Naldemedine
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Yashasvi Aryaputra[2];
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Naldemedine is a Acetylcholine release inhibitor, Adrenergic receptor agonist that is FDA approved for the (type of indication of drug) of a list of indications, separated by commas.. Common adverse reactions include a list of adverse reactions, separated by commas..
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Contraindications
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Warnings
Conidition 1
(Description)
Conidition 2
(Description)
Conidition 3
(Description)
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Condition 2
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Postmarketing Experience
(Description)
Drug Interactions
- Drug 1
- Drug 2
- Drug 3
- Drug 4
- Drug 5
Drug 1
(Description)
Drug 2
(Description)
Drug 3
(Description)
Drug 4
(Description)
Drug 5
(Description)
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA): Risk Summary
- There are no available data with naldemedine in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage. There is a potential for opioid withdrawal in a fetus when SYMPROIC is used in pregnant women. SYMPROIC should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk.
- In a rat embryo-fetal development study following oral administration of naldemedine during the period of organogenesis at doses resulting in systemic exposure approximately 23,000 times the human area under the plasma-concentration time curve (AUC) at the recommended human dose of 0.2 mg/day, no developmental abnormalities were observed. In rabbits, there were no adverse effects on embryo-fetal development following oral administration of naldemedine during the period of organogenesis at doses resulting in systemic exposure approximately 226 times the human AUC at the recommended human dose of 0.2 mg/day. No effects on pre- and postnatal development were observed in rats at exposures 12 times human exposures at the recommended human dose.
- The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
- Naldemedine crosses the placenta, and may precipitate opioid withdrawal in a fetus due to the immature fetal blood-brain barrier.
Data (Animal)
- In rats, there were no adverse effects on embryo-fetal development following oral administration of naldemedine during the period of organogenesis at doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day (approximately 23,000 times the human exposures (AUC) at the recommended human dose). In rabbits, there were no adverse effects on embryo-fetal development following oral administration of naldemedine during the period of organogenesis at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (approximately 226 times the human exposures (AUC) at the recommended human dose). At 400 mg/kg/day (approximately 844 times the human exposures (AUC) at the recommended human dose), effects in maternal animals included body weight loss/decreased body weight gain and food consumption, fetal loss, and premature delivery. Decreased fetal body weights at this dose may be related to the maternal toxicity observed.
- In the pre- and postnatal development study, pregnant rats were administered naldemedine at oral doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day from gestation day 7 through lactation day 20. No effects on pre- and postnatal development were observed in rats at 1 mg/kg/day (approximately 12 times the human exposures (AUC) at the recommended human dose). A single dam died at parturition at 1000 mg/kg/day, and decreased body weights/body weight gain and food consumption, poor nursing, and total litter loss were noted at 30 and 1000 mg/kg/day (approximately 626 and 17,000 times the human exposures (AUC) at the recommended human dose, respectively). Decreases in the offspring viability index on Day 4 after birth were noted at 30 and 1000 mg/kg/day, and low body weights and delayed pinna unfolding in pups were noted at 1000 mg/kg/day.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Naldemedine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Naldemedine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
Risk Summary
- There is no information regarding the presence of naldemedine in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Naldemedine was present in the milk of rats. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions, including opioid withdrawal in breastfed infants, a decision should be made to discontinue breastfeeding or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. If drug is discontinued in order to minimize drug exposure to a breastfed infant, advise women that breastfeeding may be resumed 3 days after the final dose of SYMPROIC.
Data
- Drug-related radioactivity was transferred into milk of lactating rats following a single oral dose of 1 mg/kg [carbonyl-14C]-naldemedine.
Pediatric Use
- The safety and effectiveness of SYMPROIC have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
- Of 1163 patients in clinical studies exposed to SYMPROIC, 183 (16%) were 65 years of age and over, while 37 (3%) were 75 years and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness between these and younger patients were observed, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. In a population pharmacokinetic analysis, no age-related alterations in the pharmacokinetics of naldemedine were observed.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Naldemedine with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Naldemedine with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Naldemedine in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
- The effect of severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) on the pharmacokinetics of naldemedine has not been evaluated. Avoid use of SYMPROIC in patients with severe hepatic impairment. No dose adjustment of SYMPROIC is required in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Naldemedine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Naldemedine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Alteration of analgesic dosing regimen prior to initiating SYMPROIC is not required.
