151544 }}</ref><ref name="pmid12135027">{{cite journal| author=Sauter GH, Moussavian AC, Meyer G, Steitz HO, Parhofer KG, Jüngst D| title=Bowel habits and bile acid malabsorption in the months after cholecystectomy. | journal=Am J Gastroenterol | year= 2002 | volume= 97 | issue= 7 | pages= 1732-5 | pmid=12135027 | doi=10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05779.x | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=12135027 }}</ref><ref name="pmid1702075">{{cite journal| author=Maiuri L, Raia V, Potter J, Swallow D, Ho MW, Fiocca R et al.| title=Mosaic pattern of lactase expression by villous enterocytes in human adult-type hypolactasia. | journal=Gastroenterology | year= 1991 | volume= 100 | issue= 2 | pages= 359-69 | pmid=1702075 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=1702075 }}</ref><ref name="pmid14439871">{{cite journal| author=RUBIN CE, BRANDBORG LL, PHELPS PC, TAYLOR HC| title=Studies of celiac disease. I. The apparent identical and specific nature of the duodenal and proximal jejunal lesion in celiac disease and idiopathic sprue. | journal=Gastroenterology | year= 1960 | volume= 38 | issue= | pages= 28-49 | pmid=14439871 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=14439871 }}</ref><ref name="pmid8209928">{{cite journal| author=Konvolinka CW| title=Acute diverticulitis under age forty. | journal=Am J Surg | year= 1994 | volume= 167 | issue= 6 | pages= 562-5 | pmid=8209928 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=8209928 }} </ref><ref name="pmid16698746">{{cite journal| author=Satsangi J, Silverberg MS, Vermeire S, Colombel JF| title=The Montreal classification of inflammatory bowel disease: controversies, consensus, and implications. | journal=Gut | year= 2006 | volume= 55 | issue= 6 | pages= 749-53 | pmid=16698746 | doi=10.1136/gut.2005.082909 | pmc=1856208 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16698746 }} </ref><ref name="pmid12700377">{{cite journal| author=Haque R, Huston CD, Hughes M, Houpt E, Petri WA| title=Amebiasis. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 2003 | volume= 348 | issue= 16 | pages= 1565-73 | pmid=12700377 | doi=10.1056/NEJMra022710 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=12700377 }} </ref><ref name="pmid8694025">{{cite journal| author=Hertzler SR, Savaiano DA| title=Colonic adaptation to daily lactose feeding in lactose maldigesters reduces lactose intolerance. | journal=Am J Clin Nutr | year= 1996 | volume= 64 | issue= 2 | pages= 232-6 | pmid=8694025 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=8694025 }} </ref><ref name="pmid9414969">{{cite journal| author=Briet F, Pochart P, Marteau P, Flourie B, Arrigoni E, Rambaud JC| title=Improved clinical tolerance to chronic lactose ingestion in subjects with lactose intolerance: a placebo effect? | journal=Gut | year= 1997 | volume= 41 | issue= 5 | pages= 632-5 | pmid=9414969 | doi= | pmc=1891556 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=9414969 }} </ref><ref name="pmid15391722">{{cite journal| author=BLACK-SCHAFFER B| title=The tinctoral demonstration of a glycoprotein in Whipple's disease. | journal=Proc Soc Exp Biol Med | year= 1949 | volume= 72 | issue= 1 | pages= 225-7 | pmid=15391722 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15391722 }} </ref>
| |
|
| |
| <span style="font-size:85%">'''Abbreviations:''' '''GI:''' [[Gastrointestinal tract|Gastrointestinal]], '''CBC''': [[Complete blood count]], '''WBC:''' [[White blood cells|White blood cell]], '''RBC''': [[Red blood cell]], '''Plt:''' [[Platelet]], '''Hgb:''' [[Hemoglobin]], '''ESR''': [[Erythrocyte sedimentation rate]], '''CRP''': [[C-reactive protein|C–reactive protein]], '''IgE:''' [[Immunoglobulin E]], '''IgA:''' [[Immunoglobulin A]], '''ETEC:''' [[Escherichia coli enteritis]], '''EPEC''': [[Escherichia coli|Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli]], '''EIEC''': [[Escherichia coli enteritis|Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli]], '''EHEC''': [[Escherichia coli|Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli]], '''EAEC''': [[Escherichia coli enteritis|Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli]], '''Nl''': Normal, '''ASCA''': [[Anti saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies]], '''ANCA''': [[Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody|Anti–neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody]], '''DNA''': [[DNA|Deoxyribonucleic acid]], '''CFTR''': [[Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator]], '''SLC10A2''': [[SLC10A2|Solute carrier family 10 member 2]], '''SeHCAT''': [[SeHCAT|Selenium homocholic acid taurine or tauroselcholic acid]], '''IEL''': Intraepithelial [[Lymphocyte|lymphocytes]], '''MRCP''': [[Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography]], '''ANA''': [[Antinuclear antibodies]], '''AMA''': [[Anti-mitochondrial antibody]], '''LDH''': [[Lactate dehydrogenase]], '''CPK''': [[Creatine phosphokinase]], '''PCR''': [[Polymerase chain reaction]], '''ELISA''': [[Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)|Enzyme–linked immunosorbent assay]], '''LT''': Heat–labile [[enterotoxin]], ST: Heat–stable [[enterotoxin]], '''RT-PCR''': Reverse–transcriptase [[polymerase chain reaction]], '''CD4:''' [[CD4|Cluster of differentiation 4]], '''HIV''': [[Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)|Human immunodeficiency virus]], '''RUQ''': [[RUQ|Right-upper quadrant]], '''VIP''': [[Vasoactive intestinal peptide]], '''GI:''' [[Gastrointestinal tract|Gastrointestinal]], '''FAP''': [[Familial adenomatous polyposis]], '''HNPCC''': [[Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer]], '''MTP''': [[Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein]], '''Scl‑70''': Anti–[[Type I topoisomerase|topoisomerase I]], '''TSH''': [[Thyroid-stimulating hormone]], '''T4''': [[Thyroxine]], '''T3''': [[Triiodothyronine]], '''DTR''': [[Deep tendon reflex]], '''RNA''': [[RNA|Ribonucleic acid]]</span>
| |
|
| |
| {| class="wikitable" style="border: 0px; font-size: 100%; margin: 3px;" align="center"
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Categories
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause
| |
| | colspan="9" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |'''Clinical manifestation'''
| |
| ! colspan="9" rowspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |'''Lab findings'''
| |
| ! rowspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Extra intestinal findings
| |
| ! rowspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause/Pathogenesis
| |
| ! rowspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Gold standard diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="8" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Symptoms
| |
| ! rowspan="4" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI signs
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Duration
| |
| ! colspan="3" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea
| |
| ! rowspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever
| |
| ! rowspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! rowspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Stool exam
| |
| | colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |'''CBC'''
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other lab findings
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Acute
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Chronic
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Watery
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bloody
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fatty
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |RBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Ova/Parasite
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Osmotic gap
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hgb
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Plt
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="15" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Gastrointestinal
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Crohns disease|Crohn's disease]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| * Oral [[mucosal]] lesions
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Anti saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies]] (ASCA)
| |
| * [[Vitamin B12]] deficiency
| |
| * Elevated [[erythrocyte sedimentation rate|ESR]]
| |
| * Elevated [[C-reactive protein|CRP]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Uveitis]]
| |
| * [[Arthritis]]
| |
| * [[Erythema nodosum]]
| |
| * [[Pyoderma gangrenosum]]
| |
| * [[Amyloidosis]]
| |
| * Venous and arterial [[thromboembolism]]
| |
| * [[Kidney stone|Renal stones]]
| |
| * [[Bronchiectasis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Abnormal immune response to self [[antigens]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Colonoscopy]] with [[biopsy]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Ulcerative colitis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| * [[Blood]] on [[rectal examination]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody|Anti–neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody]] ([[P-ANCA|P–ANCA]])
| |
| * [[Hypoalbuminemia]]
| |
| * [[Hypokalemia]]
| |
| * [[Hypomagnesemia]]
| |
| * Elevated [[Erythrocyte sedimentation rate|ESR]]
| |
| * Elevated [[C-reactive protein|CRP]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Skin rash]]
| |
| * [[Iritis]]
| |
| * [[Uveitis]]
| |
| * Seronegative [[arthritis]]
| |
| * [[Clubbing]]
| |
| * [[Erythema nodosum]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Abnormal immune response to self [[antigens]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Colonoscopy]] with [[biopsy]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Celiac disease]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Abdominal distention]]
| |
| * Increased [[bowel]] sounds
| |
| * Oral [[Mucous membrane|mucosal]] lesions
| |
| * [[Hepatosplenomegaly]]
| |
| * [[Ascites]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Fat droplets on [[sudan stain]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[IgA]] endomysial [[antibody]]
| |
| * Anti–tissue [[transglutaminase]] [[antibody]]
| |
| * [[Anti-gliadin antibodies|Anti–gliadin antibody]]
| |
| * [[Fat soluble vitamins]] deficiency
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Malabsorption]]
| |
| * [[Dementia]]
| |
| * [[Dermatitis herpetiformis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[HLA-DQ2|HLA–DQ2]]
| |
| * [[HLA-DQ8|HLA–DQ8]]
| |
| * Innate responses to wheat [[Protein|proteins]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[IgA]] endomysial [[antibody]]
| |
| * Anti–tissue [[transglutaminase]] [[antibody]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Duration
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI signs
| |
| ! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Stool exam
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |CBC
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other lab findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Extra intestinal findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause/Pathogenesis
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Gold standard diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Acute
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Chronic
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Watery
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bloody
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fatty
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |RBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Ova/Parasite
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Osmotic gap
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hgb
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Plt
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Cystic fibrosis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal distension|Abdominal distention]]
| |
| *[[Hepatosplenomegaly]]
| |
| *[[Rectal prolapse]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Fat droplets on [[sudan stain]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Positive [[DNA]] analysis for [[CFTR|cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator]] [[CFTR|(CFTR)]]
| |
| * Nasal transepithelial potential difference
| |
| * [[Fat soluble vitamins]] deficiency
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Malabsorption]]
| |
| * Recurrent [[respiratory tract infection]]
| |
| * [[Bronchiectasis]]
| |
| * [[Diabetes mellitus]]
| |
| * [[Scoliosis]]
| |
| * [[Infertility]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Mutations in the [[cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator]] ([[CFTR]]) protein
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Positive [[genetic testing]]
| |
| * Elevated [[Sweat chloride test|sweat chloride]] ≥60 mmol/L
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Chronic pancreatitis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Tenderness (medicine)|Abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Fat droplets on [[sudan stain]]
