Mirtazapine
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Pratik Bahekar, MBBS [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Mirtazapine is a noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of major depressive disorder. Common adverse reactions include increased appetite, serum triglycerides raised, weight gain, constipation, xerostomia, ALT/SGPT level raised, asthenia, dizziness, somnolence, disturbance in thinking.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
- Major depression
- 15 mg/day PO at bedtime, increase every 1-2 weeks to a max dose of 45 mg/day.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information about Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Mirtazapine in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
- Anxiety
- Cancer
- Dysthymia
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Panic disorder
There is limited information about Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Mirtazapine in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Safety in pediatric patient has not been established.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information about Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Mirtazapine in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information about Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Mirtazapine in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity
- Mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets are contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to mirtazapine or to any of the excipients.
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
- The use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) intended to treat psychiatric disorders with mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets or within 14 days of stopping treatment with mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets is contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. The use of mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets within 14 days of stopping an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders is also contraindicated.
- Starting mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets in a patient who is being treated with MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue is also contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome
Warnings
- Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk
- Patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), both adult and pediatric, may experience worsening of their depression and/or the emergence of suicidal ideation and behavior (suicidality) or unusual changes in behavior, whether or not they are taking antidepressant medications, and this risk may persist until significant remission occurs. Suicide is a known risk of depression and certain other psychiatric disorders, and these disorders themselves are the strongest predictors of suicide. There has been a long-standing concern, however, that antidepressants may have a role in inducing worsening of depression and the emergence of suicidality in certain patients during the early phases of treatment. Pooled analyses of short-term placebo-controlled trials of antidepressant drugs (SSRIs and others) showed that these drugs increase the risk of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults (ages 18–24) with major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults beyond age 24; there was a reduction in risk with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults aged 65 and older.
- The pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials in children and adolescents with MDD, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), or other psychiatric disorders included a total of 24 short-term trials of 9 antidepressant drugs in over 4400 patients. The pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials in adults with MDD or other psychiatric disorders included a total of 295 short-term trials (median duration of 2 months) of 11 antidepressant drugs in over 77,000 patients. There was considerable variation in risk of suicidality among drugs, but a tendency toward an increase in the younger patients for almost all drugs studied. There were differences in absolute risk of suicidality across different indications, with the highest incidence in MDD. The risk differences (drug vs. placebo), however, were relatively stable within age strata and across indications. These risk differences (drug-placebo difference in the number of cases of suicidality per 1000 patients treated) are provided in Table 1.

- No suicides occurred in any of the pediatric trials. There were suicides in the adult trials, but the number was not sufficient to reach any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
- It is unknown whether the suicidality risk extends to longer-term use, i.e., beyond several months. However, there is substantial evidence from placebo-controlled maintenance trials in adults with depression that the use of antidepressants can delay the recurrence of depression.
- All patients being treated with antidepressants for any indication should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, and unusual changes in behavior, especially during the initial few months of a course of drug therapy, or at times of dose changes, either increases or decreases.
- The following symptoms, anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), hypomania, and mania, have been reported in adult and pediatric patients being treated with antidepressants for major depressive disorder as well as for other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric. Although a causal link between the emergence of such symptoms and either the worsening of depression and/or the emergence of suicidal impulses has not been established, there is concern that such symptoms may represent precursors to emerging suicidality.
- Consideration should be given to changing the therapeutic regimen, including possibly discontinuing the medication, in patients whose depression is persistently worse, or who are experiencing emergent suicidality or symptoms that might be precursors to worsening depression or suicidality, especially if these symptoms are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient’s presenting symptoms.
- Families and caregivers of patients being treated with antidepressants for major depressive disorder or other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric, should be alerted about the need to monitor patients for the emergence of agitation, irritability, unusual changes in behavior, and the other symptoms described above, as well as the emergence of suicidality, and to report such symptoms immediately to health care providers. Such monitoring should include daily observation by families and caregivers. Prescriptions for mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets should be written for the smallest quantity of tablets consistent with good patient management, in order to reduce the risk of overdose.