- Patients receiving opioids for less than 4 weeks may be less responsive to SYMPROIC.
- Discontinue SYMPROIC if treatment with the opioid pain medication is also discontinued.
Monitoring
- Increased frequency of spontaneous bowel movements is indicative of efficacy.
- Development of severe, persistent, or worsening abdominal pain.
- Symptoms of opioid withdrawal.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Naldemedine and IV administrations.
Overdosage
- Single doses of naldemedine up to 100 mg (500 times the recommended dose) and multiple doses of up to 30 mg (150 times the recommended dose) for 10 days have been administered to healthy subjects in clinical studies. Dose-dependent increases in gastrointestinal-related adverse reactions, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea, were observed.
- Single doses of naldemedine up to 3 mg (15 times the recommended dose) and multiple doses of 0.4 mg (twice the recommended dose) for 28 days have been administered to patients with OIC in clinical studies. Dose-dependent increases in gastrointestinal-related adverse reactions, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, were observed. Also, chills, hyperhidrosis, and dizziness were reported more frequently at 1 and 3 mg doses and hyperhidrosis at the 0.4 mg dose.
- No antidote for naldemedine is known. Hemodialysis is not an effective means to remove naldemedine from the blood.
Pharmacology
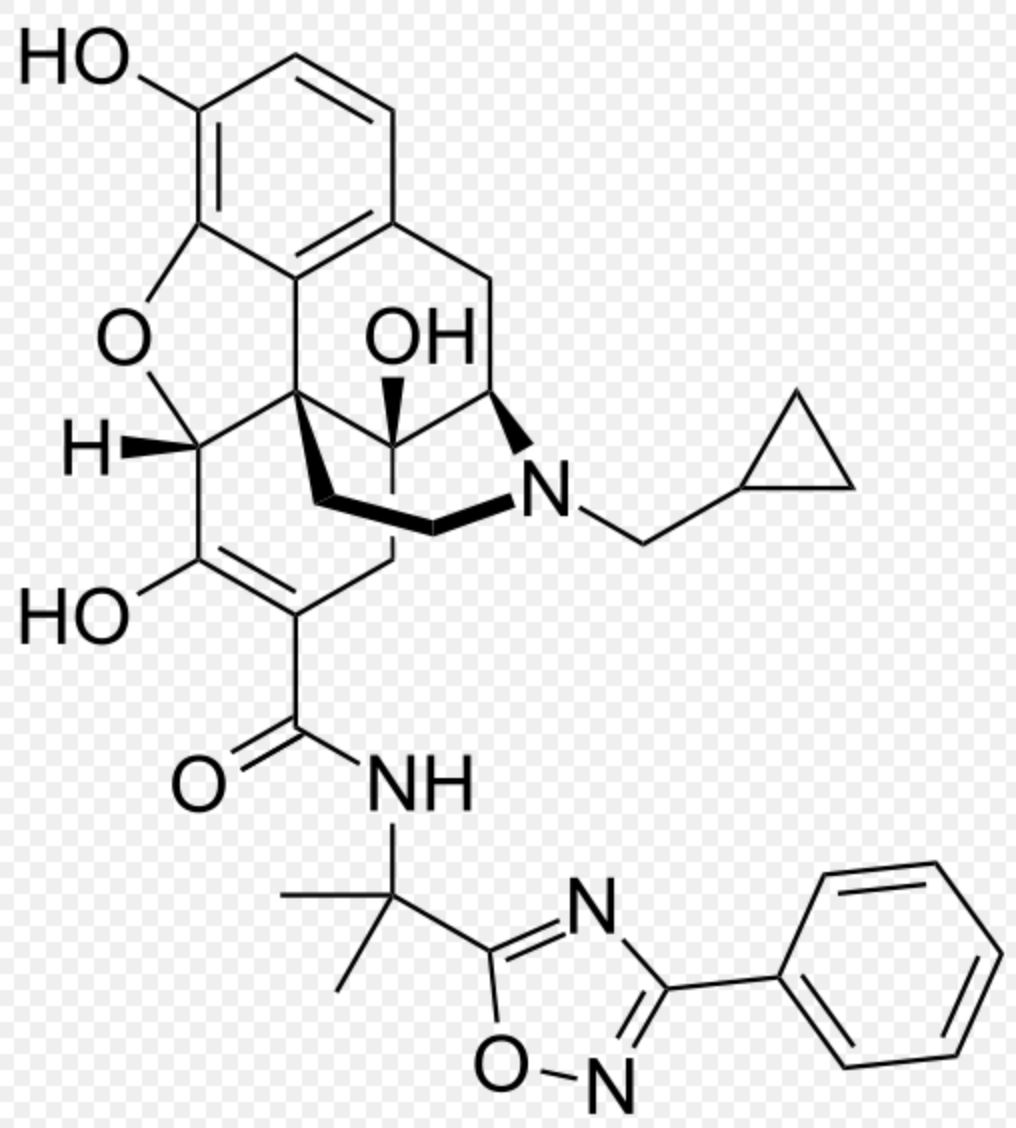
| |
Naldemedine
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| 17-(cyclopropylmethyl)-6,7-didehydro-4,5α-epoxy-3,6,14-trihydroxy-N-[2-(3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)propan-2-yl]morphinan-7-carboxamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 1345728-04-2 (tosylate) |
| ATC code | None |
| PubChem | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 570.63556 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status |
?(US) |
| Routes | Oral |
Mechanism of Action
- Naldemedine is an opioid antagonist with binding affinities for mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors. Naldemedine functions as a peripherally-acting mu-opioid receptor antagonist in tissues such as the gastrointestinal tract, thereby decreasing the constipating effects of opioids.
- Naldemedine is a derivative of naltrexone to which a side chain has been added that increases the molecular weight and the polar surface area, thereby reducing its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB).
- Naldemedine is also a substrate of the P-glycoprotein (P-gp) efflux transporter. Based on these properties, the CNS penetration of naldemedine is expected to be negligible at the recommended dose levels, limiting the potential for interference with centrally-mediated opioid analgesia.