| |
| * Positive [[fecal elastase]] measurement
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Slightly elevated [[amylase]] and [[lipase]]
| |
| * Abnormal pancreatic function test
| |
| * [[Secretin]] stimulation test
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Malabsorption]]
| |
| * [[Diabetes mellitus]]
| |
| * [[Pancreatic pseudocyst]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Toxin|Toxins]]
| |
| * Recurrent [[acute pancreatitis]]
| |
| * [[Genetics|Genetic]] predesposition
| |
| * [[Autoimmunity|Autoimmune]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography]] ([[Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography|MRCP]])
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Bile acid malabsorption]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Fat droplets on [[sudan stain]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Reduced [[cholesterol]] level
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Malabsorption]]
| |
| *[[Hypotension]]
| |
| *[[Tachycardia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Genetic defects in ''[[SLC10A2]]''
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[SeHCAT]] test
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Microscopic colitis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| * Fecal [[incontinence]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Hypokalemia]]
| |
| * Elevated [[C-reactive protein|CRP]]
| |
| * Positive [[autoantibodies]] include:
| |
| **RF
| |
| **[[ANA]]
| |
| **[[Anti-mitochondrial antibody|AMA]]
| |
| **[[ANCA]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Arthritis]]
| |
| * [[Uveitis]]
| |
| * [[Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura]]
| |
| * Pleuro [[pericarditis]]
| |
| * [[Hypothyroidism]]
| |
| * [[Psoriasis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Mucosal]] [[immune responses]] to luminal factors in a genetically predisposed individual
| |
| * Drug–induced
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Colonoscopy]] with [[mucosal]] [[biopsy]] with [[mononuclear]] infiltrates:
| |
| ** [[Collagenous colitis]] is characterized by a colonic subepithelial [[collagen]] band >10 micrometers in diameter
| |
| ** [[Lymphocytic]] [[colitis]] is characterized by ≥20 intraepithelial [[lymphocytes]] (IEL) per 100 surface epithelial cells
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Duration
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI signs
| |
| ! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Stool exam
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |CBC
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other lab findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Extra intestinal findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause/Pathogenesis
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Gold standard diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Acute
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Chronic
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Watery
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bloody
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fatty
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |RBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Ova/Parasite
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Osmotic gap
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hgb
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Plt
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Infective colitis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *Rebound [[Tenderness (medicine)|abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[stool culture]]
| |
| *Positive fecal calprotectin
| |
| *Positive fecal [[lactoferrin]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Elevated [[C-reactive protein|CRP]]
| |
| *Elevated [[Erythrocyte sedimentation rate|ESR]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Arthritis]]
| |
| * [[Uveitis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Salmonella|''Salmonella'']]
| |
| *[[Shigella|''Shigella'']]
| |
| *[[Campylobacter|''Campylobacter'']]
| |
| *''[[Escherichia coli|E. coli 0157:H7]]''
| |
| *[[Clostridium difficile|''Clostridium difficile'']]
| |
| *[[Entamoeba histolytica|''Entamoeba histolytica'']]
| |
| *[[Adenoviridae|''Adenovirus'']]
| |
| *[[Cytomegalovirus|''Cytomegalovirus'']]
| |
| *[[Herpes simplex virus|''Herpes simplex virus'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Stool culture]]
| |
| *[[Blood culture]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Ischemic colitis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *Hyperactive then absent [[Stomach rumble|bowel sounds]]
| |
| *[[Tenderness (medicine)|Abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Elevated [[C-reactive protein|CRP]]
| |
| *Elevated [[Erythrocyte sedimentation rate|ESR]]
| |
| *Elevated serum [[Lactic acid|lactate]]
| |
| *Elevated [[lactate dehydrogenase]] ([[Lactate dehydrogenase|LDH]])
| |
| *Elevated [[Creatine kinase|creatine phosphokinase]] ([[Creatine kinase|CPK]])
| |
| *Elevated [[amylase]]
| |
| *[[Hypoalbuminemia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Henoch-Schönlein purpura|IgA vasculitis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Thrombophilia|Hypercoagulability]]
| |
| *Nonocclusive [[Ischemic colitis|colonic ischemia]]
| |
| *[[Embolism|Embolic]] and [[Thrombosis|thrombotic]] arterial occlusion
| |
| *[[Mesenteric vein thrombosis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Abdominal [[Computed tomography|CT scan]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Lactose intolerance]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Abdominal tenderness ]]
| |
| * [[Abdominal distention]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Lactose tolerance test
| |
| * Genetic testing
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Headache]]
| |
| * [[Vertigo]]
| |
| * [[Memory impairment]]
| |
| * [[Lethargy]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Reduction of lactase enzyme activity or inability to produce persistent [[lactase]]
| |
| * Congenital [[lactase deficiency]]
| |
| * Secondary lactose malabsorption
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Small bowel]] [[biopsy]]
| |
| * Lactose breath hydrogen test
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Irritable bowel syndrome]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| * [[Abdominal distention]]
| |
| * Normal [[Stomach rumble|bowel sounds]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Anxiety]]
| |
| *[[Palpitation]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Unknown
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Diagnosis of exclusion
| |
| |-
| |
| ! rowspan="43" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Infection
| |
| ! rowspan="28" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bacterial
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Duration
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI signs
| |
| ! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Stool exam
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |CBC
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other lab findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Extra intestinal findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause/Pathogenesis
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Gold standard diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Acute
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Chronic
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Watery
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bloody
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fatty
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |RBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Ova/Parasite
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Osmotic gap
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hgb
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Plt
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Whipple's disease]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Hepatosplenomegaly]]
| |
| * [[Ascites]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Positive [[fecal fat]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓/↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Hypoalbuminemia]]
| |
| *[[Fat soluble vitamins]] deficiency
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Malabsorption]]
| |
| * [[Ocular motility disorders|Abnormal extraocular movement]]
| |
| * [[Lymphadenopathy]]
| |
| * [[Hyperpigmentation]]
| |
| * [[Uveitis]]
| |
| * [[Endocarditis]]
| |
| * [[Encephalitis]]
| |
| * [[Dementia]]
| |
| * [[Pleural effusion]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Tropheryma whipplei|''Tropheryma whipplei'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Small intestine]] [[biopsy]] for [[Tropheryma whipplei]] testing
| |
| * [[PCR]] testing
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Tropical sprue]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Angular [[stomatitis]]
| |
| * Oral mucosal lesion
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[stool culture]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Fat soluble vitamins]] deficiency
| |
| * [[Vitamin B12 deficiency]]
| |
| * [[Folate deficiency]]
| |
| * [[Hypokalemia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Myalgia]]
| |
| *[[Neuropathy]]
| |
| *[[Edema]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * ''[[Escherichia coli]]''
| |
| * ''[[Klebsiella pneumoniae]]''
| |
| * ''[[Enterobacter cloacae]]''
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Diagnosis of exclusion
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Small bowel bacterial overgrowth syndrome|Small bowel bacterial overgrowth]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Abdominal distension|Abdominal distention]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[stool culture]]
| |
| *Positive [[fecal fat]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Hypoalbuminemia]]
| |
| * Abnormal [[Hydrogen Breath Test|hydrogen breath test]]
| |
| * [[Lactic acidosis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Malabsorption]]
| |
| * [[Rosacea]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Excess bacteria in the [[small intestine]]
| |
| * Alterations in [[Intestine|intestinal]] [[anatomy]] or GI motility
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Diagnosis of exclusion
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Pseudomembranous enterocolitis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Generalized [[Tenderness (medicine)|abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| * [[Abdominal distention]]
| |
| * [[Rebound tenderness|Rebound abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)|Enzyme–linked immunosorbent assay]] ([[Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)|ELISA]])
| |
| * [[Polymerase chain reaction]] ([[Polymerase chain reaction|PCR]]) assay or ''[[Clostridium difficile infection|C. difficile]]'' antigen
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Elevated [[Creatinine|serum creatinine]]
| |
| * [[Hypoalbuminemia]]
| |
| * Elevated [[lactic acid]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Dehydration]]
| |
| * [[Acute kidney injury]]
| |
|
| |
| * [[Bacteremia]]
| |
| * [[Reactive arthritis]]
| |
| * [[Necrotizing fasciitis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Clostridium difficile|''Clostridium difficile'']]
| |
| * Recent [[antibiotics]] use
| |
| * Recent [[surgery]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Stool examination|Stool exam]]
| |
| * Pseudomembranes on [[colonoscopy]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Duration
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI signs
| |
| ! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Stool exam
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |CBC
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other lab findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Extra intestinal findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause/Pathogenesis
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Gold standard diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Acute
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Chronic
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Watery
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bloody
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fatty
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |RBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Ova/Parasite
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Osmotic gap
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hgb
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Plt
