Interferon-gamma
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Alberto Plate [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Interferon-gamma is an immunological agent that is FDA approved for the treatment of serious infections associated with Chronic Granulomatous Disease and delaying time to disease progression in patients with severe, malignant osteopetrosis.. Common adverse reactions include {{{adverseReactions}}}.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
The recommended dosage of ACTIMMUNE for the treatment of patients with Chronic Granulomatous Disease and severe, malignant osteopetrosis is 50 mcg/m2 (1 million IU/m2) for patients whose body surface area is greater than 0.5 m2 and 1.5 mcg/kg/dose for patients whose body surface area is equal to or less than 0.5 m2. Note that the above activity is expressed in International Units (1 million IU/50mcg). This is equivalent to what was previously expressed as units (1.5 million U/50mcg). Injections should be administered subcutaneously three times weekly (for example, Monday, Wednesday, Friday). The optimum sites of injection are the right and left deltoid and anterior thigh. ACTIMMUNE can be administered by a physician, nurse, family member or patient when trained in the administration of subcutaneous injections. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
The formulation does not contain a preservative. A vial of ACTIMMUNE is suitable for a single use only. The unused portion of any vial should be discarded. Higher doses are not recommended. Safety and efficacy has not been established for ACTIMMUNE given in doses greater or less than the recommended dose of 50 mcg/m2. The minimum effective dose of ACTIMMUNE has not been established. ACTIMMUNE should not be mixed with other drugs in the same syringe.
- Dose Modification: If severe reactions occur, the dosage should be reduced by 50 percent or therapy should be interrupted until the adverse reaction abates.
- ACTIMMUNE may be administered using either sterilized glass or plastic disposable syringes.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Interferon-gamma in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Interferon-gamma in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Interferon-gamma FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Interferon-gamma in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Interferon-gamma in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
ACTIMMUNE is contraindicated in patients who develop or have known hypersensitivity to interferon-gamma, E. coli derived products, or any component of the product.
Warnings
Cardiovascular Disorders
Acute and transient flu-like symptoms such as fever and chills induced by ACTIMMUNE at doses of 250 mcg/m2/day (greater than 10 times the weekly recommended dose) or higher may exacerbate pre-existing cardiac conditions. ACTIMMUNE should be used with caution in patients with pre-existing cardiac conditions, including ischemia, congestive heart failure or arrhythmia.
Neurologic Disorders
Decreased mental status, gait disturbance and dizziness have been observed, particularly in patients receiving ACTIMMUNE doses greater than 250 mcg/m2/day (greater than 10 times the weekly recommended dose). Most of these abnormalities were mild and reversible within a few days upon dose reduction or discontinuation of therapy. Caution should be exercised when administering ACTIMMUNE to patients with seizure disorders or compromised central nervous system function.
Bone Marrow Toxicity
Reversible neutropenia and thrombocytopenia that can be severe and may be dose related have been observed during ACTIMMUNE therapy. Caution should be exercised when administering ACTIMMUNE to patients with myelosuppression.
Hepatic Toxicity
Elevations of AST and/or ALT (up to 25-fold) have been observed during ACTIMMUNE therapy. The incidence appeared to be higher in patients less than 1 year of age compared to older children. The transaminase elevations were reversible with reduction in dosage or interruption of ACTIMMUNE treatment. Patients begun on ACTIMMUNE before age one year should receive monthly assessments of liver function. If severe hepatic enzyme elevations develop, ACTIMMUNE dosage should be modified.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
The following data on adverse reactions are based on the subcutaneous administration of ACTIMMUNE at a dose of 50 mcg/m2, three times weekly, in patients with Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD) during an investigational trial in the United States and Europe. The most common adverse events observed in patients with CGD are shown in the following table:

Miscellaneous adverse events which occurred infrequently in patients with CGD and may have been related to underlying disease included back pain (2 percent versus 0 percent), abdominal pain (8 percent versus 3 percent) and depression (3 percent versus 0 percent) for ACTIMMUNE and placebo treated patients, respectively. Similar safety data were observed in 34 patients with severe malignant osteopetrosis.
