Rhombencephalon
Overview
The rhombencephalon (or hindbrain) is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates.
The rhombencephalon can be subdivided in a variable number of transversal swellings called rhombomeres. In the human embryo we can distinguish eight rhombomeres, from caudal to rostral: Rh7-Rh1 and the isthmus (the most rostral rhombomere).
A rare disease of the rhomencephalon, "rhombencephalosynapsis" is characterized by a missing vermis resulting in a fused cerebellum. Patients generally present with cerebellar ataxia.
Myelencephalon
Rhombomeres Rh7-Rh4 form the myelencephalon.
The myelencephalon forms the medulla oblongata in the adult brain; it contains:
- a portion of the fourth ventricle,
- the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX),
- vagus nerve (CN X),
- accessory nerve (CN XI),
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII),
- and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII).
Metencephalon
Rhombomeres Rh3-Rh1 form the metencephalon.
The metencephalon is composed of the pons and the cerebellum; it contains:
- a portion of the fourth ventricle,
- the trigeminal nerve (CN V),
- abducens nerve (CN VI),
- facial nerve (CN VII),
- and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII).
Additional images
-
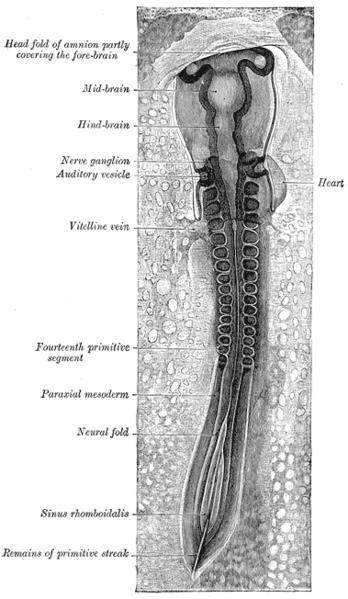
Chick embryo of thirty-three hours’ incubation, viewed from the dorsal aspect. X 30.
-
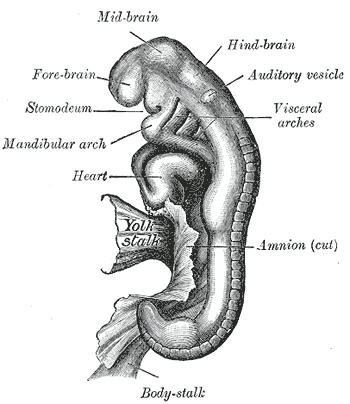
Embryo between eighteen and twenty-one days.
| File:Wiktionary-logo-en-v2.svg | Look up rhombencephalon in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
de:Rhombencephalon it:Rombencefalo nl:Rhombencephalon Template:WH Template:WS