Ovarian germ cell tumor pathophysiology
|
Ovarian germ cell tumor Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Ovarian germ cell tumor pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Ovarian germ cell tumor pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Ovarian germ cell tumor pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Monalisa Dmello, M.B,B.S., M.D. [2]
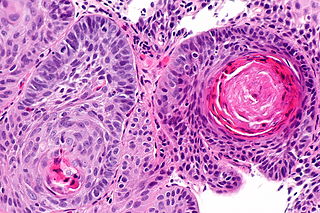
Dysgerminomas
- On gross examination,
- dysgerminomas present with a smooth, bosselated (knobby) external surface, and is soft, fleshy and either cream-coloured, gray, pink or tan when cut.
- Microscopic examination
- typically reveals uniform cells that resemble primordial germ cells. Typically, thestroma contains lymphocytes and about 20% of patients have sarcoid-like granulomas.
EST can have a multitude of morphologic patterns including: reticular, endodermal sinus-like, microcystic, papillary, solid, glandular, alveolar, polyvesicular vitelline, enteric and hepatoid. Schiller-Duval bodies on histology are pathognomonic and seen in the context of the endodermal sinus-like pattern.
The gross examination usually shows a two to three centimetre pale grey, poorly defined tumour with associated haemorrhage and necrosis.[1] The microscopic features include: indistinct cell borders, mitoses, a variable architecture (tubulopapillary, glandular, solid, embryoid bodies - ball of cells surrounded by empty space on three sides), nuclear overlap, and necrosis. Solid (55%), glandular (17%), and papillary (11%) are the most common primary patterns (predominant architectural pattern occupying at least 50%). Other less common primary patterns included nested (3%), micropapillary (2%), anastomosing glandular (1%), sieve-like glandular (<1%), pseudopapillary (<1%), and blastocyst-like (<1%).[2]
Gross Patholgy
| Ovarian germ cell tumor subtype | Features on Gross Pathology |
| Dysgerminoma |
|
| Endodermal sinus tumor or yolk sac tumors |
|
| Embryonal Carcinoma |
|
| Teratoma |
Teratoma-mature
|
| Choriocarcinoma |
http://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytumorchorio.html |
Microscopic Pathology
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Abbas, Fausto, Mitchell (2010). Basic Pathology. Elsevier. pp. 696–697. ISBN 978-81-312-1036-9.
- ↑ Kao, C. S.; Ulbright, T. M.; Young, R. H.; Idrees, M. T. (2014). "Testicular Embryonal Carcinoma: A Morphologic Study of 180 Cases Highlighting Unusual and Unemphasized Aspects". The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 38 (5): 1. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000171. PMID 24503753.