- Screening Patients for Bipolar Disorder:
- A major depressive episode may be the initial presentation of bipolar disorder. It is generally believed (though not established in controlled trials) that treating such an episode with an antidepressant alone may increase the likelihood of precipitation of a mixed/manic episode in patients at risk for bipolar disorder. Whether any of the symptoms described above represent such a conversion is unknown. However, prior to initiating treatment with an antidepressant, patients with depressive symptoms should be adequately screened to determine if they are at risk for bipolar disorder; such screening should include a detailed psychiatric history, including a family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, and depression. It should be noted that mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets are not approved for use in treating bipolar depression.
- Agranulocytosis
- In premarketing clinical trials, 2 (1 with Sjögren’s Syndrome) out of 2796 patients treated with mirtazapine tablets developed agranulocytosis [absolute neutrophil count (ANC) <500/mm3 with associated signs and symptoms, e.g., fever, infection, etc.] and a third patient developed severe neutropenia (ANC <500/mm3 without any associated symptoms). For these 3 patients, onset of severe neutropenia was detected on days 61, 9, and 14 of treatment, respectively. All 3 patients recovered after mirtazapine was stopped. These 3 cases yield a crude incidence of severe neutropenia (with or without associated infection) of approximately 1.1 per thousand patients exposed, with a very wide 95% confidence interval, i.e., 2.2 cases per 10,000 to 3.1 cases per 1000. If a patient develops a sore throat, fever, stomatitis, or other signs of infection, along with a low WBC count, treatment with mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets should be discontinued and the patient should be closely monitored.
- Serotonin Syndrome
- The development of a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome has been reported with SNRIs and SSRIs, including mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets, alone but particularly with concomitant use of serotonergic drugs (including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, and St. John"s wort) and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (in particular, MAOIs, both those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others, such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue).
- Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flusing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Patients should be monitored for the emergence of serotonin syndrome.
- The concomitant use of mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets with MAOIs intended to treat psychiatric disorders is contraindicated. Mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets should also not be started in a patient who is being treated with MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. All reports with methylene blue that provided information on the route of administration involved intravenous administration in the dose range of 1 mg/kg to 8 mg/kg. No reports involved the administration of methylene blue by other routes (such as oral tablets or local tissue injection) or at lower doses. There may be circumstances when it is necessary to initiate treatment with an MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue in a patient taking mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets. Mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets should be discontinued before initiating treatment with the MAOI (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
- If concomitant use of mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets with other serotonergic drugs, including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, buspirone, tryptophan, and St. John"s wort, is clinically warranted, be aware of a potential increased risk for serotonin syndrome, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases.
- Treatment with mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets and any concomitant serotonergic agents should be discontinued immediately if the above events occur and supportive symptomatic treatment should be initiated.
- General
- Discontinuation Symptoms There have been reports of adverse reactions upon the discontinuation of mirtazapine/mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets (particularly when abrupt), including but not limited to the following: dizziness, abnormal dreams, sensory disturbances (including paresthesia and electric shock sensations), agitation, anxiety, fatigue, confusion, headache, tremor, nausea, vomiting, and sweating, or other symptoms which may be of clinical significance. The majority of the reported cases are mild and self-limiting. Even though these have been reported as adverse reactions, it should be realized that these symptoms may be related to underlying disease.
- Patients currently taking mirtazapine should NOT discontinue treatment abruptly, due to risk of discontinuation symptoms. At the time that a medical decision is made to discontinue treatment with mirtazapine, a gradual reduction in the dose, rather than an abrupt cessation, is recommended.
- Akathisia/Psychomotor Restlessness
- The use of antidepressants has been associated with the development of akathisia, characterized by a subjectively unpleasant or distressing restlessness and need to move often accompanied by an inability to sit or stand still. This is most likely to occur within the first few weeks of treatment. In patients who develop these symptoms, increasing the dose may be detrimental.
