Neurofibromatosis type I
| Neurofibromatosis type I | |
 | |
|---|---|
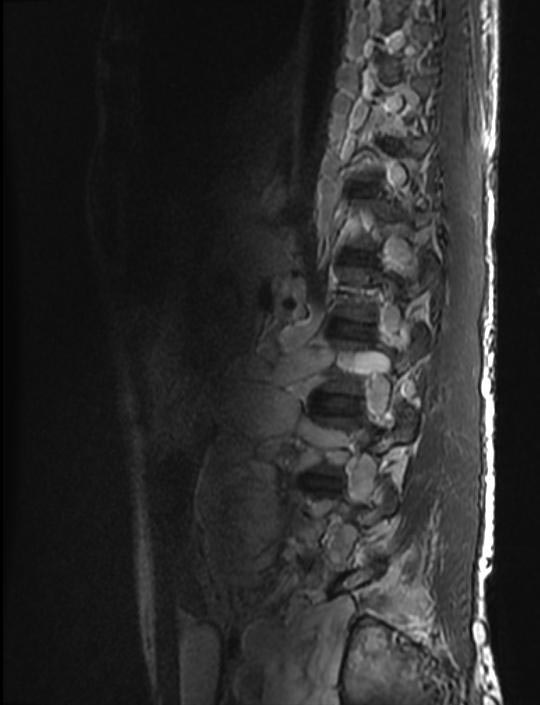
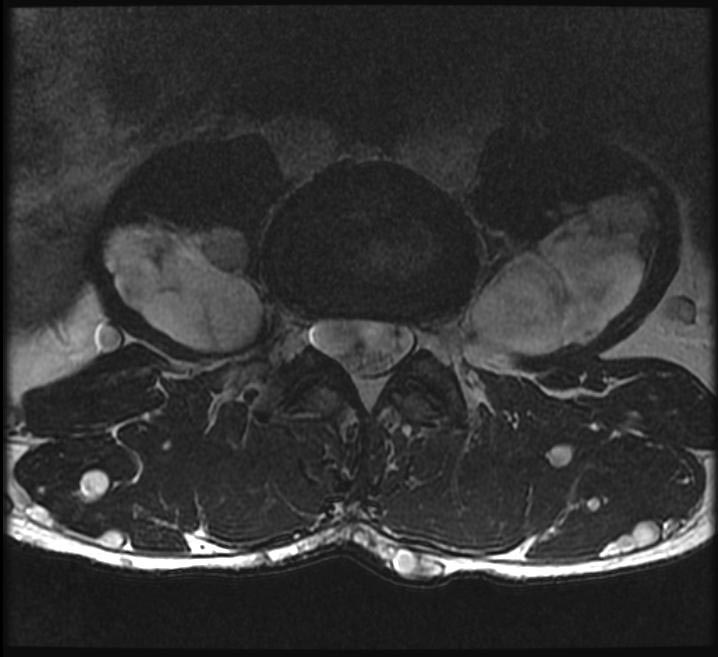
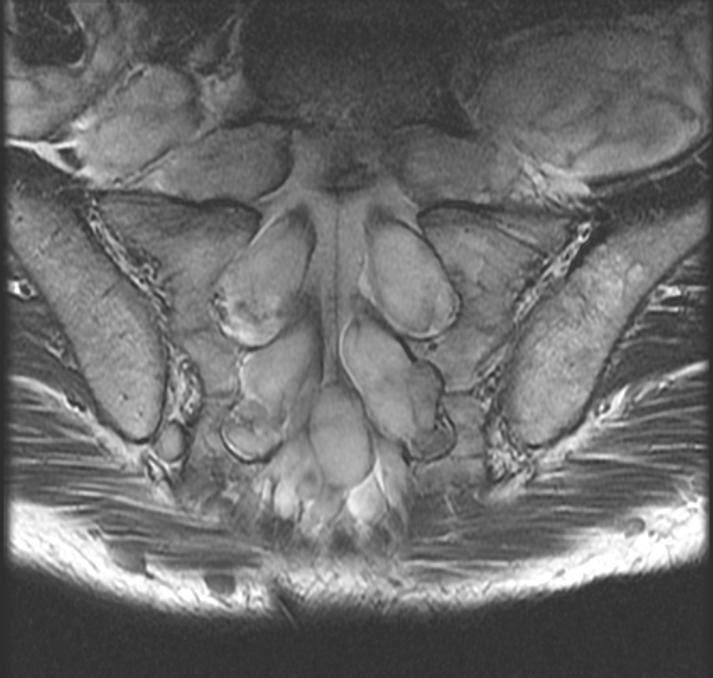
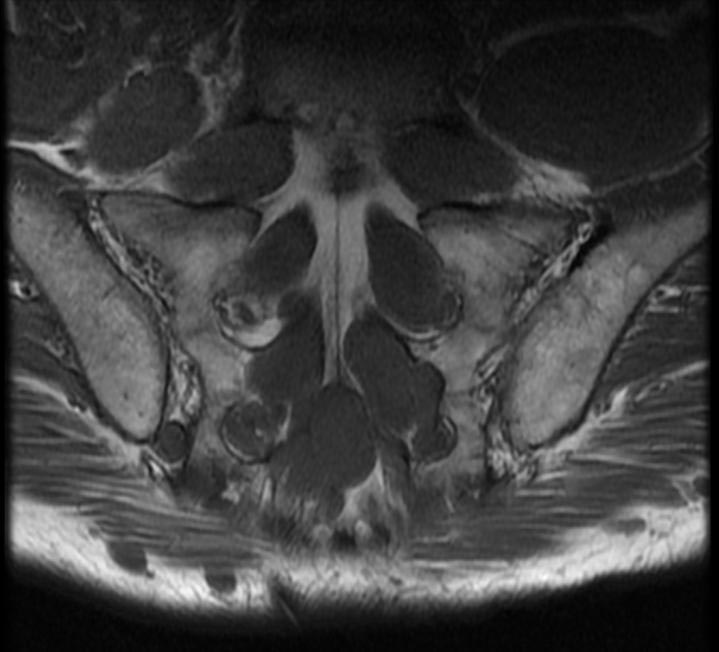
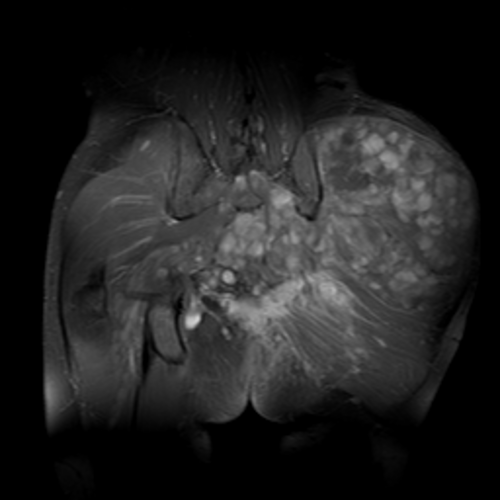
| This coronal contrast-enhanced fat-saturated T1 weighted image from an MRI of the pelvis shows the characteristic fasciculated appearance and infiltrative growth pattern of a plexiform neurofibroma. | |
| ICD-10 | Q85.0 |
| ICD-9 | 237.71 |
| OMIM | 162200 |
| DiseasesDB | 8937 |
| MedlinePlus | 000847 |
| eMedicine | derm/287 neuro/248 oph/338 radio/474 |
| MeSH | D009456 |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Neurofibromatosis type I (NF-1), also known as von Recklinghausen syndrome, is a common inherited disease.
Along with neurofibromatosis type II (a.k.a. MISME syndrome), tuberous sclerosis, Sturge-Weber, and Von Hippel-Lindau disease, NF1 is a member of the phakomatoses or neurocutaneous syndromes, all of which have both neurologic and dermatologic lesions. This grouping is historical and based on disease pathology rather than genetic diagnosis.
Genetics
NF-1 is caused by a mutation of a gene on the long arm of chromosome 17 which encodes a protein known as neurofibromin (aka NF1, not to be confused with the disorder itself) which plays a role in intracellular signaling. The neurofibromin is a negative regulator of the Ras oncogene.
The mutant gene is transmitted with an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance, but up to 50% of NF-1 cases arise due to spontaneous mutation. The incidence of NF-1 is about 1 in 3500 live births.
Clinical findings
Peripheral nervous system lesions
A neurofibroma is a mass lesion of the peripheral nervous system. Its cellular lineage is uncertain, and may derive from Schwann cells, other perineural cell lines, or fibroblasts. Neurofibromas may arise sporadically, or in association with NF-1. A neurofibroma may arise at any point along a peripheral nerve. A cutaneous neurofibroma manifests as a solitary or as multiple firm, rubbery bumps of varying sized on a person's skin. A solitary neurofibroma may also occur in a deeper nerve trunk, and only be seen on cross-sectional imaging (e.g. computed tomography or magnetic resonance) as a fusiform enlargement of a nerve.