ACTIMMUNE has also been evaluated in additional disease states in studies in which patients have generally received higher doses (>100 mcg/m2/three times weekly) administered by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection, or intravenous infusion. All of the previously described adverse reactions which occurred in patients with Chronic Granulomatous Disease have also been observed in patients receiving higher doses. Adverse reactions not observed in patients with Chronic Granulomatous Disease but reported in patients receiving ACTIMMUNE (Interferon gamma-1b) in other studies include:
Cardiovascular Effects
Central Nervous System Effects
- Confusion
- Disorientation
- Gait disturbance
- Parkinsonian symptoms
- Seizure
- Hallucinations
- Transient ischemic attacks
Gastrointestinal
- Dyspepsia
- Hepatic insufficiency
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Pancreatitis, including pancreatitis with fatal outcome.
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions
Hematologic
Immunological
Metabolic
Musculoskeletal
Pulmonary
Renal
Other
- Chest discomfort
- Exacerbation of dermatomyositis.
Abnormal Laboratory Test Values
- Elevations of ALT and AST
- Neutropenia
- Thrombocytopenia and
- Proteinuria
No neutralizing antibodies to ACTIMMUNE have been detected in any Chronic Granulomatous Disease patients receiving ACTIMMUNE.
Postmarketing Experience
Children with CGD less than 3 years of age
Data on the safety and activity of ACTIMMUNE in 37 patients under the age of 3 years was pooled from four uncontrolled post-marketing studies. The rate of serious infections per patient-year in this uncontrolled group was similar to the rate observed in the ACTIMMUNE treatment groups in controlled trials. Developmental parameters (height, weight and endocrine maturation) for this uncontrolled group conformed to national normative scales before and during ACTIMMUNE therapy.
In 6 of the 10 patients receiving ACTIMMUNE therapy before age one year 2-fold to 25-fold elevations from baseline of AST and/or ALT were observed. These elevations occurred as early as 7 days after starting treatment. Treatment with ACTIMMUNE was interrupted in all 6 of these patients and was restarted at a reduced dosage in 4. Liver transaminase values returned to baseline in all patients and transaminase elevation recurred in one patient upon ACTIMMUNE rechallenge. An 11-fold alkaline phosphatase elevation and hypokalemia in one patient and neutropenia (ANC=525 cells/mm3) in another patient resolved with interruption of ACTIMMUNE treatment and did not recur with rechallenge.
In the post-marketing safety database clinically significant adverse events observed during ACTIMMUNE therapy in children under the age of three years (n=14) included: two cases of hepatomegaly, and one case each of Stevens-Johnson syndrome, granulomatous colitis, urticaria, and atopic dermatitis.
Drug Interactions
Interactions between ACTIMMUNE and other drugs have not been fully evaluated. Caution should be exercised when administering ACTIMMUNE in combination with other potentially myelosuppressive agents.
Preclinical studies in rodents using species-specific interferon-gamma have demonstrated a decrease in hepatic microsomal cytochrome P-450 concentrations. This could potentially lead to a depression of the hepatic metabolism of certain drugs that utilize this degradative pathway.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
ACTIMMUNE has shown an increased incidence of abortions in primates when given in doses approximately 100 times the human dose. A study in pregnant primates treated with subcutaneous doses 2-100 times the human dose failed to demonstrate teratogenic activity for ACTIMMUNE.
Female mice treated subcutaneously with rmulFN-gamma at 280 times the maximum recommended clinical dose of ACTIMMUNE from shortly after birth through puberty but not during pregnancy had offspring which exhibited decreased body weight during the lactation period. The clinical significance of this finding observed following treatment of mice with rmulFN-gamma is uncertain.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. ACTIMMUNE should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Interferon-gamma in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Interferon-gamma during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether ACTIMMUNE is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from ACTIMMUNE, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, dependent upon the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Interferon-gamma in pediatric settings.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Interferon-gamma in geriatric settings.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Interferon-gamma with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Interferon-gamma with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Interferon-gamma in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Interferon-gamma in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
Impairment of Fertility
Female cynomolgus monkeys treated with daily subcutaneous doses of 30 or 150 mcg/kg ACTIMMUNE (approximately 20 and 100 times the human dose) exhibited irregular menstrual cycles or absence of cyclicity during treatment. Similar findings were not observed in animals treated with 3 mcg/kg ACTIMMUNE.