- Hyponatremia
- Hyponatremia has been reported very rarely with the use of mirtazapine. Caution should be exercised in patients at risk, such as elderly patients or patients concomitantly treated with medications known to cause hyponatremia.
- Somnolence
- In US controlled studies, somnolence was reported in 54% of patients treated with mirtazapine tablets, compared to 18% for placebo and 60% for amitriptyline. In these studies, somnolence resulted in discontinuation for 10.4% of mirtazapine-treated patients, compared to 2.2% for placebo. It is unclear whether or not tolerance develops to the somnolent effects of mirtazapine. Because of the potentially significant effects of mirtazapine on impairment of performance, patients should be cautioned about engaging in activities requiring alertness until they have been able to assess the drug’s effect on their own psychomotor performance.
- Dizziness
- In US controlled studies, dizziness was reported in 7% of patients treated with mirtazapine, compared to 3% for placebo and 14% for amitriptyline. It is unclear whether or not tolerance develops to the dizziness observed in association with the use of mirtazapine.
- Increased Appetite/Weight Gain
- In US controlled studies, appetite increase was reported in 17% of patients treated with mirtazapine, compared to 2% for placebo and 6% for amitriptyline. In these same trials, weight gain of ≥7% of body weight was reported in 7.5% of patients treated with mirtazapine, compared to 0% for placebo and 5.9% for amitriptyline. In a pool of premarketing US studies, including many patients for long-term, open-label treatment, 8% of patients receiving mirtazapine discontinued for weight gain. In an 8-week-long pediatric clinical trial of doses between 15 to 45 mg/day, 49% of mirtazapine-treated patients had a weight gain of at least 7%, compared to 5.7% of placebo-treated patients (see PRECAUTIONS: Pediatric Use).
- Cholesterol/Triglycerides
- In US controlled studies, nonfasting cholesterol increases to ≥20% above the upper limits normal were observed in 15% of patients treated with mirtazapine, compared to 7% for placebo and 8% for amitriptyline. In these same studies, nonfasting triglyceride increases to ≥500 mg/dL were observed in 6% of patients treated with mirtazapine, compared to 3% for placebo and 3% for amitriptyline.
- Transaminase Elevations
- Clinically significant ALT (SGPT) elevations (≥3 times the upper limit of the normal range) were observed in 2.0% (8/424) of patients exposed to mirtazapine in a pool of short-term US controlled trials, compared to 0.3% (1/328) of placebo patients and 2.0% (3/181) of amitriptyline patients. Most of these patients with ALT increases did not develop signs or symptoms associated with compromised liver function. While some patients were discontinued for the ALT increases, in other cases, the enzyme levels returned to normal despite continued mirtazapine treatment. Mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets should be used with caution in patients with impaired hepatic function.
- Activation of Mania/Hypomania
- Mania/hypomania occurred in approximately 0.2% (3/1299 patients) of mirtazapine-treated patients in US studies. Although the incidence of mania/hypomania was very low during treatment with mirtazapine, it should be used carefully in patients with a history of mania/hypomania.
- Seizure
- In premarketing clinical trials, only 1 seizure was reported among the 2796 US and non-US patients treated with mirtazapine. However, no controlled studies have been carried out in patients with a history of seizures. Therefore, care should be exercised when mirtazapine is used in these patients.
- Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
- Clinical experience with mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets in patients with concomitant systemic illness is limited. Accordingly, care is advisable in prescribing mirtazapine for patients with diseases or conditions that affect metabolism or hemodynamic responses. Mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets have not been systematically evaluated or used to any appreciable extent in patients with a recent history of myocardial infarction or other significant heart disease. Mirtazapine was associated with significant orthostatic hypotension in early clinical pharmacology trials with normal volunteers. Orthostatic hypotension was infrequently observed in clinical trials with depressed patients. Mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets should be used with caution in patients with known cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease that could be exacerbated by hypotension (history of myocardial infarction, angina, or ischemic stroke) and conditions that would predispose patients to hypotension (dehydration, hypovolemia, and treatment with antihypertensive medication).