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" | [[Campylobacteriosis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *Diffuse [[abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[stool culture]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Toxic megacolon]]
| |
| *[[Sepsis]]
| |
| *[[Arthritis]]
| |
| *[[Endocarditis]]
| |
| *[[Guillain-Barré syndrome|Guillain–Barré syndrome]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Campylobacter jejuni|''Campylobacter jejuni'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Stool culture]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Salmonellosis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal distention]]
| |
| *Diffuse [[abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| *[[Hepatosplenomegaly]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[stool culture]]
| |
| *Positive serologic testing
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Hypokalemia]]
| |
| *[[Hypernatremia]]
| |
| *[[Hyponatremia]]
| |
| * [[Hypercalciuria]]
| |
| * [[Hypocitraturia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Post-infectious arthritis|Post–infectious arthritis]]
| |
| * [[Obtundation]]
| |
| * [[Bacteremia]]
| |
| * [[Pericarditis]]
| |
| * [[Pyelonephritis]]
| |
| *[[Brain abscess]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Salmonella|''Salmonella'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Stool culture]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Shigellosis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| * [[Abdominal distention]]
| |
| * Hyperactive [[Stomach rumble|bowel sounds]]
| |
| * Diffuse [[abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[stool culture]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑/↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Elevated [[C-reactive protein|CRP]]
| |
| *Elevated [[Erythrocyte sedimentation rate|ESR]]
| |
| *[[Hyponatremia]]
| |
| * [[Hypoglycemia]]
| |
| * [[Azotemia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Headache]]
| |
| * [[Lethargy]]
| |
| * [[Seizures]]
| |
| * [[Delirium]]
| |
| * [[Post-infectious arthritis|Post–infectious arthritis]]
| |
| * [[Myocarditis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Shigella|''Shigella'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Stool culture]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Duration
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI signs
| |
| ! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Stool exam
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |CBC
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other lab findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Extra intestinal findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause/Pathogenesis
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Gold standard diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Acute
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Chronic
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Watery
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bloody
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fatty
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |RBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Ova/Parasite
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Osmotic gap
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hgb
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Plt
| |
| |-
| |
| ! rowspan="5" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Escherichia coli enteritis]]
| |
| | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[ETEC|'''ETEC''']]
| |
| ([[Traveler's diarrhea]])
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *Diffuse [[abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[stool culture]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Escherichia coli|''Enterotoxigenic escherichia coli'']]
| |
| *[[Enterotoxin|Enterotoxins]]:
| |
| **Heat–labile [[enterotoxin]] (LT)
| |
| **Heat–stable [[enterotoxin]] (ST)
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Stool culture]]
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[EPEC|'''EPEC''']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *Diffuse [[abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[stool culture]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *''[[Enteropathogenic E. coli]]''
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Hybridization probe|DNA probe]] or [[polymerase chain reaction]] ([[Polymerase chain reaction|PCR]]) of the ''EPEC'' adherence factor
| |
| *[[Stool culture]]
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[EIEC|'''EIEC''']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *Diffuse [[abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[stool culture]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Escherichia coli enteritis|''Enteroinvasive E. coli'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Hybridization probe|DNA probe]]
| |
| *[[Stool culture]]
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[EHEC|'''EHEC''']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *Diffuse [[abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[stool culture]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Azotemia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Hemolytic-uremic syndrome|Hemolytic uremic syndrome]] ([[Hemolytic-uremic syndrome|HUS]])
| |
| *[[Renal insufficiency|Renal failure]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Enterohemorrhagic escherichica coli|''Enterohemorrhagic E. coli'']]
| |
| *[[Shiga toxin|Shiga toxins]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Stool culture]]
| |
| |-
| |
| | style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[EAEC|'''EAEC''']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *Diffuse [[abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[stool culture]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Chronic infection in [[Immunodeficiency|immunocompromised]] patients
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Escherichia coli enteritis|''Enteroaggregative E. coli'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Stool culture]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Duration
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI signs
| |
| ! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Stool exam
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |CBC
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other lab findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Extra intestinal findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause/Pathogenesis
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Gold standard diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Acute
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Chronic
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Watery
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bloody
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fatty
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |RBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Ova/Parasite
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Osmotic gap
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hgb
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Plt
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Yersinia enterocolitica]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| * [[Abdominal distention]]
| |
| * Hyperactive [[Stomach rumble|bowel sounds]]
| |
| * Diffuse [[abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[stool culture]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Bacteremia]]
| |
| *[[Reactive arthritis]]
| |
| *[[Glomerulonephritis]]
| |
| *[[Endocarditis]]
| |
| *[[Erythema nodosum]]
| |
| *[[Abscess]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Yersinia enterocolitica|''Yersinia enterocolitica'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Stool culture]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Vibrio cholerae|Vibrio cholera]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[stool culture]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Azotemia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Severe [[dehydration]]
| |
| *Decreased [[Turgor|skin turgor]]
| |
| *[[Oliguria]]
| |
| *[[Renal insufficiency|Renal failure]]
| |
| *[[Cramp|Muscle cramps]]
| |
| *[[Seizure]]
| |
| *[[Somnolence]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Cholera toxin]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Stool culture]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Aeromonas]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| * [[Abdominal distention]]
| |
| * Hyperactive [[Stomach rumble|bowel sounds]]
| |
| * Diffuse [[abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[stool culture]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Wound [[infection]]
| |
| *[[Bacteremia]]
| |
| *[[Hemolytic-uremic syndrome|Hemolytic uremic syndrome]]
| |
| *[[Meningitis]]
| |
| *[[Ocular]] infection
| |
| *[[Pneumonia]]
| |
| *[[Urinary tract infection]]
| |
| *[[Osteomyelitis]]
| |
| *[[Peritonitis]]
| |
| *[[Acute cholecystitis]]
| |
| *[[Opportunistic infection|Opportunistic infections]] in [[Immunodeficiency|immunocompromised]] patients
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *''[[Aeromonas]]'' virulence factors including [[Endotoxin|endotoxins]], [[Hemolysin|hemolysins]], [[Enterotoxin|enterotoxins]], and adherence factors
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Blood culture]]
| |
| *Wound [[Culture collection|culture]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Duration
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI signs
| |
| ! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Stool exam
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |CBC
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other lab findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Extra intestinal findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause/Pathogenesis
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Gold standard diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Acute
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Chronic
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Watery
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bloody
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fatty
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |RBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Ova/Parasite
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Osmotic gap
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hgb
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Plt
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Plesiomonas shigelloides|Plesiomonas]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| * Hyperactive [[Stomach rumble|bowel sounds]]
| |
| * Diffuse [[abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[stool culture]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Opportunistic infection|Opportunistic infections]] in [[Immunodeficiency|immunocompromised]] patients or [[Hepato-biliary diseases|hepatobiliary disease]]
| |
| *[[Bacteremia]]
| |
| *[[Cellulitis]] and [[Skin and soft-tissue infections|skin abscesses]]
| |
| *[[Peritonitis]]
| |
| *[[Meningoencephalitis]]
| |
| *[[Ocular]] [[infection]]
| |
| *[[Pneumonia]]
| |
| *[[Prosthetic devices|Prosthetic]] joint [[infection]]
| |
| *Septic [[Pregnancy termination complications|abortion]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Plesiomonas shigelloides|''Plesiomonas shigelloides'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Blood culture]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Mycobacterium avium complex]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal distension|Abdominal distention]]
| |
| *[[Hepatosplenomegaly]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Elevated [[Liver function tests|liver enzymes]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Opportunistic infection]] in [[Immunodeficiency|immunocompromised]] patients
| |
| *[[Pulmonary]] [[infection]]
| |
| *[[Lymphadenopathy|Adenopathy]]
| |
| *[[Sleep hyperhidrosis|Night sweats]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Mycobacterium avium complex|''Mycobacterium avium complex'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Blood culture]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Foodborne illness|Food poisoning]]
| |
| * [[Staphylococcus aureus]]
| |
| * [[Bacillus cereus]]
| |
| * [[Clostridium perfringens]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal distension|Abdominal distention]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[stool culture]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *History of travel or ingestion of infected food
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Enterotoxin|Enterotoxins]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Stool culture]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! rowspan="8" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Virus
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Duration
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI signs
| |
| ! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Stool exam
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |CBC
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other lab findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Extra intestinal findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause/Pathogenesis
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Gold standard diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Acute
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Chronic
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Watery
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bloody
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fatty
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |RBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Ova/Parasite
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Osmotic gap
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hgb
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Plt
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Norovirus]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal distension|Abdominal distention]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive stool reverse–transcriptase [[polymerase chain reaction]] (RT–PCR)
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Myalgia]]
| |
| *[[Headache]]
| |
| *[[Seizure]]
| |
| *[[Encephalopathy]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Norovirus|''Norovirus'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Clinical diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Rotavirus]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| * Hyperactive [[Stomach rumble|bowel sounds]]
| |
| * Diffuse [[abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Elevated [[blood urea nitrogen]]
| |
| *[[Hyperchloremic acidosis]]
| |
| *[[Hypocalcemia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Necrotizing enterocolitis]]
| |
| *[[Intussusception]]
| |
| *[[Biliary atresia]]
| |
| *[[Central nervous system]] involvement
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Rotavirus|''Rotavirus'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Stool immune–based assays
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Echovirus]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal distension|Abdominal distention]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Hepatic failure|Liver failure]]
| |
| *[[Myocarditis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Echovirus|''Echovirus'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Clinical diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Adenoviridae|Adenovirus]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal distension|Abdominal distention]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Viral antigen assay
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Respiratory disease]]
| |
| *[[Hyperkeratosis|Follicular]] [[conjunctivitis]]
| |
| *Epidemic [[keratoconjunctivitis]]
| |
| *[[Hepatitis]]
| |
| *[[Urethritis]]
| |
| *[[Myocarditis]]
| |
| *[[Meningitis]]
| |
| *[[Bacteremia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Adenoviridae|''Adenovirus'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Clinical diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[CMV colitis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Diffuse [[Tenderness (medicine)|abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Viral antigen assay
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Decreased [[CD4]] level
| |
| *Abnormal [[Liver function tests|liver function test]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Encephalitis]]
| |
| *[[Guillain-Barré syndrome|Guillain–Barré syndrome]]
| |
| *[[Pneumonia]]
| |
| *[[Retinitis]]
| |
| *[[Pericarditis]] and [[myocarditis]]
| |
| *[[Atherosclerosis]]
| |
| *[[Venous thromboembolism|Venous thrombosis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Cytomegalovirus|''Cytomegalovirus'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Quantitative polymerase chain reaction|Quantitative PCR]] tests
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)|HIV]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal distension|Abdominal distention]]
| |
| *Diffuse [[Tenderness (medicine)|abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Decreased [[CD4]] level
| |
| *[[Electrolyte disturbance|Electrolyte imbalance]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Lymphadenopathy]]
| |
| *Disseminated [[infection]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)|''HIV'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *HIV virologic (viral load) test
| |
| *Immunoassay
| |
| |-
| |
| | rowspan="7" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Parasite
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Duration
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI signs
| |
| ! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Stool exam
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |CBC
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other lab findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Extra intestinal findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause/Pathogenesis
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Gold standard diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Acute
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Chronic
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Watery
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bloody
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fatty
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |RBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Ova/Parasite
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Osmotic gap
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hgb
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Plt
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Entamoeba histolytica]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal distension|Abdominal distention]]
| |
| *Diffuse [[Tenderness (medicine)|abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Liver abscess]]
| |
| *Pleuropulmonary infection
| |
| *[[Cardiac]] [[infection]]
| |
| *[[Brain abscess]]
| |
| *[[Skin and soft-tissue infections|Cutaneous infection]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Entamoeba histolytica|''Entamoeba histolytica'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Antigen testing
| |
| *Serology
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Giardia lamblia|Giardia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal distension|Abdominal distention]]
| |
| *Diffuse [[Tenderness (medicine)|abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Malabsorption]]
| |
| *[[Urticaria]]
| |
| *[[Depression]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *''[[Giardia lamblia]]''
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Antigen detection assays
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Cryptosporidium]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal distension|Abdominal distention]]
| |
| *Diffuse [[Tenderness (medicine)|abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive stool microscopy
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Elevated [[alkaline phosphatase]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Chronic, life–threatening illness in [[Immunodeficiency|immunocompromised]] patients
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Cryptosporidium|''Cryptosporidium'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Polymerase chain reaction
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Microsporidia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal distension|Abdominal distention]]
| |
| *Diffuse [[Tenderness (medicine)|abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive stool microscopy
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Decreased [[CD4]] count
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Malabsorption]]
| |
| *[[Keratitis]]
| |
| *[[Seizure]]
| |
| *[[Myositis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Microsporidia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Antigen detection assays
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Isospora]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal distension|Abdominal distention]]
| |
| *Diffuse [[Tenderness (medicine)|abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive stool microscopy
| |
| *Positive [[fecal fat]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Elevated [[Eosinophil granulocyte|eosinophils]]
| |
| *[[Hypokalemia]]
| |
| *Increased [[creatinine]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Chronic illness in [[Immunodeficiency|immunocompromised]] patients
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Isospora|''Isospora'']]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Detecting oocysts in the feces
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="10" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Tumors
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Duration
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI signs
| |
| ! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Stool exam
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |CBC
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other lab findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Extra intestinal findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause/Pathogenesis
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Gold standard diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Acute
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Chronic
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Watery
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bloody
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fatty
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |RBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Ova/Parasite
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Osmotic gap
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hgb
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Plt
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Carcinoid syndrome|Carcinoid tumor]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| * [[Abdominal distention]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Elevated urinary [[5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid|5–hydroxyindoleacetic acid]] ([[5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid|5–HIAA]]) level
| |
| *High [[chromogranin A]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Flushing|Facial flushing]]
| |
| *[[Jaundice]]
| |
| *[[Edema]]
| |
| *[[Valvular heart disease]]
| |
| *[[Congestive heart failure|Right–sided heart failure]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Well–differentiated [[Neuroendocrine tumors|neuroendocrine tumor]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Blood [[chromogranin A]] level
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[VIPoma]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| * [[Abdominal distention]]
| |
| * Abdominal [[RUQ]] [[tenderness]]
| |
| * [[Nausea]]
| |
| * [[Vomiting]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Elevated [[VIP]] level
| |
| *[[Hypokalemia]]
| |
| *[[Hypochlorhydria]] or [[achlorhydria]]
| |
| *Low osmotic gap (<50 mOsm/kg)
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Rash]]
| |
| * [[Facial flushing]]
| |
| * [[Dehydration]]
| |
| * [[Lethargy]]
| |
| * [[Muscle weakness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Primary secretory tumor
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Blood [[VIP]] levels
| |
| * Followed by imaging
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Zollinger-Ellison syndrome|Zollinger–Ellison syndrome]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| ** [[Tenderness|Epigastric tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Positive [[secretin]] stimulation test
| |
| * Elevated serum [[chromogranin A]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| ** [[Jaundice]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Gastrin]] producing [[tumor]] mainly in [[duodenum]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Secretin]] stimulation test
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Neuroendocrine tumors|Somatostatinoma]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| ** [[Tenderness|Epigastric tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Elevated fasting plasma [[somatostatin]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| ** [[Diabetes mellitus]]
| |
| ** [[Gallstone disease|Cholelithiasis]]
| |
| ** [[Jaundice]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Neuroendocrine tumors]] of D–cell origin
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Plasma [[somatostatin]] level
| |
| *Followed by imaging
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Duration
