|
|
| (18 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) |
| Line 15: |
Line 15: |
| }} | | }} |
| {{Lung abscess}} | | {{Lung abscess}} |
| {{CMG}} | | {{CMG}};{{AE}}{{ADG}} |
|
| |
|
| ==Overview==
| | {{SK}} Pulmonary abscess |
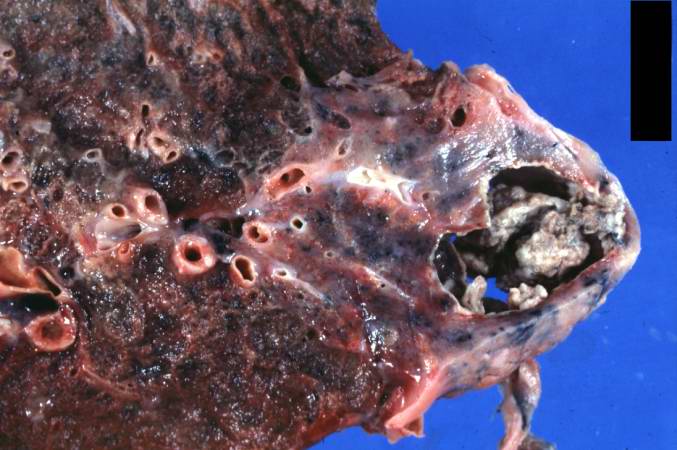
| '''Lung abscess''' is [[necrosis]] of the [[pulmonary]] tissue and formation of cavities (more than 2 cm)<ref>{{cite journal |author=Bartlett JG, Finegold SM |title=Anaerobic pleuropulmonary infections |journal=Medicine (Baltimore) |volume=51 |issue=6 |pages=413-50 |year=1972 |pmid=4564416 |doi=}}</ref> containing necrotic debris or fluid caused by microbial infection.
| |
|
| |
|
| This pus-filled cavity is often caused by aspiration, which may occur during altered consciousness. [[Alcoholism]] is the most common condition predisposing to lung abscesses.
| | == [[Lung abscess overview|Overview]] == |
|
| |
|
| Lung Abscess is considered '''primary'''(60%) when it results from existing lung parenchymal process and is termed '''secondary''' when it complicates another process e.g. [[Blood vessel|vascular]] [[emboli]] or follows rupture of extrapulmonary [[abscess]] into lung.
| | == [[Lung abscess historical perspective|Historical Perspective]] == |
|
| |
|
| == Causes == | | == [[Lung abscess classification|Classification]]== |
| Conditions contributing to lung abscess
| |
| *Aspiration of oropharyngeal or gastric secretion
| |
| *Septic emboli
| |
| *[[Necrotizing]] [[pneumonia]]
| |
| *[[Vasculitis]]: [[Wegener's granulomatosis]]
| |
| *Necrotizing [[tumors]]: 8% to 18% are due to neoplasms across all age groups, higher in older people; primary squamous carcinoma of the lung is the commonest.
| |
|
| |
|
| == Organisms == | | == [[Lung abscess pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]] == |
| In the post-antibiotic era pattern of frequency is changing. In older studies anerobes were found in upto 90% cases but they are much less frequent now<ref>{{cite journal |author=Bartlett JG |title=The role of anaerobic bacteria in lung abscess |journal=Clin. Infect. Dis. |volume=40 |issue=7 |pages=923-5 |year=2005 |pmid=15824980 |doi=10.1086/428586}}</ref>.
| |
| *Anaerobic bacteria: [[Peptostreptococcus]], [[Bacteroides]], [[Fusobacterium]] species,
| |
| *Microaerophilic [[streptococcus]] : ''Streptococcus milleri''
| |
| *Aerobic bacteria: [[Staphylococcus]], [[Klebsiella]], [[Haemophilus]], [[Pseudomonas]],[[Nocardia]], Escheria coli, [[Streptococcus]], Mycobacteria<ref name="pmid10084487">{{cite journal |author=Hirshberg B, Sklair-Levi M, Nir-Paz R, Ben-Sira L, Krivoruk V, Kramer MR |title=Factors predicting mortality of patients with lung abscess. |journal=Chest |volume=115 |issue=3 |pages=746-50 |year=1999 |pmid=10084487 |doi=}}</ref>
| |
| *[[Fungus|Fungi]]: [[Candida (genus)|Candida]], [[Aspergillus]]
| |
| *Parasites: [[Entamoeba histolytica]],
| |
|
| |
|
| == Symptoms and signs == | | == [[Lung abscess causes|Causes]] == |
| Onset of symptoms is often gradual, but in necrotizing staphylococcal or gram-negative bacillary pneumonias patients can be acutely ill. [[Cough]], fever with shivering and night sweats are often present. Cough can be productive with foul smelling purulent [[sputum]] (≈70%) or less frequently with blood (i.e. [[hemoptysis]] in one third cases) <ref name="Moreira">{{cite journal |author=Moreira Jda S, Camargo Jde J, Felicetti JC, Goldenfun PR, Moreira AL, Porto Nda S |title=Lung abscess: analysis of 252 consecutive cases diagnosed between 1968 and 2004 |journal=Jornal brasileiro de pneumologia : publicaça̋o oficial da Sociedade Brasileira de Pneumologia e Tisilogia |volume=32 |issue=2 |pages=136-43 |year=2006 |pmid=17273583 |doi=}}</ref>. Affected individuals may also complaint chest pain, shortness of breath, [[lethargy]] and other features of chronic illness.