Structure

Pharmacodynamics
- Use of opioids induces slowing of gastrointestinal motility and transit. Antagonism of gastrointestinal mu-opioid receptors by naldemedine inhibits opioid-induced delay of gastrointestinal transit time.
Effect on Cardiac Repolarization
- At a dose up to 5-times the recommended dose, SYMPROIC does not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
- Following oral administration, naldemedine is absorbed with the time to achieve peak concentrations (Tmax) of approximately 0.75 hours in a fasted state. Across the range of doses evaluated, the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) increased in a dose-proportional or almost dose-proportional manner. Accumulation was minimal following multiple daily doses of naldemedine.
Food Effect
- A high-fat meal decreased the rate, but not the extent of naldemedine absorption. The Cmax was decreased by approximately 35% and time to achieve Cmax was delayed from 0.75 hours in the fasted state to 2.5 hours in the fed state, whereas there was no meaningful change in the AUC in the fed state.
Distribution
- Plasma protein binding of naldemedine in humans is 93% to 94%. The mean apparent volume of distribution during the terminal phase (Vz/F) is 155 L.
Elimination
- The terminal elimination half-life of naldemedine is 11 hours.
Metabolism
- Naldemedine is primarily metabolized by CYP3A to nor-naldemedine, with minor contribution from UGT1A3 to form naldemedine 3-G. Nor-naldemedine and naldemedine 3-G have been shown to have antagonistic activity for opioid receptors, with less potent effect than naldemedine.
- Following oral administration of [14C]-labeled naldemedine, the primary metabolite in plasma was nor-naldemedine, with a relative exposure compared to naldemedine of approximately 9% to 13%. Naldemedine 3-G was a minor metabolite in plasma, with a relative exposure to naldemedine of less than 3%.
- Naldemedine also undergoes cleavage in the GI tract to form benzamidine and naldemedine carboxylic acid.
Excretion
- Following oral administration of [14C]-labeled naldemedine, the total amount of radioactivity excreted in the urine and feces was 57% and 35% of the administered dose of naldemedine, respectively. The amount of naldemedine excreted unchanged in the urine was approximately 16% to 18% of the administered dose. Benzamidine was the most predominant metabolite excreted in the urine and feces, representing approximately 32% and 20% of the administered dose of naldemedine, respectively. The percentage of unchanged drug in feces has not been estimated.
