|
|
| (29 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) |
| Line 11: |
Line 11: |
| OMIM_mult = {{OMIM2|242650}} | | | OMIM_mult = {{OMIM2|242650}} | |
| MedlinePlus = | | | MedlinePlus = | |
| eMedicineSubj = med |
| |
| eMedicineTopic = 1220 |
| |
| eMedicine_mult = {{eMedicine2|ped|1166}} |
| |
| MeshID = D002925 | | | MeshID = D002925 | |
| }} | | }} |
| {{SI}} | | {{Primary ciliary dyskinesia}} |
|
| |
|
| {{CMG}} | | {{CMG}}''' Associate Editor-In-Chief:''' {{CZ}} |
| __NOTOC__
| |
| '''Associate Editor-In-Chief:''' {{CZ}} | |
|
| |
|
| {{Editor Join}} | | {{SK}} PCD; immotile ciliary syndrome; Kartagener Syndrome; ciliary motility disorder; immotile cilia; ciliary dyskinesia |
|
| |
|
| '''Primary ciliary dyskinesia''' ('''PCD'''), also known as '''immotile ciliary syndrome''' or '''Kartagener Syndrome''' '''(KS)''', is a rare [[autosomal recessive]] [[genetic disorder]] caused by a defect in the action of the tiny hairs ([[cilia]]) lining the [[respiratory tract]]. Specifically, it is a defect in a gene coding for left-right [[dynein]] (''lrd''), a key structural protein in cilia.<ref>Chodhari R, Mitchison HM, Meeks M. Cilia, primary ciliary dyskinesia and molecular genetics. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2004 Mar;5(1):69-76.</ref>
| | ==[[Primary ciliary dyskinesia overview|Overview]]== |
| | |
| ==Classification==
| |
| When accompanied by the triad of [[situs inversus]] (reversal of the internal organs), [[chronic sinusitis]], and [[bronchiectasis]], it is known as '''Kartagener syndrome'''. Use of '''immotile ciliary syndrome''' is no longer favoured, as [[Spermatozoon|sperm]] in affected men often have some motility - the term was coined in the mistaken belief that they had none.
| |
| | |
| ==Signs and symptoms==
| |
| The main consequence of impaired ciliary function is reduced or absent [[mucus]] clearance in the [[lung]]s, and susceptibility to chronic, recurrent respiratory infections, including [[sinusitis]], [[bronchitis]], [[pneumonia]], and [[otitis media]]. Susceptibility to these infections can be drastically reduced by an early diagnosis, as treatment with various chest physiotherapy techniques during childhood helps prevent the lungs being damaged or colonised by infection during this vulnerable period. Many patients experience [[hearing loss]] and show symptoms of [[otitis media|glue ear]] which demonstrate variable responsiveness to the insertion of myringotomy tubes or [[grommet|grommets]]. A poor sense of smell accompanies high [[mucus]] production in the sinuses. [[Infertility]] is common, but IVF techniques have been successful for some parents with PCD. Clinical progression of the disease is variable with lung [[organ transplant|transplantation]] required in severe cases. For most patients, aggressive measures to enhance clearance of mucus, prevent respiratory infections, and treat bacterial super infections are recommended. Although the true incidence of the disease is unknown, it is estimated to be 1 in 32.000<ref>Ceccaldi PF, Carre-Pigeon F, Youinou Y, Delepine B, Bryckaert PE, Harika G, Quereux C, Gaillard D. Kartagener's syndrome and infertility: observation, diagnosis and treatment J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2004 May;33 (3):192-4.</ref>, although the actual incidence may be as high as 1 in 150.000.
| |
| | |
| ==Causes==
| |
| This disease in genetically inherited. Both inner and/or outer [[dynein]] arms are dysfunction and thus the [[axoneme]] structure lacks the ability to move. [[Axoneme]]s are the elongated structures that make up [[cilia]] and [[flagella]]. The dysfunction of the cilia begins during the [[embryo]]logic phase of development. Since the cilia aid in the movement of [[growth factor]]s resulting in the normal rotation of the internal organs during early embryological development, 50% of these individuals will develop [[situs inversus]], as the laterality of the [[viscera|internal organs]] is determined by chance.
| |
| | |
| ==History==
| |
| The classical triad was first described by A. K. Zivert in 1904 while Kartagener published his first report in 1933.
