Protein S deficiency
| Protein S deficiency | |
| ICD-9 | 289.81 |
|---|---|
| OMIM | 176880 |
| DiseasesDB | 10814 |
| MedlinePlus | 000559 |
| MeSH | D018455 |
For patient information click here
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Roukoz A. Karam, M.D.[2]
Synonyms and keywords: Protein S deficiency disease
Overview
Protein S deficiency is an autosomal dominant thrombophilia, which leads to an increased risk of thromboembolic events. Protein S is a vitamin K-dependent glycoprotein and plays a role in anticoagulation. It is mainly a cofactor to the activated protein C (APC), which inactivates coagulation factors Va and VIIIa and thereby controlling the coagulation cascade.
Historical Perspective
- Protein S was first discovered and purified in Seattle, Washington in 1979, and it was arbitrarily named protein S after the initial of the city it was discovered in.
- The function of this protein was still unknown; however, it was hypothesized that protein S plays a role in activating protein C.[1]
- Protein S deficiency was first discovered in 1984 when two related individuals with recurrent thromboembolic events and normal coagulation tests were studied. At the time, protein C deficiency was usually associated with recurrent familial thrombosis. These individuals were found to have diminished anticoagulation activity with normal coagulation tests (including a normal protein C level), and when purified human protein S was added to their plasma, effective anticoagulation was restored.[2]
Classification
Protein S deficiency can be subdivided into three types depending on whether the abnormality affects total protein S level, free protein S level, and/or protein S function:[3][4][5][6]
| Type | Total Protein S | Free Protein S | Protein S Function | Characteristics | Genetics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type I | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | Classic form | Usually results from missense or nonsense mutations |
| Type II | ↔ | ↔ | ↓ | Rare qualitative defect | Linked to missense mutations |
| Type III | ↔ | ↓ | ↓ | Quantitative defect | Unknown |
Pathophysiology
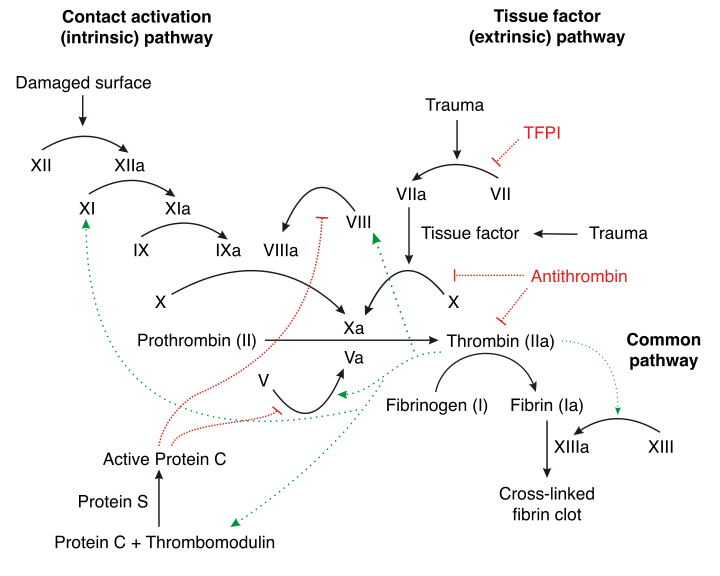 |
- Protein S is a natural anticoagulant that works with other proteins to regulate coagulation in the body.
- After it gets produced by the hepatocytes, endothelial cells, and megakaryocytes, protein S undergoes activation via vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylation.[8]
- The vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxyalse enzyme acts by modifying the glutamic acid residues in protein S to gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues.
- These gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues are needed to ensure calcium-dependent binding to membrane surfaces.
- The now mature and activated protein S will circulate in the blood in two states:
- Free protein S:[9]
- This form constitutes 30 to 40 percent of the total protein S in the body.
- It is the only form that will take part in the coagulation cascade.
- C4b-bound protein S: [10]
- There is a high affinity interaction between protein S and C4b-binding protein.
- C4b-binding protein is a complement regulator; hence, it is responsible for controlling the activity of protein S.
- Around 70 percent of circulating protein S is in the bound form.
- Free protein S:[9]
- The activated free protein S acts as a cofactor to activated protein C, and with the help of phospholipids and Ca2+, it inactivates procoagulant factor Va and factor VIIIa thereby reducing thrombin formation.[8]
- Protein S deficiency is a hereditary disease that results from mutations in the PROS1 gene, located on chromosome 3.
- This disease usually occurs due to heterozygous gene mutations in the PROS1 gene; however, rare cases of homozygous protein S deficiencies have been reported.