Use in Specific Populations
Age: Geriatric Population, Sex, Race/Ethnicity
- A population pharmacokinetic analysis from clinical studies with naldemedine did not identify a clinically meaningful effect of age, sex, or race on the pharmacokinetics of naldemedine.
Renal Impairment
- The pharmacokinetics of naldemedine after administration of a 0.2 mg single oral dose of SYMPROIC was studied in 8 subjects with mild (n=8, estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] of 60 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m2), moderate (n=8, eGFR 30 to 59 mL/min/1.73 m2), and severe (n=6, eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2) renal impairment, and subjects with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) requiring hemodialysis (n=8), and compared to healthy subjects with normal renal function (n=8, estimated creatinine clearance of at least 90 mL/min). The pharmacokinetics of naldemedine between subjects in all groups were similar.
- Plasma concentrations of naldemedine in subjects with ESRD requiring hemodialysis were similar when SYMPROIC was administered either pre- or post-hemodialysis, indicating that naldemedine was not removed from the blood by hemodialysis.
Hepatic Impairment
- The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of a 0.2 mg single oral dose of SYMPROIC was studied in subjects with hepatic impairment classified as mild (n=8, Child-Pugh Class A) or moderate (n=8, Child-Pugh Class B) and compared with healthy subjects with normal hepatic function (n=8). The pharmacokinetics of naldemedine between subjects in all groups were similar.
- The effect of severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) on the pharmacokinetics of naldemedine was not evaluated.
Drug Interaction Studies
Effect of Naldemedine on Other Drugs
- In in vitro studies at clinically relevant concentrations, naldemedine did not inhibit the major CYP enzymes (including CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, CYP3A4/5, or CYP4A11 isozymes) and is not an inhibitor of transporters (including OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1, OCT2, OAT1, OAT3, BCRP, or P-gp). Naldemedine did not cause significant induction of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP3A4, UGT1A2, UGT1A6, or UGT2B7 isozymes.
Effect of Other Drugs on Naldemedine
- Naldemedine is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 enzyme with minor contribution from UGT1A3. Naldemedine is a substrate of P-gp. The effects of co-administered drugs on the pharmacokinetics of naldemedine are summarized in Figure 1.

Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
- In 2-year carcinogenicity studies, there were no drug-related neoplastic findings following oral administration of naldemedine to mice and rats at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (approximately 17,500 and 6,300 times the human exposures (AUC) at the recommended human dose, respectively).
Mutagenesis
- Naldemedine was not genotoxic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay, a chromosomal aberration assay with cultured Chinese hamster lung cells, and an in vivo micronucleus assay with rat bone marrow cells.
Impairment of Fertility
- Naldemedine was found to have no effect on fertility or reproductive performance in male and female rats at oral doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day (approximately 17,000 times the human exposures (AUC) at the recommended human dose). In female rats, prolongation of diestrous phase was noted at 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 179 times the human exposures (AUC) at the recommended human dose).
Clinical Studies
- SYMPROIC was evaluated in two replicate, 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (Study 1 and Study 2) in which SYMPROIC was used without laxatives in patients with OIC and chronic non-cancer pain.
- Patients receiving a stable opioid morphine equivalent daily dose of at least 30 mg for at least 4 weeks before enrollment and self-reported OIC were eligible for clinical trial participation.
- Patients with evidence of significant structural abnormalities of the GI tract were not enrolled in these trials.
- In Studies 1 and 2, patients had to either be not using laxatives or willing to discontinue laxative use at the time of screening and willing to use only the provided rescue laxatives during the screening and treatment periods.
- In Studies 1 and 2, OIC was confirmed through a two-week run in period and was defined as no more than 4 spontaneous bowel movements (SBMs) total over 14 consecutive days and less than 3 SBMs in a given week with at least 25% of the SBMs associated with one or more of the following conditions: (1) straining; (2) hard or lumpy stools; (3) having a sensation of incomplete evacuation; and (4) having a sensation of anorectal obstruction/blockage.