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI signs
| |
| ! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Stool exam
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |CBC
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other lab findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Extra intestinal findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause/Pathogenesis
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Gold standard diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Acute
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Chronic
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Watery
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bloody
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fatty
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |RBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Ova/Parasite
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Osmotic gap
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hgb
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Plt
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Lymphoma]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *Diffuse [[Tenderness (medicine)|abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| *[[Hepatosplenomegaly]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Paraproteinemia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Malabsorption]]
| |
| * [[Lactose intolerance]]
| |
| * [[Ascites]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Primary [[tumor]] of GI tract
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Colonoscopy]] with [[biopsy]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Colorectal cancer]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Diffuse [[Tenderness (medicine)|abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Positive [[carcinoembryonic antigen]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Metastasis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[FAP|FAP gene]]
| |
| *[[Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer|HNPCC gene]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| ** [[Colonoscopy]] and [[biopsy]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="7" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Medication/Toxicity
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |Medications
| |
| * [[ACE inhibitor|ACE inhibitors]]
| |
| * [[Digoxin]]
| |
| * [[Cephalosporin|Cephalosporins]]
| |
| * [[Statins]]
| |
| * [[Thiazide|Thiazide diuretics]]
| |
| * [[Triptans]]
| |
| * [[Lactulose]]
| |
| * [[HIV AIDS medical therapy|Anti retroviral agents]]
| |
| * [[Chemotherapy|Chemotherapeutic agents]]
| |
| * [[Antifungal drug|Antifungals]]
| |
| * [[Magnesium]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal distention]]
| |
| *[[Dehydration]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑/↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Elevated plasma level of drug
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Inflammation]]
| |
| *[[Pseudomembranous enterocolitis|Pseudomembranous colitis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Clinical evaluation after discontinuation of the drugs
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |Factitious diarrhea
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal distention]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↑/↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Hypokalemia]]
| |
| *[[Metabolic alkalosis]]
| |
| *[[Hypermagnesemia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Malabsorption]]
| |
| *[[Lethargy]]
| |
| *[[Generalized weakness]]
| |
| *[[Acute kidney injury|Acute renal failure]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Medication|Medications]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Clinical evaluation after discontinuation of the drugs
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Duration
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI signs
| |
| ! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Stool exam
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |CBC
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other lab findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Extra intestinal findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause/Pathogenesis
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Gold standard diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Acute
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Chronic
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Watery
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bloody
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fatty
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |RBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Ova/Parasite
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Osmotic gap
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hgb
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Plt
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Heavy metal ingestion]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal distention]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Elevated plasma heavy metal level
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Headache]]
| |
| *[[Paresthesia|Numbness]]
| |
| *[[Alopecia]]
| |
| *[[Vertigo]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Heavy metal ingestion]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Plasma level of heavy metal
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Organophosphate poisoning]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *[[Saliva|Salivation]]
| |
| *[[Nausea and vomiting|Vomiting]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Reduced RBC acetylcholinesterase
| |
| *Plasma [[cholinesterase]] activity
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Dysautonomia|Autonomic dysfunction]]
| |
| *Motor deficit
| |
| *Sensory deficit
| |
| *[[Bronchospasm]]
| |
| *[[Urination]]
| |
| *[[Miosis]]
| |
| *[[Bradycardia]]
| |
| *[[Lacrimation]]
| |
| *[[Sweating]]
| |
| *[[Cardiac arrhythmia|Cardiac arrhythmias]]
| |
| *[[Acute kidney injury|Acute renal injury]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Neurotoxin|Neurotoxins]] bind to [[ACHE|acetylcholinesterase]] (AChE)
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Clinical diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Opium withdrawal]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *Hyperactive [[Stomach rumble|bowel sounds]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Azotemia]]
| |
| *[[Hypokalemia]]
| |
| *[[Metabolic alkalosis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Dysphoria]]
| |
| *[[Agitation (emotion)|Restlessness]]
| |
| *[[Perspiration|Sweating]]
| |
| *[[Rhinorrhea]]
| |
| *[[Tears|Lacrimation]]
| |
| *[[Myalgia]]
| |
| *[[Arthralgia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Opium|Opium withdrawal]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Clinical diagnosis following [[opium withdrawal]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Iatrogenic
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Duration
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI signs
| |
| ! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Stool exam
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |CBC
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other lab findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Extra intestinal findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause/Pathogenesis
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Gold standard diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Acute
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Chronic
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Watery
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bloody
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fatty
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |RBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Ova/Parasite
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Osmotic gap
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hgb
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Plt
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Short bowel syndrome]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Abdominal distension|Abdominal distention]]
| |
| * [[Tenderness (medicine)|Abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[fecal fat]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | ↑
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Hypoalbuminemia]]
| |
| * High level of [[Acute phase protein|acute phase reactant]]
| |
| * Abnormal [[liver function tests]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Prior [[Intestine|intestinal]] surgery
| |
| * [[Malabsorption]]
| |
| * [[Crohn's disease]]
| |
| * [[Cancer|Malignancy]]
| |
| * Peripheral [[edema]]
| |
| * [[Muscle atrophy]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Surgical [[bowel resection]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Clinical diagnosis following [[bowel resection]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Radiation enteropathy|Radiation enteritis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| * [[Tenderness (medicine)|Abdominal tenderness]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[fecal fat]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Vitamin B12 deficiency
| |
| *[[Hypoalbuminemia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Prior history of [[Cancer|malignancy]] and [[radiation therapy]]
| |
| *[[Malabsorption]]
| |
| *[[Telangiectasia|Telangiectasias]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Radiation therapy|Radiation]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Segmental bowel [[inflammation]] on [[endoscopy]] or [[colonoscopy]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Gastric dumping syndrome|Dumping syndrome]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *Hyperactive [[bowel sound]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Hypoglycemia]]
| |
| * [[Hydrogen Breath Test|Hydrogen breath test]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Malnutrition]]
| |
| *[[Fat soluble vitamins|Fat soluble vitamin]] deficiency
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Post operative complications|Postgastrectomy]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Clinical diagnosis following [[gastrectomy]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="6" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Others
| |
| ! colspan="2" rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Duration
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Diarrhea
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fever
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Abdominal pain
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Weight loss
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |GI signs
| |
| ! colspan="5" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Stool exam
| |
| ! colspan="3" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |CBC
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other lab findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Extra intestinal findings
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Cause/Pathogenesis
| |
| ! rowspan="2" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Gold standard diagnosis
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Acute
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Chronic
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Watery
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Bloody
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Fatty
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |RBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Ova/Parasite
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Osmotic gap
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Other
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |WBC
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Hgb
| |
| ! style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" align="center" |Plt
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Abetalipoproteinemia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Abdominal distension]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Low [[triglyceride]]
| |
| * Low total [[cholesterol]] levels
| |
| * [[Acanthocytes]]
| |
| * Low [[vitamin E]] levels
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Ataxia]]
| |
| * [[Visual field defect]]
| |
| * [[Dysarthria]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Autosomal recessive]] disorder caused by mutations encoding the [[microsomal triglyceride transfer protein]] (MTP)
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Clinical findings and low [[triglyceride]] and [[cholesterol]] level
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Hyperthyroidism]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |–