- Although another gene, PROS2, has been isolated on the same chromosome 3, it does not seem to have any relevance and has since been classified as a pseudogene.[11][12]
Causes
- In addition to the common hereditary form of protein S deficiency, there are rare circumstances in which acquired causes can result in diminished protein S levels. These situations arise due to different mechanisms:[13]
- Protein S consumption:
- Decreased synthesis of protein S:
- Redistribution of complexed protein S:
Differentiating Protein S Deficiency From Other Diseases
Protein S deficiency must be differentiated from other diseases that cause symptoms of DVT and pulmonary embolism such as:
- Factor V Leiden mutation
- Antithrombin III deficiency
- Protein C deficiency
- Prothrombin gene mutation
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
- Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
For more information on differentiating protein S deficiency, click here.
Epidemiology and Demographics
- The prevalence of protein S deficiency in the general population is unknown.
- However, its prevalence in individuals with a history of venous thromboembolism is approximately 900 per 100,000 individuals worldwide. [20]
Age
- Patients of all age groups may be diagnosed with protein S deficiency.[20]
- It is, however, more commonly observed among patients younger than 40 to 50 years old.
Gender
- There is no difference in the prevalence of the disease between men and women.[20]
Race
- Protein S deficiency usually affects the individuals of the Asian race.[20]
- Caucasian individuals are less likely to develop protein S deficiency.
Risk Factors
- There are no established risk factors for protein S deficiency.
- Family history of thrombosis poses increased risk for a mutation.[21]
Screening
- There is insufficient evidence to recommend routine screening for protein S deficiency in the general population.
- A simple positive family history incident of thrombosis is not enough to recommend screening in an asymptomatic low risk individual.[22]
- High risk patients with a positive family history (first degree relative with protein S deficiency or first degree relative with multiple venous thromboembolic events at an age younger than 50), warrant a screening preferably prior to initiation of the high risk events including taking oral contraceptives or pregnancy.[23][24]
- The free protein S antigen assay is the best screening test.
Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis
- If left untreated, patients with protein S deficiency are at high risk to develop life-threatening venous thromboembolic events.
- For specific complications and prognosis associated with pulmonary embolism, click here.
- For specific complications and prognosis associated with deep vein thrombosis, click here.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic Study of Choice
- There is no established criteria for a definitive diagnosis of protein S deficiency.
- The diagnosis of protein S deficiency is the toughest out of all the hereditary thrombophilias due to the interaction of protein S with other proteins, its complex genetic regulation, and its biologic variation.
- The diagnosis is made even more strenuous due to the relatively high prevalence of acquired protein S deficiency causes including pregnancy, liver disease, and DIC.
- Three tests are used to assess protein S in plasma:[13][25]
- Free protein S antigen:
- Determines free protein S level in plasma
- Most reliable of the three tests
- Evaluates the function of protein S indirectly
- ELISA technique
- Total protein S antigen:
- Determines both free and bound protein S
- ELISA technique
- Protein S activity assay:[26]
- Assesses the function of protein S as a cofactor for activated protein C
- Indirectly measured based on a coagulation assay and the time to clot
- Not very reliable due to inability to differentiate from factor V Leiden mutation (resistance to activated protein C)
- Free protein S antigen:
History and Symptoms
- The hallmark of protein S deficiency is venous thromboembolism.
- A positive history of a venous thromboembolic event prior to age 50, a strong family history of venous thromboembolic events, and/or a known protein S deficient family member is suggestive of a protein S deficiency.
- The most common sites of venous thromboembolism include deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.[21] For detailed symptoms associated with protein S deficiency refer to deep vein thrombosis history and symptoms and pulmonary embolism history and symptoms.
- Less common sites of venous thromboembolism include cerebral, axillary, and mesenteric veins.[27][28]
Physical Examination
- Physical examination of patients with protein S deficiency is usually remarkable for signs of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism.
- For detailed findings associated with protein S deficiency refer to deep vein thrombosis physical examination and pulmonary embolism physical examination.
Laboratory Findings
- A reduced concentration of serum free protein S is diagnostic of protein S deficiency; however, there is no standard cutoffs for diagnosis.
- The exact levels used to differentiate patients with protein S deficiency from those without this deficiency depends on the patient's risk factors.[29]
- Free protein S levels < 65 IU/dL are diagnostic of protein S deficiency in patients with a history of thromboembolic events or a strong family history of these events.
- Lower levels of free protein S are required to diagnose patients who are asymptomatic or have no strong family history.
- For specific laboratory findings in patients with associated pulmonary embolism, click here
- For specific laboratory findings in patients with associated deep vein thrombosis, click here.
Electrocardiogram
- There are no specific ECG findings associated with protein S deficiency.
- For ECG findings related to pulmonary embolism, click here.
X-ray
- There are no specific x-ray findings associated with protein S deficiency.