- An SBM was defined as a bowel movement (BM) without rescue laxative taken within the past 24 hours. Patients with no BMs over the 7 consecutive days prior to and during the 2 week screening period or patients who have never taken laxatives were excluded.
- In the screening and treatment periods, bisacodyl was used as rescue laxative if patients had not had a BM for 72 hours and were allowed one-time use of an enema, if after 24 hours of taking bisacodyl they still had not had a BM.
- A total of 547 patients in Study 1 and 553 patients in Study 2 were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive SYMPROIC 0.2 mg once daily or placebo for 12 weeks. Study medication was administered without regard to meals.
- The mean age of subjects in Studies 1 and 2 was 54 years; 59% were women; and 80% were white. The most common types of pain in Studies 1 and 2 were back or neck pain (61%). The mean baseline number of SBMs was 1.3 and 1.2 per week for Studies 1 and 2, respectively.
- Prior to enrollment, patients were using their current opioid for a mean duration of approximately 5 years. A wide range of types of opioids were used. The mean baseline opioid morphine equivalent daily dosage was 132 mg and 121 mg per day for Studies 1 and 2, respectively.
- The efficacy of SYMPROIC was assessed in Studies 1 and 2 using a responder analysis. A responder was defined as a patient who had at least 3 SBMs per week and a change from baseline of at least 1 SBM per week for at least 9 out of the 12 weeks and 3 out of the last 4 weeks in Studies 1 and 2.
- The responder rates in Studies 1 and 2 are shown in Table 4.

- In Studies 1 and 2, the mean increase in frequency of SBMs per week from baseline to the last 2 weeks of the 12-week treatment period was 3.1 for SYMPROIC vs. 2.0 for placebo (difference 1.0, 95% CI 0.6, 1.5), and 3.3 for SYMPROIC vs. 2.1 for placebo (difference 1.2, 95% CI 0.8, 1.7), respectively.
- During week 1 of the treatment period, the mean increase in frequency of SBMs per week from baseline was 3.3 for SYMPROIC vs. 1.3 for placebo (difference 2.0, 95% CI 1.5, 2.5) in Study 1 and 3.7 for SYMPROIC vs. 1.6 for placebo (difference 2.1, 95% CI 1.5, 2.6) in Study 2.
- The mean increase in the frequency of complete SBM (CSBM) per week from baseline to the last 2 weeks of 12-week treatment period was 2.3 for SYMPROIC vs. 1.5 for placebo (difference 0.8, 95% CI 0.4, 1.2) in Study 1 and 2.6 for SYMPROIC vs. 1.6 for placebo (difference 1.1, 95% CI 0.6, 1.5) in Study 2. A CSBM was defined as a SBM that was associated with a sense of complete evacuation.
- The change in the frequency of SBMs without straining per week from baseline to the last 2 weeks of the treatment period was 1.3 for SYMPROIC vs. 0.7 for placebo (difference 0.6, 95% CI 0.2, 0.9) in Study 1 and 1.8 for SYMPROIC vs. 1.1 for placebo (difference 0.7, 95% CI 0.3, 1.2) in Study 2.
How Supplied
- SYMPROIC is supplied as 0.2 mg naldemedine tablets in:
- bottle of 30 tablets - NDC 59011-523-30
- bottle of 90 tablets - NDC 59011-523-90
Storage
- Store SYMPROIC in light resistant container at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Naldemedine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel




{{#ask: Label Page::Naldemedine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Administration
- Advise patients to discontinue SYMPROIC if treatment with the opioid pain medication is also discontinued.
Gastrointestinal Perforation
- Advise patients to discontinue SYMPROIC and to promptly seek medical attention if they develop unusually severe, persistent or worsening abdominal pain.
Opioid Withdrawal
- Advise patients that clusters of symptoms consistent with opioid withdrawal may occur while taking SYMPROIC and to contact their healthcare provider if these symptoms occur.
Pregnancy
- Advise females of reproductive potential, who become pregnant or are planning to become pregnant, that the use of SYMPROIC during pregnancy may precipitate opioid withdrawal in a fetus due to the undeveloped blood-brain barrier.
Lactation
- Advise women that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with SYMPROIC and for 3 days after the final dose.

Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Naldemedine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor regarding the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Symproic
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Naldemedine Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Drug Shortage
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.