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[fecal fat]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Elevated [[T4]]
| |
| * Elevated [[T3]]
| |
| * Decreased [[TSH]]
| |
| * High serum [[alkaline phosphatase]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Lump in the neck
| |
| * Lid lag
| |
| * [[Malabsorption]]
| |
| * [[Sweating]]
| |
| * [[Hyperpigmentation]]
| |
| * [[Proptosis]]
| |
| * [[Tremor]]
| |
| * Increased [[Deep tendon reflex|DTR]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[Graves' disease]]
| |
| * [[Hashimoto's thyroiditis]]
| |
| * [[Toxic adenoma]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * [[TSH]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Diabetic neuropathy]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *[[Fecal incontinence]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[fecal fat]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Hyperglycemia]]
| |
| *[[Azotemia]]
| |
| *[[Hypokalemia]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Malabsorption]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Unclear
| |
| *Disordered [[motility]]
| |
| *Increased [[Intestine|intestinal]] secretion
| |
| *[[Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Clinical diagnosis in a patient with long lasting [[diabetes mellitus]]
| |
| |-
| |
| ! colspan="2" style="background:#DCDCDC;" align="center" |[[Scleroderma|Systemic sclerosis]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |±
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="Left" |
| |
| *[[Abdominal pain|Epigastric tenderness]]
| |
| *[[Fecal incontinence]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | +
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | –
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Positive [[fecal fat]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" |↓
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="center" | Nl
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| * Anti–[[Type I topoisomerase|topoisomerase I]] (Scl‑70) antibodies
| |
| * [[Antinuclear antibodies]] ([[Antinuclear antibodies|ANA]])
| |
| * [[Anti-centromere antibodies|Anti–centromere antibodies]]
| |
| * Anti–[[RNA polymerase III]] antibody
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Malabsorption]]
| |
| *[[Skin changes]]
| |
| *[[Raynaud's phenomenon|Raynaud phenomenon]]
| |
| *[[Pulmonary hypertension]]
| |
| *[[Arthritis]]
| |
| *[[Telangiectasia]]
| |
| *[[Chronic renal failure]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *[[Autoimmunity|Autoimmune reaction]]
| |
| | style="padding: 5px 5px; background: #F5F5F5;" align="left" |
| |
| *Clinical diagnosis
| |
| *Followed by serologic tests
| |
| |- }
| |
| |}
| |
|
| |
|
| ==References== | | ==References== |
| {{Reflist|2}} | | {{Reflist|2}} |
|
| |
|
| == Risk Factors ==
| | |
| * Antibiotic use
| |
| * High-risk sexual behavior (STDs)
| |
| * Immunosuppression
| |
| * Recent travel to endemic area
| |
| ===Pathophysiology prev=== | | ===Pathophysiology prev=== |
| <div style="-webkit-user-select: none;"> | | <div style="-webkit-user-select: none;"> |
| Line 2,647: |
Line 21: |
| {{CMG}} {{AE}} | | {{CMG}} {{AE}} |
|
| |
|
| == Risk Factors ==
| | |
| * Antibiotic use
| |
| * High-risk sexual behavior (STDs)
| |
| * Immunosuppression
| |
| * Recent travel to endemic area
| |
| ===Pathophysiology prev=== | | ===Pathophysiology prev=== |
| <div style="-webkit-user-select: none;"> | | <div style="-webkit-user-select: none;"> |
| Line 2,662: |
Line 32: |
| {{Cirrhosis}} | | {{Cirrhosis}} |
| {{CMG}} {{AE}} | | {{CMG}} {{AE}} |
|
| |
| == Risk Factors ==
| |
| * Antibiotic use
| |
| * High-risk sexual behavior (STDs)
| |
| * Immunosuppression
| |
| * Recent travel to endemic area
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| == History and Symptoms == | | == History and Symptoms == |
| Line 2,678: |
Line 41: |
| ** Immune status | | ** Immune status |
| ** Woodland exposure | | ** Woodland exposure |
| ==table causes==
| |
| '''Causes''' <ref name="pmid29344358">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mokomane M, Kasvosve I, de Melo E, Pernica JM, Goldfarb DM |title=The global problem of childhood diarrhoeal diseases: emerging strategies in prevention and management |journal=Ther Adv Infect Dis |volume=5 |issue=1 |pages=29–43 |year=2018 |pmid=29344358 |pmc=5761924 |doi=10.1177/2049936117744429 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| <ref name="pmid21483709">{{cite journal |vauthors=Chowdhury F, Rahman MA, Begum YA, Khan AI, Faruque AS, Saha NC, Baby NI, Malek MA, Kumar AR, Svennerholm AM, Pietroni M, Cravioto A, Qadri F |title=Impact of rapid urbanization on the rates of infection by Vibrio cholerae O1 and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in Dhaka, Bangladesh |journal=PLoS Negl Trop Dis |volume=5 |issue=4 |pages=e999 |year=2011 |pmid=21483709 |pmc=3071362 |doi=10.1371/journal.pntd.0000999 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| <ref name="pmid23680352">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kotloff KL, Nataro JP, Blackwelder WC, Nasrin D, Farag TH, Panchalingam S, Wu Y, Sow SO, Sur D, Breiman RF, Faruque AS, Zaidi AK, Saha D, Alonso PL, Tamboura B, Sanogo D, Onwuchekwa U, Manna B, Ramamurthy T, Kanungo S, Ochieng JB, Omore R, Oundo JO, Hossain A, Das SK, Ahmed S, Qureshi S, Quadri F, Adegbola RA, Antonio M, Hossain MJ, Akinsola A, Mandomando I, Nhampossa T, Acácio S, Biswas K, O'Reilly CE, Mintz ED, Berkeley LY, Muhsen K, Sommerfelt H, Robins-Browne RM, Levine MM |title=Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): a prospective, case-control study |journal=Lancet |volume=382 |issue=9888 |pages=209–22 |year=2013 |pmid=23680352 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60844-2 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| <ref name="pmid23757337">{{cite journal |vauthors=Chhabra P, Payne DC, Szilagyi PG, Edwards KM, Staat MA, Shirley SH, Wikswo M, Nix WA, Lu X, Parashar UD, Vinjé J |title=Etiology of viral gastroenteritis in children <5 years of age in the United States, 2008-2009 |journal=J. Infect. Dis. |volume=208 |issue=5 |pages=790–800 |year=2013 |pmid=23757337 |doi=10.1093/infdis/jit254 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| <ref name="pmid21173676">{{cite journal |vauthors=Dennehy PH |title=Viral gastroenteritis in children |journal=Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. |volume=30 |issue=1 |pages=63–4 |year=2011 |pmid=21173676 |doi=10.1097/INF.0b013e3182059102 |url=}}</ref>
| |
| <ref name="pmid2007955">{{cite journal |vauthors=Cohen MB |title=Etiology and mechanisms of acute infectious diarrhea in infants in the United States |journal=J. Pediatr. |volume=118 |issue=4 Pt 2 |pages=S34–9 |year=1991 |pmid=2007955 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| <ref name="pmid10804140">{{cite journal |vauthors=Pang XL, Honma S, Nakata S, Vesikari T |title=Human caliciviruses in acute gastroenteritis of young children in the community |journal=J. Infect. Dis. |volume=181 Suppl 2 |issue= |pages=S288–94 |year=2000 |pmid=10804140 |doi=10.1086/315590 |url=}}</ref> <ref name="pmid25772777">{{cite journal |vauthors=Dikman AE, Schonfeld E, Srisarajivakul NC, Poles MA |title=Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Associated Diarrhea: Still an Issue in the Era of Antiretroviral Therapy |journal=Dig. Dis. Sci. |volume=60 |issue=8 |pages=2236–45 |year=2015 |pmid=25772777 |pmc=4499110 |doi=10.1007/s10620-015-3615-y |url=}}</ref> <ref name="pmid26584048">{{cite journal |vauthors=Irikura D, Monma C, Suzuki Y, Nakama A, Kai A, Fukui-Miyazaki A, Horiguchi Y, Yoshinari T, Sugita-Konishi Y, Kamata Y |title=Identification and Characterization of a New Enterotoxin Produced by Clostridium perfringens Isolated from Food Poisoning Outbreaks |journal=PLoS ONE |volume=10 |issue=11 |pages=e0138183 |year=2015 |pmid=26584048 |pmc=4652906 |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0138183 |url=}}</ref> <ref name="pmid29262044">{{cite journal |vauthors=Chiejina M, Samant H |title= |journal= |volume= |issue= |pages= |year= |pmid=29262044 |doi= |url=}}</ref>
| |
| {| class="wikitable"
| |
| !Population
| |
| !Life threatening causes
| |
| !Common causes
| |
| !Less common causes
| |
| |-
| |
| |'''Children'''
| |
| |
| |
|
| |
| *Staphylococcus aureus'' (staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome [TSS])''
| |
| *Salmonella septicemia
| |
| *Hemolytic uraemic syndrome (Shiga toxin producing E. coli ETEC)
| |
| |'''Infectious''':
| |
| *Viral:
| |
| **Rota virus
| |
| **Noro virus
| |
| *Bacterial:
| |
| **Shigella species ( S.dysentriae, S.flexneri, S.sonneii, S.boydii)
| |
| **E.coli species ( Enterotoxigenic E.coli, Enterohemorrhagic E.coli, Enteroinvasive E.coli)
| |
| **Vibrio cholerae
| |
| **Non Typhoidal Salmonella: S.typhimurium, S.enterica
| |
| **[[Campylobacter jejuni]]
| |
| **Clostridium difficle
| |
| **Yersinia enterocolitica
| |
| *Protozoa: Entamoeba histolytica,Cryptosporidium parvum
| |
|
| |
| |
| |
| *Adeno virus
| |
| *Astro virus
| |
| *Calcivirus
| |
| *Aeromonas
| |
|
| |
| *'''Systemic conditions associated with diarrhea''':
| |
| Influenza, measles, dengue fever, human immunodeficiency virus. Systemic infections associated with diarrhea include pneumonia,Otitis media, sepsis,urinary tract infection.
| |
| |-
| |
| |'''Adults'''
| |
| |There are no life-threatening causes of Acute diarrhea; however, complications resulting from untreated Acute diarrhea are common.
| |
| |
| |
| '''Infections''':
| |
| *'''Bacterial:'''
| |
| **Shigella species
| |
| **Non typhoidal Salmonella
| |
| **Clostridium difficile
| |
| **Campylobacter jejuni
| |
| ** Escherichia coli :
| |
| ***ETEC
| |
| ***EPEC
| |
| ***EHEC
| |
| ***EIEC
| |
| ***EAEC
| |
| **Yersinia enterocolitica
| |
| **Vibrio cholera
| |
| **Vibrio parahemolyticus
| |
| **Aeromonas
| |
| **Plesiomonas shigelloides
| |
| **Mycobacterium Avium complex
| |
|
| |
| *'''Food poisoning:'''
| |
| **Staphylococcal aureus
| |
| **Bacillus cereus
| |
| **Clostridium perfringens
| |
|
| |
| *'''Viral''':
| |
| **Noro virus
| |
| **Rota virus
| |
| ** Enteric Adeno virus
| |
| **HIV Infection
| |
| **CMV
| |
| **Astro virus
| |
| **Norwalk virus
| |
|
| |
| *'''Protozoan and Parasitic:'''
| |
| **Entamoeba histolytica
| |
| **Giardia lamblia
| |
| **Microsporidia
| |
| **Isospora
| |
|
| |
| '''Medicatons''':
| |
| *Antibiotics mostly with Cephalosporins
| |
| *Magnesium containing antacids
| |
| *Laxatives
| |
| *Anti retroviral agents
| |
| *Chemotherapeutic agents
| |
| *Antifungals
| |
| *ACE inhibitors
| |
| *Digoxin
| |
| *Statins
| |
| *Thiazide diuretics
| |
| *Lactulose
| |
|
| |
| '''Ingestion of plants''' (eg, hyacinths, daffodils, Amanita species mushrooms)
| |
|
| |
| '''Food allergies''':
| |
| *Cow's milk protein allergy
| |
| *Soy protein allergy
| |
|
| |
| '''Tropical sprue (initial stages)'''
| |
|
| |
| '''Ischemic colitis(initial stages)'''
| |
|
| |
| '''Tumors''': VIPoma
| |
|
| |
| '''Organophosphate poisoning'''
| |
|
| |
| '''Opium withdrawal'''
| |
|
| |
| '''Short bowel syndrome'''(initial stages)
| |
|
| |
| '''Radiation enteritis'''(initial stages)
| |
| |''Listeria monocytogenes'' (in immuno compromised)
| |
|
| |
| '''Hyperthyroidism'''
| |
|
| |
| '''Irritable bowel syndrome'''
| |
|
| |
| '''Disorders of digestive/absorptive processes''':
| |
| *Glucose-galactose malabsorption
| |
| *Sucrase-isomaltase deficiency
| |
| *Late-onset (adult-type) hypolactasia, leads to lactose intolerance
| |
| '''Intra abdominal emergencies''' including appendicitis, Intussusception.
| |
|
| |
| |-
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |}'''References:'''
| |
| <references />
| |
|
| |
| ==References== | | ==References== |
| {{reflist|2}} | | {{reflist|2}} |
| Line 2,819: |
Line 46: |
| {{WH}} | | {{WH}} |
| {{WS}} | | {{WS}} |
|
| |
| [[Category:Primary care]]
| |
| [[Category:Gastroenterology]]
| |
|
| |
| [[Category:Needs overview]]
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Other Imaging Findings== | | ==Other Imaging Findings== |
| Line 2,841: |
Line 63: |
|
| |
|
| ==Overview== | | ==Overview== |
|
| |
| ==Medical Therapy==
| |
| * Fluid resuscitation (oral, if not IV)
| |
| * Patients should be advised to do the following until symptoms subside:
| |
| ** Hydrate with liquids that are [[caffeine]] free and contain [[glucose]]
| |
| ** Avoid [[lactose]]
| |
| ** Chew gum that is free of [[sorbitol]]
| |
| ** Eat raw fruit
| |
| * For patients with [[lactose intolerance]], a lactose-free diet is advised
| |
| * For patients with malabsorption diseases, a gluten free diet is advised
| |
| * Consultation with [[oncology]], surgery and/or gastroenterology may be required for intestinal [[neoplasm]]
| |
| * Control blood sugar ([[diabetic neuropathy]])
| |
|
| |
| ===Empirical Therapy===
| |
| Empirical therapy is used as an initial treatment before diagnostic testing or after diagnostic testing has failed to confirm a diagnosis or when there is no specific treatment or when specific treatment fails to effect a cure.