- For specific x-ray findings seen with pulmonary embolism, click here.
Echocardiography or Ultrasound
- There are no specific echocardiography/ultrasound findings associated with protein S deficiency.
- For ultrasound findings related to deep vein thrombosis, click here.
- For echocardiography findings associated with pulmonary embolism, click here.
CT scan
- There are no specific CT scan findings associated with protein S deficiency.
- For CT scan findings related to pulmonary embolism, click here.
MRI
- There are no MRI findings associated with protein S deficiency.
Other Imaging Findings
- There are no other imaging findings associated with protein S deficiency.
Other Diagnostic Studies
- There are no other diagnostic studies associated with protein S deficiency.
Treatment
Medical Therapy
- Patients with protein S deficiency that remain asymptomatic and have no history of venous thromboembolic events do not require medical therapy.
- Patients with an acute event of venous thrombosis require same initial medical therapy regardless of whether the cause was hereditary or not.
- For management of patients suffering from pulmonary embolism, click here.
- For management of patient suffering from deep venous thrombosis, click here.
- Patients with protein S deficiency that suffer from a venous thromboembolic event are advised to continue anticoagulation indefinitely especially if the event was unprovoked (occurred without a preceding major risk event like surgery, trauma, oral contraceptives, and immobility).
Surgery
- Surgical intervention is not recommended for the management of protein S deficiency.
Primary Prevention
- There are no established measures for the primary prevention of protein S deficiency.
Secondary Prevention
- Effective measures for the secondary prevention of protein S deficiency include:
- Avoiding oral contraceptives in women
- Prophylactic anticoagulation postoperatively
- Considering anticoagulation during pregnancy
- Education concerning signs and symptoms of venous thromboembolic events
References
- ↑ Di Scipio RG, Hermodson MA, Yates SG, Davie EW (1977). "A comparison of human prothrombin, factor IX (Christmas factor), factor X (Stuart factor), and protein S." Biochemistry. 16 (4): 698–706. PMID 836809.
- ↑ Comp PC, Nixon RR, Cooper MR, Esmon CT (1984). "Familial protein S deficiency is associated with recurrent thrombosis". J Clin Invest. 74 (6): 2082–8. doi:10.1172/JCI111632. PMC 425398. PMID 6239877.
- ↑ Gandrille S, Borgel D, Sala N, Espinosa-Parrilla Y, Simmonds R, Rezende S; et al. (2000). "Protein S deficiency: a database of mutations--summary of the first update". Thromb Haemost. 84 (5): 918. PMID 11127877.
- ↑ Schwarz HP, Fischer M, Hopmeier P, Batard MA, Griffin JH (1984). "Plasma protein S deficiency in familial thrombotic disease". Blood. 64 (6): 1297–300. PMID 6238642.
- ↑ Simmonds RE, Ireland H, Kunz G, Lane DA (1996). "Identification of 19 protein S gene mutations in patients with phenotypic protein S deficiency and thrombosis. Protein S Study Group". Blood. 88 (11): 4195–204. PMID 8943854.
- ↑ Gandrille S, Borgel D, Eschwege-Gufflet V, Aillaud M, Dreyfus M, Matheron C; et al. (1995). "Identification of 15 different candidate causal point mutations and three polymorphisms in 19 patients with protein S deficiency using a scanning method for the analysis of the protein S active gene". Blood. 85 (1): 130–8. PMID 7803790.
- ↑ "Protein C - Wikipedia".
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Esmon CT (1992). "Protein S and protein C Biochemistry, physiology, and clinical manifestation of deficiencies". Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2 (6): 214–9. doi:10.1016/1050-1738(92)90027-P. PMID 21239244.
- ↑ Rezende SM, Simmonds RE, Lane DA (2004). "Coagulation, inflammation, and apoptosis: different roles for protein S and the protein S-C4b binding protein complex". Blood. 103 (4): 1192–201. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-05-1551. PMID 12907438.
- ↑ Dahlbäck B (2011). "C4b-binding protein: a forgotten factor in thrombosis and hemostasis". Semin Thromb Hemost. 37 (4): 355–61. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1276584. PMID 21805441.
- ↑ Ploos van Amstel JK, van der Zanden AL, Bakker E, Reitsma PH, Bertina RM (1987). "Two genes homologous with human protein S cDNA are located on chromosome 3". Thromb Haemost. 58 (4): 982–7. PMID 2895503.
- ↑ Schmidel DK, Tatro AV, Phelps LG, Tomczak JA, Long GL (1990). "Organization of the human protein S genes". Biochemistry. 29 (34): 7845–52. PMID 2148110.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Marlar RA, Gausman JN (2011). "Protein S abnormalities: a diagnostic nightmare". Am J Hematol. 86 (5): 418–21. doi:10.1002/ajh.21992. PMID 21523802.