- Mirtazapine clearance is decreased in patients with moderate [glomerular filtration rate (GFR) = 11–39 mL/min/1.73 m2] and severe [GFR <10 mL/min/1.73 m2] renal impairment, and also in patients with hepatic impairment. Caution is indicated in administering mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets to such patients
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Mirtazapine Clinical Trials Experience in the drug label.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Mirtazapine Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Mirtazapine Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
There is no FDA guidance on usage of Mirtazapine in women who are pregnant.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Mirtazapine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Mirtazapine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mirtazapine in women who are nursing.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of mirtazapine in the pediatric population have not been established
Geriatic Use
Following oral administration of mirtazapine tablets 20 mg/day for 7 days to subjects of varying ages (range, 25–74), oral clearance of mirtazapine was reduced in the elderly compared to the younger subjects. The differences were most striking in males, with a 40% lower clearance in elderly males compared to younger males, while the clearance in elderly females was only 10% lower compared to younger females. Caution is indicated in administering mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets to elderly patients
Gender
The mean elimination half-life of mirtazapine after oral administration ranges from approximately 20 to 40 hours across age and gender subgroups, with females of all ages exhibiting significantly longer elimination half-lives than males (mean half-life of 37 hours for females vs. 26 hours for males)
Race
There have been no clinical studies to evaluate the effect of race on the pharmacokinetics of mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets.
Renal Impairment
The disposition of mirtazapine was studied in patients with varying degrees of renal function. Elimination of mirtazapine is correlated with creatinine clearance. Total body clearance of mirtazapine was reduced approximately 30% in patients with moderate (Clcr = 11–39 mL/min/1.73 m2) and approximately 50% in patients with severe (Clcr = <10 mL/min/1.73 m2) renal impairment when compared to normal subjects. Caution is indicated in administering mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets to patients with compromised renal function.
Hepatic Impairment
Following a single 15-mg oral dose of mirtazapine, the oral clearance of mirtazapine was decreased by approximately 30% in hepatically impaired patients compared to subjects with normal hepatic function. Caution is indicated in administering mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets to patients with compromised hepatic function.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mirtazapine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Mirtazapine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Mirtazapine Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Mirtazapine Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Mirtazapine and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Mirtazapine overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Mirtazapine Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
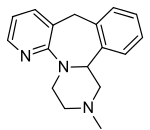
Structure
Mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets USP are an orally administered drug. Mirtazapine has a tetracyclic chemical structure and belongs to the piperazino-azepine group of compounds. It is designated 1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydro-2-methylpyrazino [2,1-a] pyrido [2,3-c] benzazepine and has the empirical formula of C17H19N3. Its molecular weight is 265.36. The structural formula is the following and it is the racemic mixture:

Mirtazapine is a white to creamy white crystalline powder which is slightly soluble in water. Mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets are available for oral administration as an orally disintegrating tablet containing 15 or 30 mg of mirtazapine. It disintegrates in the mouth within seconds after placement on the tongue, allowing its contents to be subsequently swallowed with or without water. Mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets also contain the following inactive ingredients: aspartame powder, colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, natural and artificial orange flavor, sodium stearyl fumarate and xylitol.
Pharmacodynamics
- The mechanism of action of mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets, as with other drugs effective in the treatment of major depressive disorder, is unknown.
- Evidence gathered in preclinical studies suggests that mirtazapine enhances central noradrenergic and serotonergic activity. These studies have shown that mirtazapine acts as an antagonist at central presynaptic α2-adrenergic inhibitory autoreceptors and heteroreceptors, an action that is postulated to result in an increase in central noradrenergic and serotonergic activity.
- Mirtazapine is a potent antagonist of 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptors. Mirtazapine has no significant affinity for the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors.
- Mirtazapine is a potent antagonist of histamine (H1) receptors, a property that may explain its prominent sedative effects.
- Mirtazapine is a moderate peripheral α1-adrenergic antagonist, a property that may explain the occasional orthostatic hypotension reported in association with its use.
- Mirtazapine is a moderate antagonist at muscarinic receptors, a property that may explain the relatively low incidence of anticholinergic side effects associated with its use.
Pharmacokinetics
- Mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets are rapidly and completely absorbed following oral administration and have a half-life of about 20 to 40 hours. Peak plasma concentrations are reached within about 2 hours following an oral dose. The presence of food in the stomach has a minimal effect on both the rate and extent of absorption and does not require a dosage adjustment. Mirtazapine orally disintegrating tablets are bioequivalent to mirtazapine tablets.
- Mirtazapine is extensively metabolized after oral administration. Major pathways of biotransformation are demethylation and hydroxylation followed by glucuronide conjugation. In vitro data from human liver microsomes indicate that cytochrome 2D6 and 1A2 are involved in the formation of the 8-hydroxy metabolite of mirtazapine, whereas cytochrome 3A is considered to be responsible for the formation of the N-desmethyl and N-oxide metabolite. Mirtazapine has an absolute bioavailability of about 50%. It is eliminated predominantly via urine (75%) with 15% in feces. Several unconjugated metabolites possess pharmacological activity but are present in the plasma at very low levels. The (–) enantiomer has an elimination half-life that is approximately twice as long as the (+) enantiomer and therefore achieves plasma levels that are about 3 times as high as that of the (+) enantiomer.
- Plasma levels are linearly related to dose over a dose range of 15 to 80 mg. The mean elimination half-life of mirtazapine after oral administration ranges from approximately 20 to 40 hours across age and gender subgroups, with females of all ages exhibiting significantly longer elimination half-lives than males (mean half-life of 37 hours for females vs. 26 hours for males). Steady state plasma levels of mirtazapine are attained within 5 days, with about 50% accumulation (accumulation ratio = 1.5).
- Mirtazapine is approximately 85% bound to plasma proteins over a concentration range of 0.01 to 10 mcg/mL.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Mirtazapine Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
The efficacy of mirtazapine tablets as a treatment for major depressive disorder was established in 4 placebo-controlled, 6-week trials in adult outpatients meeting DSM-III criteria for major depressive disorder. Patients were titrated with mirtazapine from a dose range of 5 mg up to 35 mg/day. Overall, these studies demonstrated mirtazapine to be superior to placebo on at least 3 of the following 4 measures: 21-Item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS) total score; HDRS Depressed Mood Item; CGI Severity score; and Montgomery and Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS). Superiority of mirtazapine over placebo was also found for certain factors of the HDRS, including anxiety/somatization factor and sleep disturbance factor. The mean mirtazapine dose for patients who completed these 4 studies ranged from 21 to 32 mg/day. A fifth study of similar design utilized a higher dose (up to 50 mg) per day and also showed effectiveness.
Examination of age and gender subsets of the population did not reveal any differential responsiveness on the basis of these subgroupings.
In a longer-term study, patients meeting (DSM-IV) criteria for major depressive disorder who had responded during an initial 8 to 12 weeks of acute treatment on mirtazapine were randomized to continuation of mirtazapine or placebo for up to 40 weeks of observation for relapse. Response during the open phase was defined as having achieved a HAM-D 17 total score of ≤8 and a CGI-Improvement score of 1 or 2 at 2 consecutive visits beginning with week 6 of the 8 to 12 weeks in the open-label phase of the study. Relapse during the double-blind phase was determined by the individual investigators. Patients receiving continued mirtazapine treatment experienced significantly lower relapse rates over the subsequent 40 weeks compared to those receiving placebo. This pattern was demonstrated in both male and female patients.
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Mirtazapine How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Mirtazapine Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Mirtazapine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Mirtazapine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Mirtazapine Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Mirtazapine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Mirtazapine Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Mirtazapine Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Timmer, CJ; Sitsen, JM; Delbressine, LP (June 2000). "Clinical pharmacokinetics of mirtazapine". Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 38 (6): 461–74. doi:10.2165/00003088-200038060-00001. PMID 10885584.