| |
|
| |
| * Empirical trials of antimicrobial therapy like [[metronidazole]] for protozoal diarrhea or [[fluoroquinolone]] for enteric bacterial diarrhea if the prevalence of bacterial or protozoal infection is high in a specific community or situation.
| |
|
| |
| * Most cases of diarrhea, except for high-volume secretory states, respond to a sufficiently high dose of [[opium]] or [[morphine]]. [[Codeine]], synthetic opioids [[diphenoxylate]] and [[loperamide]] are less potent. However loperamide is generally used because of its less abuse potential.
| |
|
| |
| * The somatostatin analogue [[octreotide]] has proven effectiveness in [[carcinoid tumors]] and other peptide-secreting tumors, dumping syndrome, and chemotherapy-induced diarrhea.
| |
|
| |
| * Intraluminal agents include adsorbants, such as activated charcoal, and binding resins like [[bismuth]] and stool modifiers, such as medicinal fiber.
| |
|
| |
| ===Pharmacotherapy===
| |
| * [[Antibiotics]] (malabsorption diseases)
| |
| * [[Anticholinergics]] (IBS)
| |
| * Antimolality agents
| |
| * Antibiotic therapy (severe disease)
| |
| * [[Metoclopramide]] (diabetic neuropathy)
| |
| * Nonspecific antidiarrheal agents
| |
|
| |
| ===Symptomatic Treatment===
| |
| * Symptomatic treatment for diarrhea involves the patient consuming adequate amounts of water to replace that loss, preferably mixed with [[electrolyte]]s to provide essential [[salt]]s and some amount of [[nutrient]]s. For many people, further treatment is unnecessary.
| |
| * The following types of diarrhea indicate medical supervision is required:
| |
| ** Diarrhea in infants;
| |
| ** Moderate or severe diarrhea in young children;
| |
| ** Diarrhea associated with [[blood]];
| |
| ** Diarrhea that continues for more than two weeks;
| |
| ** Diarrhea that is associated with more general illness such as non-cramping [[abdominal pain]], [[fever]], [[weight loss]], etc;
| |
| ** [[Traveler's diarrhea|Diarrhea in travelers]], since they are more likely to have exotic infections such as parasites;
| |
| ** Diarrhea in food handlers, because of the potential to infect others;
| |
| ** Diarrhea in institutions such as hospitals, child care centers, or geriatric and convalescent homes.
| |
|
| |
| A severity score is used to aid diagnosis.<ref name="pmid2371542">{{cite journal |author=Ruuska T, Vesikari T |title=Rotavirus disease in Finnish children: use of numerical scores for clinical severity of diarrhoeal episodes |journal=Scand. J. Infect. Dis. |volume=22 |issue=3 |pages=259–67 |year=1990 |pmid=2371542 |doi=}}</ref>
| |
|
| |
| ===Pathogen Specific===
| |
| ====Immunocompetent====
| |
| *'''Bacterial''' <ref name="pmid11170940">{{cite journal| author=Guerrant RL, Van Gilder T, Steiner TS, Thielman NM, Slutsker L, Tauxe RV et al.| title=Practice guidelines for the management of infectious diarrhea. | journal=Clin Infect Dis | year= 2001 | volume= 32 | issue= 3 | pages= 331-51 | pmid=11170940 | doi=10.1086/318514 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11170940 }} </ref>
| |
|
| |
| :* '''1. Shigella species'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen (1):
| |
| :::*Adult dose: [[TMP-SMZ]], 160 and 800 mg, respectively bid for 3 days (if susceptible ) {{or}} [[Fluoroquinolone]] (e.g., 300 mg [[Ofloxacin]], 400 mg [[Norfloxacin]], {{or}} 500 mg [[Ciprofloxacin]] bid for 3 days)
| |
| :::*Pediatric dose: [[TMP-SMZ]], 5 and 25 mg/kg, respectively bid for 3 days
| |
|
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen (2):
| |
| :::*Adult dose: [[Nalidixic acid]] 1 g/d for 5 days {{or}} [[Ceftriaxone]]; [[Azithromycin]]
| |
| :::*Pediatric dose: [[Nalidixic acid]], 55 mg/kg/d for 5 days
| |
|
| |
| :*'''2. Non-typhi species of Salmonella'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: Not recommended routinely, but if severe or patient is younger than 6 monthes or older than 50 year old or has prostheses, valvular heart disease, severe atherosclerosis, malignancy, or uremia, [[TMP-SMZ]] (if susceptible) {{or}} [[Fluoroquinolone]], bid for 5 to 7 days; [[Ceftriaxone]], 100 mg/kg/d in 1 or 2 divided doses
| |
|
| |
| :*'''3. Campylobacter species'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: [[Erythromycin]] 500 mg bid for 5 days
| |
|
| |
| :*'''4. Escherichia coli species'''
| |
| ::*'''4.1. Enterotoxigenic'''
| |
| :::*Preferred regimen: [[TMP-SMZ]], 160 and 800 mg, respectively, bid, for 3 days (if susceptible), {{or}} [[Fluoroquinolone]] (e.g., 300 mg [[Ofloxacin]], 400 mg [[Norfloxacin]], or 500 mg [[Ciprofloxacin]] bid for 3 days)
| |
|
| |
| ::*'''4.2. Enteropathogenic'''
| |
| :::*Preferred regimen: [[TMP-SMZ]], 160 and 800 mg, respectively, bid, for 3 days (if susceptible), {{or}} [[Fluoroquinolone]] (e.g., 300 mg [[Ofloxacin]], 400 mg [[Norfloxacin]], or 500 mg [[Ciprofloxacin]] bid for 3 days)
| |
|
| |
| ::*'''4.3. Enteroinvasive'''
| |
| :::*Preferred regimen: [[TMP-SMZ]], 160 and 800 mg, respectively, bid, for 3 days (if susceptible), {{or}} [[Fluoroquinolone]] (e.g., 300 mg [[Ofloxacin]], 400 mg [[Norfloxacin]], or 500 mg [[Ciprofloxacin]] bid for 3 days)
| |
|
| |
| ::*'''4.4. Enterohemorrhagic'''
| |
| :::*Preferred regimen: Avoid antimotility drugs; role of antibiotics unclear, and administration should be avoided.
| |
|
| |
| :*'''5. Aeromonas/Plesiomonas'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: [[TMP-SMZ]], 160 and 800 mg, respectively, bid for 3 days (if susceptible), [[Fluoroquinolone]] (e.g., 300 mg [[Ofloxacin]], 400 mg [[Norfloxacin]], or 500 mg [[Ciprofloxacin]] bid for 3 days)
| |
|
| |
| :*'''6. Yersinia species'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: Antibiotics are not usually required; [[Deferoxamine]] therapy should be withheld; for severe infections or associated bacteremia treat as for immunocompromised hosts, using combination therapy with [[Doxycycline]], [[Aminoglycoside]], [[TMP-SMZ]], {{or}} [[Fluoroquinolone]]
| |
|
| |
| :*'''7. Vibrio cholerae O1 or O139'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen (1): [[Doxycycline]] 300-mg single dose
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen (2): [[Tetracycline]] 500 mg qid for 3 days
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen (3): [[TMP-SMZ]] 160 and 800 mg, respectively, bid for 3 days
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen (4): single-dose [[Fluoroquinolone]]
| |
|
| |
| :*'''8. Toxigenic Clostridium difficile'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: Offending antibiotic should be withdrawn if possible; [[Metronidazole]], 250 mg qid to 500 mg tid for 3 to 10 days
| |
|
| |
| *'''Parasites''' <ref name="pmid11170940">{{cite journal| author=Guerrant RL, Van Gilder T, Steiner TS, Thielman NM, Slutsker L, Tauxe RV et al.| title=Practice guidelines for the management of infectious diarrhea. | journal=Clin Infect Dis | year= 2001 | volume= 32 | issue= 3 | pages= 331-51 | pmid=11170940 | doi=10.1086/318514 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11170940 }} </ref>
| |
| :*'''1. Giardia'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: [[Metronidazole]] 250-750 mg tid for 7-10 days
| |
|
| |
| :*'''2. Cryptosporidium species'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: If severe, consider [[Paromomycin]], 500 mg tid for 7 days
| |
|
| |
| :*'''3. Isospora species'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: [[TMP-SMZ]], 160 and 800 mg, respectively, bid for 7 to 10 days
| |
|
| |
| :*'''4. Cyclospora species'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: [[TMP/SMZ]], 160 and 800 mg, respectively, bid for 7 days
| |
|
| |
| :*'''5. Microsporidium species'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: Not determined
| |
|
| |
| :*'''6. Entamoeba histolytica'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen (1): [[Metronidazole]] 750 mg tid for 5 to 10 days {{and}} [[Diiodohydroxyquinoline|Diiodohydroxyquin]] 650 mg tid for 20 days
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen (2): [[Metronidazole]] 750 mg tid for 5 to 10 days {{and}} [[Paromomycin]] 500 mg tid for 7 days
| |
|
| |
| ====Immunocompromised====
| |