The hallmark lesion of NF-1 is the plexiform neurofibroma. These lesions are composed of sheets of neurofibromatous tissue which may infiltrate and encase major nerves, blood vessels, and other vital structures. Because of this, these lesions are impossible to routinely resect.
If a plexiform fibroma manifests on a leg or arm, it will cause extra blood circulation, and may thus accelerate the growth of the limb. This may cause considerable difference in length between left and right limbs. To equalise the difference during childhood, there is an orthopedic surgery called "epiphysiodesis", in which the epiphyseal (growth) plate is removed. It can be removed in one of the bone's end to slow down the growth, or in both ends to stop growth of that bone completely. The surgery must also be carefully planned with regard to timing, as it is non-reversible, so that the limbs are at near equal length at end of growth.
Schwannomas are peripheral nerve-sheath tumor seen with increased frequency in NF-1. In practice, the major distinction between a schwannoma and a solitary neurofibroma is that a schwannoma can be resected while sparing the underlying nerve, while resection of a neurofibroma requires the sacrifice of the underlying nerve.
Malignant peripheral nerve-sheath tumors, or neurofibrosarcomas, can arise from degeneration of a plexiform neurofibroma; this is, fortunately, a rare complication.
Dermatologic manifestations
In addition to the cutaneous neurofibroma, patients with NF-1 develop flat pigmented lesions of the skin called café au lait spots.[2].
NF-1 patients may also get freckles of the axillae (armpits).
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plexiform_neurofibroma
Central nervous system manifestations
The primary neurologic involvement is of the peripheral nervous system, as described above.
Intracranially, NF-1 patients have a predisposition to develop glial tumors of the central nervous system; primarily: optic gliomas and astrocytomas. Another CNS manifestation of NF1 is the so-called "unidentified bright object" or UBO, which is a lesion which has increased signal on a T2 weighted sequence of a magnetic resonance imaging examination of the brain. These UBOs are typically found in the cerebellar peduncles, pons, midbrain, globus pallidus, thalamus, and optic radiations. Their exact identity remains a bit of a mystery since they disappear over time (usually, by age 16), and they are not typically biopsied or resected. They may represent a focally degenerative bit of myelin.
Within the CNS, this manifests as a weakness of the dura, which is the tough covering of the brain and spine. Weakness of the dura leads to focal enlargement (termed dural ectasia) due to chronic exposure to the pressures of CSF pulsation.
Radiographically, dural ectasia can lead to scalloping of the posterior vertebral bodies and to the formation of cystic diverticula of the dura of the spine (termed meningoceles).
Skeletal lesions
Bones, especially the ribs, can develop chronic erosions (pits) from the constant pressure of adjacent neurofibromas and schwannomas. Similarly, the neural foramen of the spine can be widened due to the presence of a nerve root neurofibroma or schwannoma.
In NF-1, these is also a generalized abnormality of the soft tissues, which is referred to as mesodermal dysplasia. This manifests as maldevelopment of skeletal structures, including
- Focal scoliosis and/or kyphosis, which is the most common skeletal manifestation of NF-1, occurring in 20% of affected patients. Approximately one quarter of patients will require corrective surgery.
- Bowing of a long bone with a tendency to fracture and not heal, yielding a pseudarthrosis. The most common bone to be affected is the tibia (causing congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia or CPT). CPT occurs in 2-4% of individuals with NF-1.
- Malformation of the facial bones or of the eye sockets (lambdoid suture defects, sphenoid dysplasia)
- Unilateral overgrowth of a limb
Cognitive problems and learning disabilities in NF-1
The most common complication in patients with NF-1 is cognitive and learning disability. These cognitive problems have been shown to be present in approximately 80% of children with NF-1 and have significant effects on their schooling and everyday life.[1] The most common cognitive problems are with perception, executive functioning and attention. ADHD has been shown to be present in approximately 38% of children with NF-1. Language, maths and motor deficits are also common. These cognitive problems have been shown to be stable into adulthood and do not get worse unlike some of the other physical symptoms of NF-1.[2]
Diagnosis
The National Institute of Health (NIH) has created specific criteria for the diagnosis of NF-1. Two of these seven "Cardinal Clinical Features" are required for positive diagnosis.[3]
- 6 or more café-au-lait macules over 5 mm in greatest diameter in pre-pubertal individuals and over 15 mm in greatest diameter in post-pubertal individuals
- 2 or more neurofibromas of any type or 1 plexiform neurofibroma
- Freckling in the axillary or inguinal regions
- Optic glioma
- 2 or more Lisch nodules (iris harmartomas)
- A distinctive osseous lesion such as sphenoid dysplasia or thinning of the long bone cortex with or without pseudarthrosis
- A first degree relative (parent, sibling, or offspring) with NF1 by the above criteria
DIfferentiating Neurofibromatosis type 1 from other diseases
| Disease | Gene | Chromosome | Differentiating Features | Components of MEN | Diagnosis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parathyroid | Pitutary | Pancreas | |||||
| von Hippel-Lindau syndrome | Von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor | 3p25.3 |
|
- | - | + |
|
| Carney complex | PRKAR1A | 17q23-q24 |
|
- | - | - |
|
| Neurofibromatosis type 1 | RAS | 17 | - | - | - | Prenatal
Postnatal Cardinal Clinical Features" are required for positive diagnosis.
| |
| Li-Fraumeni syndrome | TP53 | 17 | Early onset of diverse amount of cancers such as | - | - | - |
Criteria
|
| Gardner's syndrome | APC | 5q21 |
|
- | - | - |
|
| Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 | RET | - |
|
+ | - | - |
Criteria Two or more specific endocrine tumors
|
| Cowden syndrome | PTEN | - | Hamartomas | - | - | - |
|
| Acromegaly/gigantism | - | - |
|
- | + | - |
|
| Pituitary adenoma | - | - |
|
- | + | - |
|
| Hyperparathyroidism | - | - | - | + | - | - |
|
| Pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma |
VHL RET NF1 SDHB SDHD |
- | Characterized by | - | - | - |
|
| Adrenocortical carcinoma |
|
17p, 13q |
|
- | - | - |
|
| Adapted from Toledo SP, Lourenço DM, Toledo RA. A differential diagnosis of inherited endocrine tumors and their tumor counterparts, journal=Clinics (Sao Paulo), volume= 68, issue= 7, 07/24/2013[4] | |||||||
Prognosis
There is wide variability in how different individuals with the NF-1 gene manifest the disorder. Some individuals may have no symptoms, while others may have rapidly progressive disorder.
The primary problem of NF-1 is the disfigurement due to the cutaneous neurofibromas, pigmented lesions, and occasional limb abnormalities.
Several more severe complications of NF-1 are listed in the following section.
Complications
- Chronic pain, numbness, Pritchetts face, and/or paralysis due to the peripheral nerve sheath tumors
- Blindness due to optic nerve gliomas
- Brain tumors
- Neurologic impairment due to severe spinal scoliosis and/or kyphosis
- Amputation due to a tibial pseudarthrosis
- Malignant degeneration of a plexiform neurofibroma into malignant periphreal nerve sheath tumor (MPNST), occurring in 10-12%
- Depression, It is very common of NF sufferers to suffer severe depression because of the disfigurement it can cause to the body and face.
- Social Anxiety is also common among NF sufferers because of the reaction of others to the condition.
Therapy
Therapy for a patient with neurofibromatosis type I is aimed at palliating symptoms and improving quality of life. Treatment modalities offered may include:
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Surgical resection or decompression of an enlarging lesion
- The third face transplant was performed on a patient with this condition.[5]
References
- ↑ Hyman, SL. et al.(2005). The Nature and Frequency of Cognitive Deficits in Children with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Neurology, 65, 1037-1044.
- ↑ Hyman, S.L. et al. (2003). Natural History of Neuropsychological Ability and T2-Hyperintensities in Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Neurology, 60(7), 1139-1145.
- ↑ Huson SM, Hughes RAC. The Neurofibromatoses. London, UK: Chapman and Hall; 1994;1.3.2:9
- ↑ Toledo SP, Lourenço DM, Toledo RA (2013). "A differential diagnosis of inherited endocrine tumors and their tumor counterparts". Clinics (Sao Paulo). 68 (7): 1039–56. doi:10.6061/clinics/2013(07)24. PMC 3715026. PMID 23917672.
- ↑ http://today.reuters.com/news/articlenews.aspx?type=healthNews&storyID=2007-01-23T185518Z_01_L23896370_RTRUKOC_0_US-FRANCE-TRANSPLANT.xml
- Cotran R, Kumar V, Robbins S (eds). Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 5th ed. WB Saunders, 1994.
Template:Phakomatoses and other congenital malformations not elsewhere classified
Template:Link FA
de:Neurofibromatose Typ 1
nl:Ziekte van Von Recklinghausen
sr:Неурофиброматоза тип 1
fi:Neurofibromatoosi 1