Phentolamine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Regitine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Usually IV or IM |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 19 minutes |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
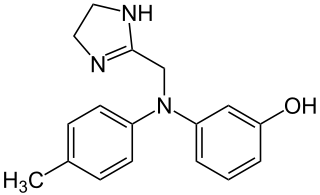
| Formula | C17H19N3O |
| Molar mass | 281.352 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Phentolamine |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Phentolamine Most cited articles on Phentolamine |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Phentolamine |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Phentolamine at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Phentolamine at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Phentolamine
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Phentolamine Discussion groups on Phentolamine Patient Handouts on Phentolamine Directions to Hospitals Treating Phentolamine Risk calculators and risk factors for Phentolamine
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Phentolamine |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Phentolamine (Regitine) is a reversible[1] nonselective alpha-adrenergic antagonist.[2]
Mechanism
Its primary action is vasodilation due to α1 blockade.[3]
It also can lead to reflex tachycardia because of hypotension and α2 inhibition, which increases sympathetic tone.[4]
Uses
The primary application for phentolamine is for the control of hypertensive emergencies, most notably due to pheochromocytoma. [5]
It also has usefulness in the treatment of cocaine-induced cardiovascular complications, where one would generally avoid Beta-blockers (e.g. metoprolol), as they can cause unopposed alpha-adrenergic mediated coronary vasoconstriction, worsening myocardial ischemia and hypertension. It is important to note that phentolamine is not a first-line agent for this indication. Phentolamine should only be given to patients who do not fully respond to benzodiazepines, nitroglycerin, and calcium channel blockers. [6][7]
When given by injection it causes blood vessels to expand, thereby increasing blood flow. When injected into the penis (intracavernosal), it increases blood flow to the penis, which results in an erection.[8]
It may be stored in crash carts to counteract severe peripheral vasoconstriction secondary to extravasation of peripherally placed vasopressor infusions, typically of norepinephrine. Epinephrine infusions are less vasoconstrictive than norepinephrine as they primarily stimulate beta receptor more than alpha receptors, but the effect remains dose dependent.
Phentolamine also has diagnostic and therapeutic roles in complex regional pain syndrome (reflex sympathetic dystrophy).[9]
Phentolamine has recently been introduced in the dental field as a local anesthetic reversal agent. Distributed by Septodont, OraVerse is a Phentolamine Mesylate injection designed to reverse the local vasoconstrictor properties used in many local anesthetics to prolong anesthesia.[10] OraVerse has been shown to accelerate the reversal of the lingering soft-tissue numbness associated with the widely used anesthetic-vasoconstrictor combinations.[11]
Chemistry
Phentolamine can be synthesized by alkylation of 3-(4-methylanilino)phenol using 2-chloromethylimidazoline:[12][13]
References
- ↑ Jewell, John R.; Longworth, David L.; Stoller, James K.; Casey, David (2003). The Cleveland Clinic internal medicine case reviews. Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 32. ISBN 0-7817-4266-8.
- ↑ Phentolamine at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ↑ Brock G. Oral phentolamine (Vasomax). Drugs Today (Barcelona). 2000 Feb-Mar;36(2-3):121-4.
- ↑ Shen, Howard (2008). Illustrated Pharmacology Memory Cards: PharMnemonics. Minireview. p. 14. ISBN 1-59541-101-1.
- ↑ Tuncel M, Ram VC. Hypertensive emergencies. Etiology and management. American Journal of Cardiovascular Drugs. 2003;3(1):21-31.
- ↑ Hollander JE, Henry TD. Evaluation and management of the patient who has cocaine-associated chest pain. Cardiology Clinics. 2006 Feb;24(1):103-14.
- ↑ Chan GM, Sharma R, Price D, Hoffman RS, Nelson LS. Phentolamine Therapy for Cocaine-Association Acute Coronary Syndrome (CAACS). Journal of Medical Toxicology. 2006 Sep;2(3):108-11.
- ↑ Bella AJ, Brock GB. Intracavernous pharmacotherapy for erectile dysfunction. Endocrine. 2004 Mar-Apr;23(2-3):149-55.
- ↑ Rowbotham MC. Pharmacologic management of complex regional pain syndrome. Clinical Journal of Pain. 2006 Jun;22(5):425-9.
- ↑ http://www.novalar.com/oraverse-dental-specialty-pharmaceutical
- ↑ Malamed S. What's new in local anaesthesia? Society For The Advancement Of Anaesthesia In Dentistry Digest. 2009 Jan;25:4-14.
- ↑ K. Miescher, A. Marxer, E. Urech, Template:US Patent (1950)
- ↑ E. Urech, A. Marxer, K. Miescher, Helv. Chim. Acta, 33, 1386 (1950)
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list
- Template:drugs.com link with non-standard subpage
- Articles with changed EBI identifier
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Drugs with no legal status
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- Antihypertensive agents
- Alpha blockers
- Diuretics
- Cardiovascular Drugs
- Drug
- Vasodilators