| *'''Bacterial''' <ref name="pmid11170940">{{cite journal| author=Guerrant RL, Van Gilder T, Steiner TS, Thielman NM, Slutsker L, Tauxe RV et al.| title=Practice guidelines for the management of infectious diarrhea. | journal=Clin Infect Dis | year= 2001 | volume= 32 | issue= 3 | pages= 331-51 | pmid=11170940 | doi=10.1086/318514 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11170940 }} </ref>
| |
| :* '''1. Shigella species:'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen (1):
| |
| :::*Adult dose: [[TMP-SMZ]], 160 and 800 mg, respectively bid for 7 to 10 days (if susceptible ) {{or}} [[Fluoroquinolone]] (e.g., 300 mg [[Ofloxacin]], 400 mg [[Norfloxacin]], {{or}} 500 mg [[Ciprofloxacin]] bid for 7 to 10 days)
| |
| :::*Pediatric dose:[[TMP-SMZ]], 5 and 25 mg/kg, respectively bid for 7 to 10 days
| |
|
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen (2):
| |
| :::*Adult dose: [[Nalidixic acid]] 1 g/d for 7 to 10 days {{or}} [[Ceftriaxone]]; [[Azithromycin]]
| |
| :::*Pediatric dose: [[Nalidixic acid]], 55 mg/kg/d for 7 to 10 days
| |
|
| |
| :*'''2. Non-typhi species of Salmonella'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: Not recommended routinely, but if severe or patient is younger than 6 monthes or older than 50 old or has prostheses, valvular heart disease, severe atherosclerosis, malignancy, or uremia, [[TMP-SMZ]] (if susceptible) {{or}} [[Fluoroquinolone]], bid for 14 days (or longer if relapsing); [[ceftriaxone]], 100 mg/kg/d in 1 or 2 divided doses
| |
|
| |
| :*'''3. Campylobacter species'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: [[Erythromycin]], 500 mg bid for 5 days (may require prolonged treatment)
| |
|
| |
| :*'''4. Escherichia coli species'''
| |
| ::*'''4.1. Enterotoxigenic'''
| |
| :::*Preferred regimen: [[TMP-SMZ]], 160 and 800 mg, respectively, bid for 3 days (if susceptible), {{or}} [[Fluoroquinolone]] (e.g., 300 mg [[Ofloxacin]], 400 mg [[Norfloxacin]], or 500 mg [[Ciprofloxacin]] bid for 3 days) (Consider fluoroquinolone as for enterotoxigenic E. coli)
| |
|
| |
| ::*'''4.2. Enteropathogenic'''
| |
| :::*Preferred regimen: [[TMP-SMZ]], 160 and 800 mg, respectively, bid,for 3 days (if susceptible), {{or}} [[Fluoroquinolone]] (e.g., 300 mg [[Ofloxacin]], 400 mg [[Norfloxacin]], or 500 mg [[Ciprofloxacin]] bid for 3 days)
| |
|
| |
| ::*'''4.3. Enteroinvasive'''
| |
| :::*Preferred regimen: [[TMP-SMZ]], 160 and 800 mg, respectively, bid,for 3 days (if susceptible), {{or}} [[Fluoroquinolone]] (e.g., 300 mg [[Ofloxacin]], 400 mg [[Norfloxacin]], or 500 mg [[Ciprofloxacin]] bid for 3 days)
| |
|
| |
| ::*'''4.4. Enterohemorrhagic'''
| |
| :::*Preferred regimen: Avoid antimotility drugs; role of antibiotics unclear, and administration should be avoided.
| |
|
| |
| :*'''5. Aeromonas/Plesiomonas'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: [[TMP-SMZ]], 160 and 800 mg, respectively, bid for 3 days (if susceptible), [[Fluoroquinolone]] (e.g., 300 mg [[ofloxacin]], 400 mg [[norfloxacin]], or 500 mg [[Ciprofloxacin]] bid for 3 days)
| |
|
| |
| :*'''6. Yersinia species'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: [[Doxycycline]], [[Aminoglycoside]] (in combination) or [[TMP-SMZ]] or [[Fluoroquinolone]]
| |
|
| |
| :*'''7. Vibrio cholerae O1 or O139'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: [[Doxycycline]], 300-mg single dose; or [[Tetracycline]], 500 mg qid for 3 days; or [[TMP-SMZ]], 160 and 800 mg, respectively, bid for 3 days; or single-dose [[Fluoroquinolone]]
| |
|
| |
| :*'''8. Toxigenic Clostridium difficile'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: Offending antibiotic should be withdrawn if possible; [[Metronidazole]], 250 mg qid to 500 mg tid for 3 to 10 days
| |
|
| |
| *'''Parasites''' <ref name="pmid11170940">{{cite journal| author=Guerrant RL, Van Gilder T, Steiner TS, Thielman NM, Slutsker L, Tauxe RV et al.| title=Practice guidelines for the management of infectious diarrhea. | journal=Clin Infect Dis | year= 2001 | volume= 32 | issue= 3 | pages= 331-51 | pmid=11170940 | doi=10.1086/318514 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=11170940 }} </ref>
| |
| :*'''1. Giardia'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: [[Metronidazole]], 250-750 mg tid for 7-10 days
| |
|
| |
| :*'''2. Cryptosporidium species'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: [[Paromomycin]], 500 mg tid for 14 to 28 days, then bid if needed; highly active antiretroviral therapy including a protease inhibitor is warranted for patients with AIDS
| |
|
| |
| :*'''3. Isospora species'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: [[TMP-SMZ]], 160 and 800 mg, respectively, qid for 10 days, followed by [[TMP-SMZ]] thrice weekly, or weekly [[Sulfadoxine]] (500 mg) and [[Pyrimethamine]] (25 mg) indefinitely for patients with AIDS
| |
|
| |
| :*'''4. Cyclospora species'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: [[TMP-SMZ]], 160 and 800 mg, respectively, qid for 10 days, followed by [[TMP-SMZ]] thrice weekly indefinitely
| |
|
| |
| :*'''5. Microsporidium species'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: [[Albendazole]], 400 mg bid for 3 weeks; highly active antiretroviral therapy including a protease inhibitor is warranted for patients with AIDS
| |
|
| |
| :*'''6. Entamoeba histolytica'''
| |
| ::*Preferred regimen: [[Metronidazole]], 750 mg tid for 5 to 10 days, plus either [[Diiodohydroxyquinoline|Diiodohydroxyquin]], 650 mg tid for 20 days, or [[Paromomycin]], 500 mg tid for 7 days
| |
|
| |
| ===Contraindicated medications===
| |
| {{MedCondContrAbs
| |
|
| |
| |MedCond =Diarrhea|Ethacrynic acid}}
| |
|
| |
|
| ==References== | | ==References== |
| Line 3,025: |
Line 69: |
| {{WH}} | | {{WH}} |
| {{WS}} | | {{WS}} |
|
| |
| [[Category:Primary care]]
| |
| [[Category:Gastroenterology]]
| |
|
| |
| [[Category:Needs overview]]
| |
|
| |
|
| ===Pathophysiology prev=== | | ===Pathophysiology prev=== |
| Line 3,080: |
Line 119: |
| ===Image and text to the right=== | | ===Image and text to the right=== |
|
| |
|
| <figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline>[[File:Global distribution of leptospirosis.jpg|577x577px]]</figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline> Recent out break of leptospirosis is reported in Bronx, New York and found 3 cases in the months January and February, 2017. | | <figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline><figure-inline>[[File:Global distribution of leptospirosis.jpg|577x577px]]</figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline> Recent out break of leptospirosis is reported in Bronx, New York and found 3 cases in the months January and February, 2017. |
|
| |
|
| ===Gallery=== | | ===Gallery=== |
| Line 3,095: |
Line 134: |
| ==References== | | ==References== |
| {{Reflist|2}} | | {{Reflist|2}} |
|
| |
| [[Category:Gastroenterology]]
| |
| [[Category:Hepatology]]
| |
| [[Category:Disease]]
| |
|
| |
| {{WS}} | | {{WS}} |
| {{WH}} | | {{WH}} |
| Line 3,106: |
Line 140: |
| REFERENCES | | REFERENCES |
| <references /> | | <references /> |
| | |
| | [[Category:Gastroenterology]] |
| | [[Category:Needs overview]] |
| | [[Category:Hepatology]] |
| | [[Category:Disease]] |
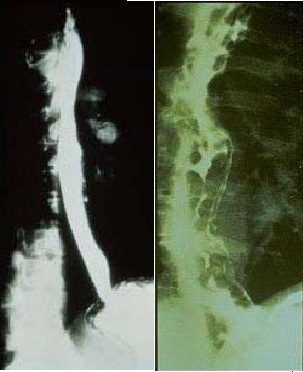
 </figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline> Recent out break of leptospirosis is reported in Bronx, New York and found 3 cases in the months January and February, 2017.
</figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline></figure-inline> Recent out break of leptospirosis is reported in Bronx, New York and found 3 cases in the months January and February, 2017.
![Histopathology of a pancreatic endocrine tumor (insulinoma). Source:https://librepathology.org/wiki/Neuroendocrine_tumour_of_the_pancreas[1]](/images/2/2f/Pancreatic_insulinoma_histology_2.JPG)
![Histopathology of a pancreatic endocrine tumor (insulinoma). Chromogranin A immunostain. Source:https://librepathology.org/wiki/Neuroendocrine_tumour_of_the_pancreas[1]](/images/a/a3/Pancreatic_insulinoma_histopathology_3.JPG)
![Histopathology of a pancreatic endocrine tumor (insulinoma). Insulin immunostain. Source:https://librepathology.org/wiki/Neuroendocrine_tumour_of_the_pancreas[1]](/images/d/d5/Pancreatic_insulinoma_histology_4.JPG)