Female mice receiving recombinant murine IFN-gamma (rmulFN-gamma) at 32 times the maximum recommended clinical dose of ACTIMMUNE for 4 weeks via intramuscular injection exhibited an increased incidence of atretic ovarian follicles.
Male cynomolgus monkeys treated intravenously for 4 weeks with 8 times the maximum recommended clinical dose of ACTIMMUNE exhibited decreased spermatogenesis. The impact of this finding on fertility is not known. Male mice receiving rmulFN-gamma at 32 times the maximum recommended clinical dose of ACTIMMUNE for 4 weeks via intramuscular injection exhibited decreased spermatogenesis.
Male mice treated subcutaneously with rmuIFN-gamma from shortly after birth through puberty, with 280 times the maximum recommended clinical dose of ACTIMMUNE exhibited profound yet reversible decreases in sperm counts and fertility, and an increase in the number of abnormal sperm.
The clinical significance of these findings observed following treatment of mice with rmulFN-gamma is uncertain.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Interferon-gamma in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- 1.- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before preparing the medication. This helps prevent infection.
- 2.- Check the date on the ACTIMMUNE vial to be sure the drug has not expired.
- 3.- Remove the protective plastic cap and wipe the rubber stopper located on top of the ACTIMMUNE vial with an alcohol swab.
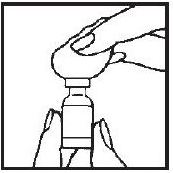
- 4.- Draw air into the syringe by pulling back on the plunger. The amount of air should be equal to the ACTIMMUNE dose.
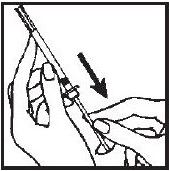
- 5.- Remove and save the needle guard. Slowly insert the needle straight through the center of the rubber stopper into the ACTIMMUNE vial.

- 6.- Gently push the plunger to discharge the air into the vial.
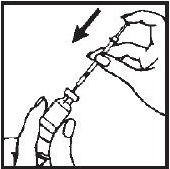
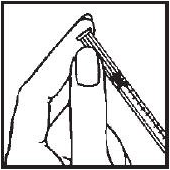
- 7.- Turn the vial upside down with the syringe needle still in it and hold it in one hand. Be sure the tip of the needle is in the solution. Using your other hand slowly pull back on the plunger in a continuous motion until the correct amount of ACTIMMUNE® solution is in the syringe.
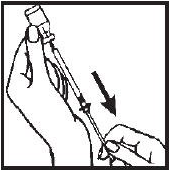
- 8.- Remove the needle from the ACTIMMUNE vial and replace the needle guard until time of administration or injection. Administration should be as soon after filling the syringe as possible; do not store ACTIMMUNE in the syringe.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Interferon-gamma Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Interferon-gamma and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Interferon-gamma overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
| Template:Px | |
Interferon-gamma
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| Human interferon gamma-1b | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 98059-61-1 |
| ATC code | L03 |
| PubChem | ? |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 17145.6 g/mol |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | ? |
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Interferon-gamma Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Interferon-gamma Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Interferon-gamma Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Interferon-gamma Pharmacokinetics in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Interferon-gamma Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Interferon-gamma Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Interferon-gamma How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Interferon-gamma Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Interferon-gamma |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Interferon-gamma |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Interferon-gamma Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Interferon-gamma interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Interferon-gamma Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Interferon-gamma Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
| Interferon, gamma | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Interferon gamma, line representation | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| Symbols | IFNG ; IFG; IFI | ||
| External IDs | Template:OMIM5 Template:MGI HomoloGene: 55526 | ||
| RNA expression pattern | |||
 | |||
| More reference expression data | |||
| Orthologs | |||
| Template:GNF Ortholog box | |||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |
| Entrez | n/a | n/a | |
| Ensembl | n/a | n/a | |
| UniProt | n/a | n/a | |
| RefSeq (mRNA) | n/a | n/a | |
| RefSeq (protein) | n/a | n/a | |
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |