Procaine
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Chetan Lokhande, M.B.B.S [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Procaine is a local anesthetic that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of local Anesthetic for local infiltration and peripheral nerve block. Common adverse reactions include MYOCARDIAL DEPRESSION, HYPOTENSION and sometimes HYPERTENSION, BRADYCARDIA, VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS, and CARDIAC ARREST,NAUSEA/VOMITING CUTANEOUS LESIONS of delayed onset, URTICARIA, and EDEMA related to ALLERGIC REACTIONS ,NERVOUSNESS, DIZZINESS, BLURRED VISION, and TREMORS may occur due to systemic toxicity; however, DROWSINESS or CONVULSIONS with subsequent unconsciousness and RESPIRATORY ARREST.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
There is limited information regarding Procaine FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Procaine in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Procaine in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Procaine FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Procaine in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Procaine in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
There is limited information regarding Procaine Contraindications in the drug label.
Warnings
There is limited information regarding Procaine Warnings' in the drug label.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Procaine Clinical Trials Experience in the drug label.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Procaine Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Procaine Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
There is no FDA guidance on usage of Procaine in women who are pregnant.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Procaine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Procaine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Procaine in women who are nursing.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Procaine in pediatric settings.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Procaine in geriatric settings.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Procaine with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Procaine with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Procaine in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Procaine in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Procaine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Procaine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Procaine Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Procaine Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Procaine and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Procaine overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Procaine Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Procaine Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Procaine Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Procaine Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Procaine Pharmacokinetics in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Procaine Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Procaine Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Procaine How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Procaine Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Procaine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Procaine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Procaine Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Procaine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Procaine Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Procaine Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [3] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
Overview
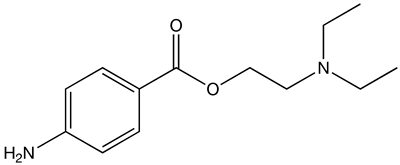 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Parenteral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | n/a |
| Metabolism | Hydrolysis by plasma esterases |
| Elimination half-life | 40–84 seconds |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H20N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 236.31 g/mol |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Procaine |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Procaine |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Procaine at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Procaine at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Procaine
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Procaine Risk calculators and risk factors for Procaine
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Procaine |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Procaine is a local anesthetic drug of the amino ester group. It is used primarily to reduce the pain of intramuscular injection of penicillin, and is also used in dentistry. Owing to the ubiquity of the trade name Novocain, procaine is sometimes referred to generically as novocaine or novacaine.
Procaine was first synthesized in 1905, and was the first injectable man-made local anesthetic used. It was created by the German chemist Alfred Einhorn (1857–1917) who gave the chemical the trade name Novocaine, from the Latin Novus (meaning New) and caine, a common ending for alkaloids used as anesthetics. It was introduced into medical use by surgeon Heinrich Braun (1862–1934).
Procaine is used less frequently today since more effective (and hypoallergenic) alternatives such as lidocaine (xylocaine) exist. Prior to the discovery of procaine, cocaine was the most commonly used local anesthetic. Procaine (like cocaine) has the advantage of constricting blood vessels, which reduces bleeding, unlike other local anesthetics like lidocaine, and without the euphoric and addictive qualities of cocaine.
Procaine, an ester anesthetic, is metabolized in the plasma by the enzyme pseudocholinesterase through hydrolysis into para-amino benzoic acid (PABA), which is then excreted by the kidneys into the urine. Allergic reactions to procaine are usually not in response to procaine itself, but to PABA. About 1 in 3000 people have an atypical form of pseudocholinesterase, which doesn't hydrolyze ester anesthetics such as procaine, resulting in a prolonged period of high levels of the anesthetic in the blood and increased toxicity.
Procaine is the primary ingredient in the controversial preparation Gerovital H3, which is claimed by its advocates to remedy many effects of aging. The mainstream medical view is that these claims were seriously studied and discredited in the 1960s.
See also
Template:SIB Template:Vasoprotectives
de:Procain it:Procaina nl:Novocaïne simple:Procaine sv:Prokain
- Pages with script errors
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Dental equipment
- Local anesthetics
- 1905 introductions