- ↑ Heeb MJ, Mosher D, Griffin JH (1989). "Activation and complexation of protein C and cleavage and decrease of protein S in plasma of patients with intravascular coagulation". Blood. 73 (2): 455–61. PMID 2521800.
- ↑ Comp PC, Doray D, Patton D, Esmon CT (1986). "An abnormal plasma distribution of protein S occurs in functional protein S deficiency". Blood. 67 (2): 504–8. PMID 2935211.
- ↑ Matsuzaka T, Tanaka H, Fukuda M, Aoki M, Tsuji Y, Kondoh H (1993). "Relationship between vitamin K dependent coagulation factors and anticoagulants (protein C and protein S) in neonatal vitamin K deficiency". Arch Dis Child. 68 (3 Spec No): 297–302. PMC 1590375. PMID 8466266.
- ↑ Comp PC, Thurnau GR, Welsh J, Esmon CT (1986). "Functional and immunologic protein S levels are decreased during pregnancy". Blood. 68 (4): 881–5. PMID 2944555.
- ↑ Gilabert J, Fernandez JA, España F, Aznar J, Estelles A (1988). "Physiological coagulation inhibitors (protein S, protein C and antithrombin III) in severe preeclamptic states and in users of oral contraceptives". Thromb Res. 49 (3): 319–29. PMID 2966452.
- ↑ Vigano-D'Angelo S, D'Angelo A, Kaufman CE, Sholer C, Esmon CT, Comp PC (1987). "Protein S deficiency occurs in the nephrotic syndrome". Ann Intern Med. 107 (1): 42–7. PMID 2954500.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 Pintao MC, Ribeiro DD, Bezemer ID, Garcia AA, de Visser MC, Doggen CJ; et al. (2013). "Protein S levels and the risk of venous thrombosis: results from the MEGA case-control study". Blood. 122 (18): 3210–9. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-04-499335. PMID 24014240.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Engesser L, Broekmans AW, Briët E, Brommer EJ, Bertina RM (1987). "Hereditary protein S deficiency: clinical manifestations". Ann Intern Med. 106 (5): 677–82. PMID 2952034.
- ↑ Wu O, Robertson L, Twaddle S, Lowe G, Clark P, Walker I; et al. (2005). "Screening for thrombophilia in high-risk situations: a meta-analysis and cost-effectiveness analysis". Br J Haematol. 131 (1): 80–90. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05715.x. PMID 16173967.
- ↑ Wu O, Robertson L, Langhorne P, Twaddle S, Lowe GD, Clark P; et al. (2005). "Oral contraceptives, hormone replacement therapy, thrombophilias and risk of venous thromboembolism: a systematic review. The Thrombosis: Risk and Economic Assessment of Thrombophilia Screening (TREATS) Study". Thromb Haemost. 94 (1): 17–25. doi:10.1160/TH04-11-0759. PMID 16113779.
- ↑ Dalen JE (2008). "Should patients with venous thromboembolism be screened for thrombophilia?". Am J Med. 121 (6): 458–63. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.10.042. PMID 18501222.
- ↑ Alshaikh NA, Rosing J, Thomassen MCLGD, Castoldi E, Simioni P, Hackeng TM (2017). "New functional assays to selectively quantify the activated protein C- and tissue factor pathway inhibitor-cofactor activities of protein S in plasma". J Thromb Haemost. 15 (5): 950–960. doi:10.1111/jth.13657. PMID 28211163.
- ↑ Faioni EM, Franchi F, Asti D, Sacchi E, Bernardi F, Mannucci PM (1993). "Resistance to activated protein C in nine thrombophilic families: interference in a protein S functional assay". Thromb Haemost. 70 (6): 1067–71. PMID 8165605.
- ↑ Hwang ET, Kang WS, Park JW, Lee JH, Han HJ, Shin SY; et al. (2014). "[Portal-splenic-mesenteric venous thrombosis in a patients with protein S deficiency due to novel PROS1 gene mutation]". Korean J Gastroenterol. 64 (2): 110–4. PMID 25168054.
- ↑ Simioni P, Zanardi S, Prandoni P, Girolami A (1992). "Combined inherited protein S and heparin co-factor II deficiency in a patient with upper limb thrombosis: a family study". Thromb Res. 67 (1): 23–30. PMID 1440513.
- ↑ Lijfering WM, Mulder R, ten Kate MK, Veeger NJ, Mulder AB, van der Meer J (2009). "Clinical relevance of decreased free protein S levels: results from a retrospective family cohort study involving 1143 relatives". Blood. 113 (6): 1225–30. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-08-174128. PMID 18945960.