Mannitol
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gerald Chi
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Mannitol is a osmotic diuretic that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of oliguric phase of acute renal failure, cerebral edema, and elevated intraocular pressure. Mannitol is also indicated for promoting the urinary excretion of toxic substances. Common adverse reactions include nausea, vomiting, rhinitis, skin necrosis, thrombophlebitis, chills, dizziness, urticaria, hypotension, hypertension, tachycardia, fever, and angina-like chest pains.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
- Mannitol should be administered only by intravenous infusion. The total dosage, concentration, and rate of administration should be governed by the nature and severity of the condition being treated, fluid requirement, and urinary output.
- The usual adult dosage ranges from 20 to 100 g in a 24 hour period, but in most instances an adequate response will be achieved at a dosage of approximately 50 to 100 g in a 24 hour period. The rate of administration is usually adjusted to maintain a urine flow of at least 30 to 50 mL/hour. This outline of administration and dosage is only a general guide to therapy.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. Use of a final filter is recommended during administration of all parenteral solutions, where possible.
- Test Dose: A test dose of mannitol should be given prior to instituting Mannitol therapy for patients with marked oliguria, or those believed to have inadequate renal function. Such a test dose may be approximately 0.2 g/kg body weight (about 75 mL of a 20% solution or 100 mL of a 15% solution) infused in a period of three to five minutes to produce a urine flow of at least 30 to 50 mL/hour. If urine flow does not increase, a second test dose may be given; if there is an inadequate response, the patient should be reevaluated.
- Measurement of glomerular filtration rate by creatinine clearance may be useful for determination of dosage.
Prevention of Acute Renal Failure (Oliguria)
- Dosing Information
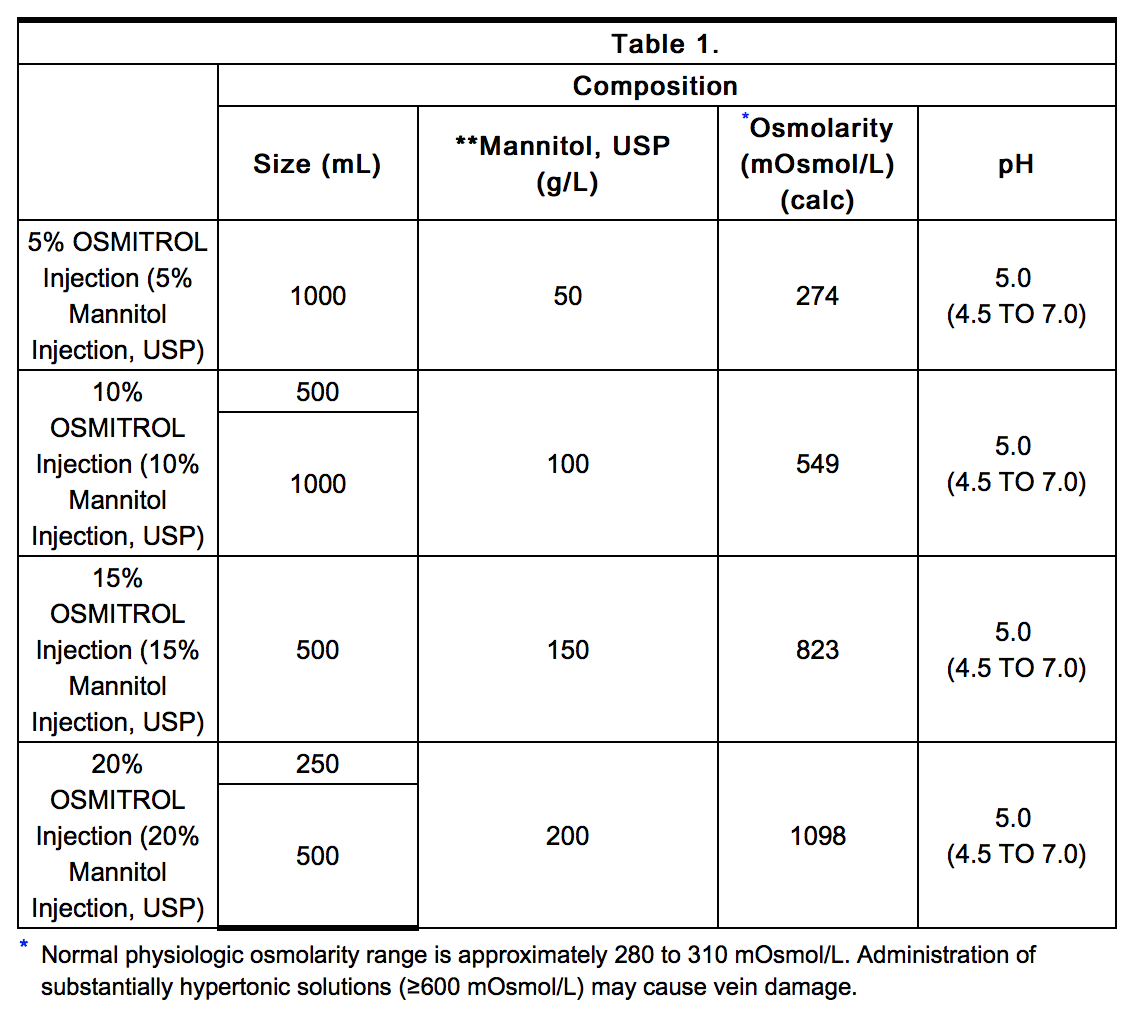
- When used during cardiovascular and other types of surgery, 50 to 100 g of mannitol as a 5, 10, or 15% solution may be given. The concentration will depend upon the fluid requirements of the patient.
Treatment of Oliguria
- Dosing Information
- The usual dose for treatment of oliguria is 100 g administered as a 15 or 20% solution.
Reduction of Intraocular Pressure
- Dosing Information
- A dose of 1.5 to 2.0 g/kg as a 20% solution (7.5 to 10 mL/kg) or as a 15% solution (10 to 13 mL/kg) may be given over a period as short as 30 minutes in order to obtain a prompt and maximal effect. When used preoperatively the dose should be given one to one and one-half hours before surgery to achieve maximal reduction of intraocular pressure before operation.
Reduction of Intracranial Pressure
- Dosing Information
- Usually a maximum reduction in intracranial pressure in adults can be achieved with a dose of 0.25 g/kg given not more frequently than every six to eight hours. An osmotic gradient between the blood and cerebrospinal fluid of approximately 10 mOsmol will yield a satisfactory reduction in intracranial pressure.
Adjunctive Therapy for Intoxications
- Dosing Information
- As an agent to promote diuresis in intoxications, 5%, 10%, 15% or 20% mannitol is indicated. The concentration will depend upon the fluid requirement and urinary output of the patient.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Mannitol in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Dysequilibrium Syndrome
- Dosing Information
Intracranial Tumor
- Dosing Information
- 10 mL of mannitol 25% (2.5 g) over 30 to 60 seconds.[3]
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- Safety and effectiveness in children below the age of 12 have not been established.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Mannitol in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Dysequilibrium Syndrome
- Dosing Information
- 40 g/m2 administered over 1 hour orally as a 5.5% or a 20% solution[4]
Contraindications
- Condition1
Warnings
- Description
Precautions
- Description
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Mannitol in the drug label.
Central Nervous System
Cardiovascular
Respiratory
Gastrointestinal
Hypersensitivity
Miscellaneous
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Mannitol in the drug label.
Central Nervous System
Cardiovascular
Respiratory
Gastrointestinal
Hypersensitivity
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Mannitol in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Mannitol during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mannitol with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mannitol with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mannitol with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mannitol with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mannitol with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mannitol in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mannitol in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Mannitol in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Mannitol in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Mannitol in the drug label.
Condition1
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Mannitol in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Mannitol in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Mannitol Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Mannitol in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Mannitol in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Mannitol in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Mannitol in the drug label.
Condition1
- Description
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Mannitol Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Mannitol |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Mannitol |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Mannitol in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Mannitol interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Osmitrol®[5]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[6]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Rosa, A. A. (1981). "The importance of osmolality fall and ultrafiltration rate on hemodialysis side effects. Influence of intravenous mannitol". Nephron. 27 (3): 134–141. ISSN 0028-2766. PMID 6783970. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ Warren, S. E. (1981-03). "Mannitol". Archives of Internal Medicine. 141 (4): 493–497. ISSN 0003-9926. PMID 6782963. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ↑ Fortin, D. (2000-05). "Iatrogenic arterial spasm relieved by intraarterial mannitol infusion". AJNR. American journal of neuroradiology. 21 (5): 968–970. ISSN 0195-6108. PMID 10815679. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ↑ Poulton, A. (1987-07). "Oral mannitol in control of fluid balance". Archives of Disease in Childhood. 62 (7): 729–731. ISSN 1468-2044. PMC 1779249. PMID 3115192. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ↑ "OSMITROL (mannitol) injection".
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Mannitol |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Mannitol |Label Name=Mannitol11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Mannitol |Label Name=Mannitol11.png
}}