| |
|
| |
|
| | ==[[Primary ciliary dyskinesia historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== |
| | ==[[Primary ciliary dyskinesia classification|Classification]]== |
| | ==[[Primary ciliary dyskinesia pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== |
| | ==[[Primary ciliary dyskinesia causes|Causes]]== |
| | ==[[Primary ciliary dyskinesia differential diagnosis|Differentiating Primary ciliary dyskinesia from other Diseases]]== |
| | ==[[Primary ciliary dyskinesia epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== |
| | ==[[Primary ciliary dyskinesia risk factors|Risk Factors]]== |
| | ==[[Primary ciliary dyskinesia natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]]== |
| ==Diagnosis== | | ==Diagnosis== |
|
| |
|
| ===Multi Sliced CT===
| | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia diagnostic study of choice|Diagnostic study of choice]] |
| | |
| <div align="left">
| |
| <gallery heights="175" widths="150">
| |
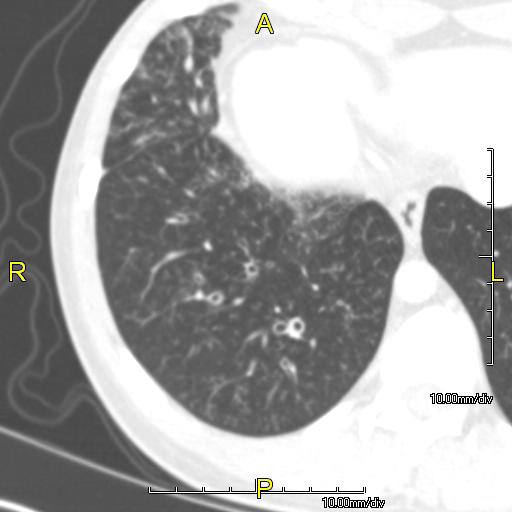
| Image:PCD1.jpg|CT image showing dilated and thickened medium sized airways ([[bronchiectasis]])in a patient with [[Kartagener syndrome]]
| |
| Image:PCD6.jpg|Oblique sagittal CT image showing lower lobe [[bronchiectasis|cylinidrical bronchiectasis]] in the same patient
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| </div>
| |
| | |
| | |
| <div align="left">
| |
| <gallery heights="175" widths="150">
| |
| Image:PCD7.jpg|Axial CT image showing [[situs inversus]] with the liver and IVC on the left and the spleen and aorta on the right
| |
| Image:PCD10.jpg|Axial CT image showing [[dextrocardia]] with the IVC and morphologic right ventricle on the left and the left ventricle on the right
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| </div>
| |
|
| |
|
| <div align="left">
| | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] |
| <gallery heights="175" widths="150">
| |
| Image:PCD8.jpg|Axial CT image showing chronic sinusitis in a patient with [[Kartagener syndrome]].
| |
| Image:PCD12.jpg|Sagittal CT image showing "tree in bud" appearance of mucous impaction in distal small airways related to primary ciliary dyskinesia
| |
| Image:Kartagener-syndrome-008.jpg|[[Situs inversus]] in a patient with [[Kartagener syndrome]] <small>(Image courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted)</small>
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| </div>
| |
|
| |
|
| ===Cardiac MRI===
| | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia electrocardiogram|Electrocardiogram]] | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia x ray|X-Ray Findings]] | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia echocardiography and ultrasound|Echocardiography and Ultrasound]] | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia CT scan|CT-Scan Findings]] | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia MRI|MRI Findings]] | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia other imaging findings|Other Imaging Findings]] | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] |
|
| |
|
| Images shown below are courtesy of RadsWiki and copylefted
| | ==Treatment== |
| <div align="left">
| | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] |
| <gallery heights="175" widths="125">
| |
| Image:Dextrocardia-002.jpg|Dextrocardia in [[Kartagener syndrome]]
| |
| Image:Dextrocardia-003.jpg|Dextrocardia in [[Kartagener syndrome]]
| |
| Image:Dextrocardia-001.jpg|Dextrocardia in [[Kartagener syndrome]]
| |
| </gallery>
| |
| </div>
| |
|
| |
|
| == Footnotes ==
| | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia interventions|Interventions]] |
| <references/>
| |
|
| |
|
| == References ==
| | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia surgery|Surgery]] |
| * Zivert, A.K. Über einen Fall von Bronchiectasie bei einem Patienten mit situs inversus viscerum. Berliner klinische Wochenschrift, 1904, 41: 139-141.
| |
| * Kartagener, M. Zur Pathogenese der Bronchiektasien: Bronchiektasien bei Situs viscerum inversus. Beiträge zur Klinik der Tuberkulose, 1933, 83: 489-501.
| |
| * Afzelius, B., 1976. A human syndrome caused by immotile cilia. Science 193, 317–319.
| |
| * Coren ME, Meeks M, Morrison I, Buchdahl RM, Bush A. Primary ciliary dyskinesia: age at diagnosis and symptom history. Acta Paediatr. 2002; 91 (6):667-9.
| |
| * Ann S. Fulcher, and Mary Ann Turner. [http://radiographics.rsnajnls.org/cgi/content/abstract/22/6/1439 Abdominal Manifestations of Situs Anomalies in Adults.] RadioGraphics 2002 22: 1439-1456.
| |
|
| |
|
| == Videos ==
| | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia primary prevention|Primary Prevention]] |
| *<youtube v=EKW9kVqorN0/>
| |
|
| |
|
| ==External links==
| | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia secondary prevention|Secondary Prevention]] |
| * http://www.pcdfoundation.org
| |
| * http://www.pcdsupport.org.uk
| |
| * http://www.med.unc.edu/cystfib/PCD.htm
| |
| * http://www.cheo.on.ca/english/9301c.shtml
| |
| * http://health.groups.yahoo.com/group/kartagener_syndrome/
| |
| * http://www.pcdforum.com/
| |
| * [http://www.whonamedit.com/synd.cfm/880.html Kartagener's syndrome on Who Named It]
| |
|
| |
|
| | | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia cost-effectiveness of therapy|Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy]] | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia future or investigational therapies|Future or Investigational Therapies]] |
|
| |
|
| ''This article contains some text from the public domain source "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Rare Diseases Report FY 2001" available at http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/resources/docs/raredisrpt01.htm Please adapt as necessary.''
| | ==Case Studies== |
| | [[Primary ciliary dyskinesia case study one|Case#1]] |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| Line 113: |
Line 65: |
| [[Category:Genetic disorders]] | | [[Category:Genetic disorders]] |
| [[Category:Pulmonology]] | | [[Category:Pulmonology]] |
| [[Category:Infectious disease]]
| | |
| [[Category:Cardiology]] | | [[Category:Cardiology]] |
|
| |
|
| {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | | {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} |
| {{WikiDoc Sources}} | | {{WikiDoc Sources}} |