| |
|
| |
|
| Patients are generally [[cachexia|cachectic]] at presentation. Finger [[clubbing]] is present in one third of patients<ref name="Moreira"/>. Dental decay is common especially in alcoholics and children. On examination of chest there will be features of consolidation such as localised dullness on percussion, [[Breath sounds|bronchial breath sound]] etc.
| | == [[Lung abscess differential diagnosis|Differentiating Lung abscess from other Diseases]] == |
| | |
| | == [[Lung abscess epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== |
| | |
| | == [[Lung abscess risk factors|Risk Factors]] == |
| | |
| | == [[Lung abscess screening|Screening]]== |
| | |
| | == [[Lung abscess natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]] == |
|
| |
|
| == Diagnosis == | | == Diagnosis == |
| ;Chest Xray and other imaging studies
| |
| Abscess is often unilateral and single involving posterior segments of the upper lobes and the apical segments of the lower lobes as these areas are gravity dependent when lying down. Presence of air-fluid levels implies rupture into the bronchial tree or rarely growth of gas forming organism.
| |
| ;Laboratory studies
| |
| Raised inflammatory markers ( high [[Erythrocyte sedimentation rate|ESR]], [[C-reactive protein|CRP]]) are usual but not specific. Examination of sputum is important in any pulmonary infections and here often reveals mixed flora. [[Respiration (physiology)|Transtracheal]] of [[bronchus|Transbronchial]] (via bronchoscopy) aspirates can also be cultured. Fibre optic [[bronchoscopy]] is often performed to exclude obstructive lesion; it also helps in bronchial drainage of pus.
| |
|
| |
|
| == Management==
| | [[Lung abscess history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Lung abscess physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Lung abscess laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Lung abscess chest x ray|Chest X Ray]] | [[Lung abscess CT|CT]] | [[Lung abscess MRI|MRI]] | [[Lung abscess other imaging findings|Other Imaging Findings]] | [[Lung abscess other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] |
| Broadspectrum [[antibiotic]] to cover mixed flora is the mainstay of treatment. Pulmonary physiotherapy and postural drainage are also important. Surgical procedures are required in selective patients for drainage or pulmonary resection.
| |
|
| |
|
| == Complications == | | == Treatment == |
| Rare now a days but include spread of infection to other lung segments, [[bronchiectasis]], [[empyema]], and bacteraemia with [[metastasis|metastatic]] infection such as [[brain abscess]]<ref name="medscape"/>.
| |
|
| |
|
| == Prognosis ==
| | [[Lung abscess medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Lung abscess surgery|Surgery]] | [[Lung abscess primary prevention|Primary Prevention]] | [[Lung abscess secondary prevention|Secondary Prevention]] | [[Lung abscess cost-effectiveness of therapy| Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy]] | [[Lung abscess future or investigational therapies|Future or Investigational Therapies]] |
| Most cases respond to antibiotic and prognosis is usually excellent unless there is a debilitating underlying condition. Mortality from lung abscess alone is around 5% and is improving.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==See also== | | ==Case Studies== |
| | [[Lung abscess case study one|Case #1]] |
| | |
| | ==Related Chapters== |
| *Other chronic lung infections | | *Other chronic lung infections |
| **[[Empyema]] | | **[[Empyema]] |
| Line 66: |
Line 56: |
| *[[Abscess]] | | *[[Abscess]] |
| *[[Pleural effusion]] | | *[[Pleural effusion]] |
| == Reference ==
| |
| {{Reflist|2}}
| |
|
| |
|
| {{Respiratory pathology}} | | {{Respiratory pathology}} |
| Line 76: |
Line 64: |
| [[fi:Keuhkopaise]] | | [[fi:Keuhkopaise]] |
| [[ru:Абсцесс лёгких]] | | [[ru:Абсцесс лёгких]] |
|
| |
| [[Category:Pulmonology]]
| |
| [[Category:Infectious disease]]
| |
|
| |
|
| [[pl:Ropień płuc]] | | [[pl:Ropień płuc]] |
| Line 84: |
Line 69: |
| {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | | {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} |
| {{WikiDoc Sources}} | | {{WikiDoc Sources}} |
| | |
| | [[Category:Pulmonology]] |
| | [[Category:Emergency mdicine]] |
| | [[Category:Disease]] |
| | [[Category:Up-To-Date]] |
| | [[Category:Infectious disease]] |